|
Clark Still
William Clark Still (born 1946) is an American organic chemistry, organic chemist. As a distinguished professor at Columbia University, Clark Still made significant contributions to the field of organic chemistry, particularly in the areas of natural product synthesis, reaction development, conformational analysis, macrocyclic stereocontrol, and computational chemistry. Still and coworkers also developed the purification technique known as flash column chromatography which is widely used for the purification of organic compounds. Major contributions Total synthesis Periplanone B In 1979, Still reported the first total synthesis of periplanone B, the potent sex pheromone of the American cockroach. Although the structural connectivity of this compound had been established spectroscopically, Still's synthesis confirmed the relative stereochemical relationships present in this natural product. A key step in this synthesis makes use of an anionic oxy-Cope rearrangement to form th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta, Georgia
Augusta is a city on the central eastern border of the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. The city lies directly across the Savannah River from North Augusta, South Carolina at the head of its navigable portion. Augusta, the third most populous city in Georgia (following Columbus, Georgia, Columbus), is situated in the Fall Line region of the state. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Augusta had a 2020 population of 202,081, not counting the independent cities of Blythe, Georgia, Blythe and Hephzibah, Georgia, Hephzibah located within the boundaries of Augusta-Richmond County. It is the List of United States cities by population, 124th most populous city in the United States and the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 92nd-largest metropolitan area. The process of consolidation between the city of Augusta and Richmond County, Georgia, Richmond County began with a 1995 referendum in the two jurisdictions. The merger was completed on July 1, 1996, but it excluded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotin
Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known, but are less imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,3-sigmatropic Rearrangement
2,3-Sigmatropic rearrangements are a type of sigmatropic rearrangements and can be classified into two types. Rearrangements of allylic sulfoxides, amine oxides, selenoxides are neutral. Rearrangements of carbanions of allyl ethers are anionic. The general scheme for this kind of rearrangement is: Atom Y may be sulfur, selenium, or nitrogen. If Y is nitrogen, the reaction is referred to as the Sommelet–Hauser rearrangement if a quaternary ammonium salt is involved or the aza-Wittig reaction if an alpha-metalated tertiary amine is involved; if Y is oxygen, then it is called a 2,3-Wittig rearrangement (not to be confused with the well-known Wittig reaction, which involves a phosphonium ylide). If Y is sulfur, the product can be treated with a thiophil to generate an allylic alcohol in what is known as the Mislow–Evans rearrangement. A ,3rearrangement may result in carbon-carbon bond formation. It can also be used as a ring-expansion reaction.''Ring expansion by 2,3-sigma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,3-Wittig Rearrangement
The ,3Wittig rearrangement is the transformation of an allylic ether into a homoallylic alcohol via a concerted, pericyclic process. Because the reaction is concerted, it exhibits a high degree of stereocontrol, and can be employed early in a synthetic route to establish stereochemistry. The Wittig rearrangement requires strongly basic conditions, however, as a carbanion intermediate is essential. ,2Wittig rearrangement is a competitive process. Introduction ,3 Sigmatropic rearrangements occur for a variety of groups X and Y (see below). When X is a carbanion and Y an alkoxide, the rearrangement is called the ,3Wittig rearrangement and the products are pent-1-en-5-ols. The ,2Wittig rearrangement, which produces isomeric pent-5-en-1-ols, is a competitive process that takes place at high temperatures. Because of the high atom economy and stereoselectivity of the ,3rearrangement, it has gained considerable synthetic utility. The carbanion is generated by direct lithiation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
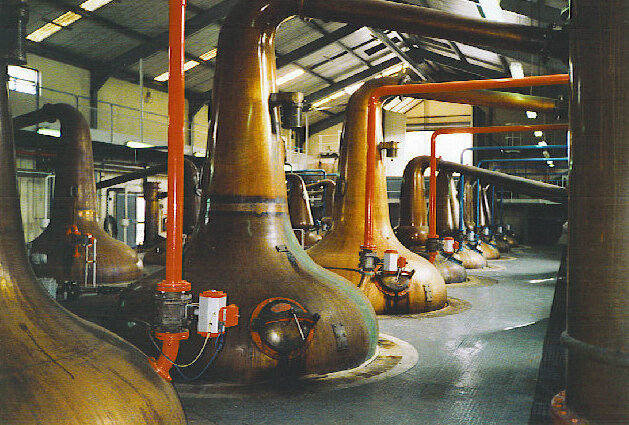
Still Monensin
A still is an apparatus used to distill liquid mixtures by heating to selectively boil and then cooling to condense the vapor. A still uses the same concepts as a basic distillation apparatus, but on a much larger scale. Stills have been used to produce perfume and medicine, water for injection (WFI) for pharmaceutical use, generally to separate and purify different chemicals, and to produce distilled beverages containing ethanol. Application Since ethanol boils at a much lower temperature than water, simple distillation can separate ethanol from water by applying heat to the mixture. Historically, a copper vessel was used for this purpose, since copper removes undesirable sulfur-based compounds from the alcohol. However, many modern stills are made of stainless steel pipes with copper linings to prevent erosion of the entire vessel and lower copper levels in the waste product (which in large distilleries is processed to become animal feed). Copper is the preferred material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |