|
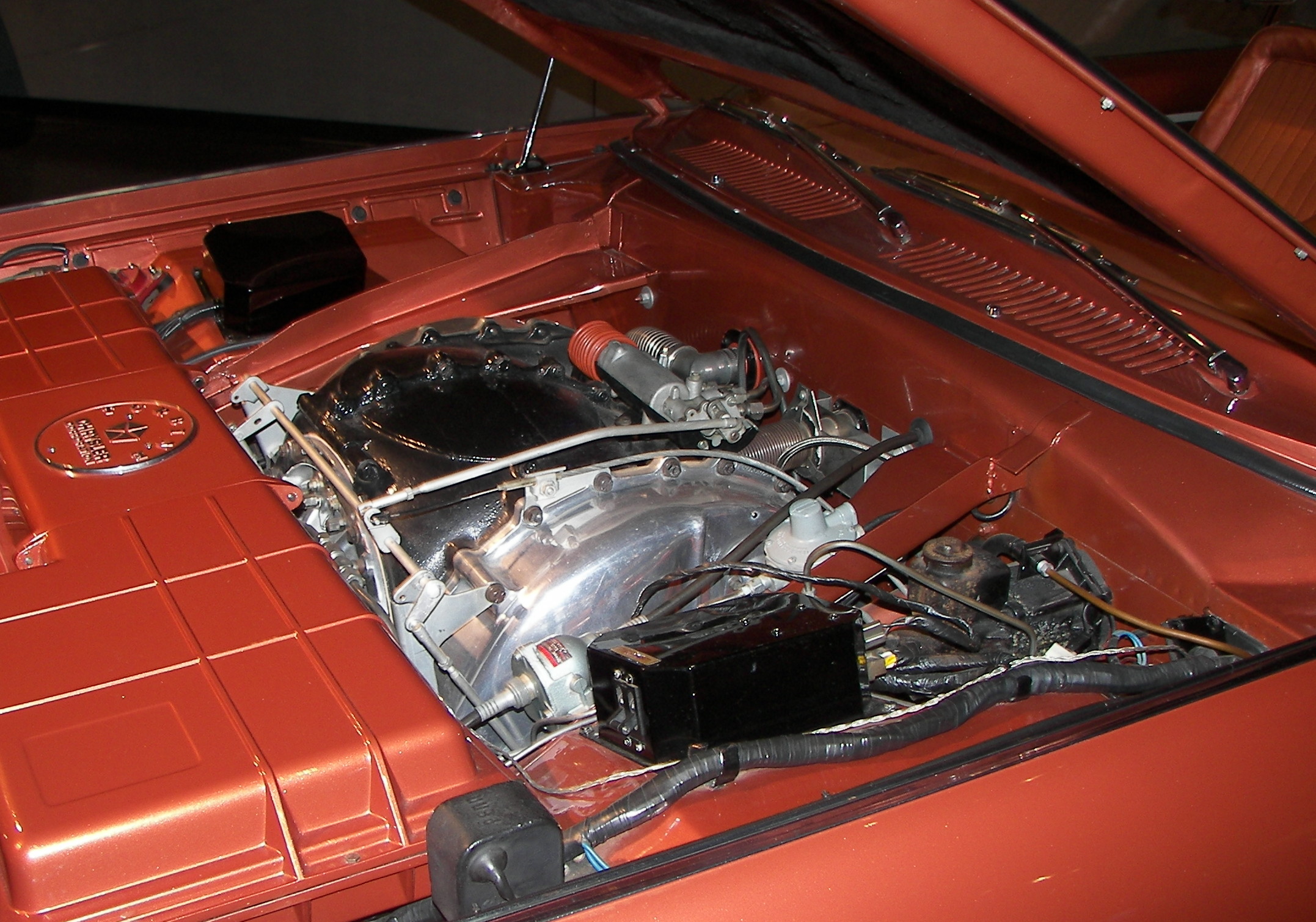
Chrysler Turbine Car
The Chrysler Turbine Car is an experimental two-door hardtop coupé, coupe powered by a gas turbine, turbine engine and was manufactured by Chrysler Corporation, Chrysler from 1963 to 1964. Italian design studio Carrozzeria Ghia constructed the bodywork, and Chrysler completed the final assembly in Detroit. A total of 55 cars were manufactured: five prototypes and a limited run of fifty cars for a public user program. All have a signature metallic paint named "turbine bronze", roughly the color of root beer. The car was styled by Elwood Engel and Chrysler studios. They featured power brakes, power steering, and a TorqueFlite transmission. The Chrysler turbine engines, Chrysler turbine engine program that produced the Turbine Car began during the late 1930s and created prototypes that completed long-distance trips in the 1950s and early 1960s. The A-831 engines that powered the Ghia-designed Turbine Car could operate on many fuels, required less maintenance, and lasted longer tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysler Turbine Engines
The Chrysler turbine engine is a series of gas turbine#In surface vehicles, gas turbine engines developed by Chrysler intended to be used in road vehicles. In 1954, Chrysler Corporation disclosed the development and successful road testing of a production model Plymouth sport coupe which was powered by a turbine engine. Development Tests of the Chrysler Turbine were first run in 1954 and proved successful enough to convince project lead George Huebner of the engine's viability for further development. With the aim of keeping price competitive with its contemporaries, the team sought to address concerns with the engine of throttle response, noise, and to see if it was even possible to power a car using a jet engine. Likewise, new materials were developed to be resistant to the high temperatures of the engine's combustion chamber while remaining economical to manufacture at the scale of a mass-produced automobile. A number of benefits were also identified; the turbine engine bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin
Turin ( , ; ; , then ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is mainly on the western bank of the Po (river), River Po, below its Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga hill. The population of the city proper is 856,745 as of 2025, while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million. The city was historically a major European political centre. From 1563, it was the capital of the Duchy of Savoy, then of the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia ruled by the House of Savoy, and the first capital of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1865. Turin is sometimes called "the cradle of Italian liberty" for having been the politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Steering
Power steering is a system for reducing a driver's effort to turn a steering wheel of a motor vehicle, by using a power source to assist steering. Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver can provide less effort to turn the steered wheels when driving at typical speeds, and considerably reduce the physical effort necessary to turn the wheels when a vehicle is stopped or moving slowly. Power steering can also be engineered to provide some artificial feedback of forces acting on the steered wheels. Hydraulic power steering systems for cars augment steering effort via an actuator, a hydraulic cylinder that is part of a servo system. These systems have a direct mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the steering linkage that steers the wheels. This means that power-steering system failure (to augment effort) still permits the vehicle to be steered using manual effort alone. Electric power steering systems use elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Belvedere
The Plymouth Belvedere is a series of United States, American automobile models made by Plymouth (automobile), Plymouth from 1954 until 1970. The Belvedere name was first used for a new hardtop body style in the Plymouth Cranbrook line for the 1951 model year. In 1954, the Belvedere replaced the Cranbrook as the top trim and became a full model line with sedan (car), sedans, station wagons, and convertible body styles. The Belvedere continued as Plymouth's full-sized car until 1965 when it became an intermediate. It was replaced after the 1970 model year by the Plymouth Satellite, Satellite, a name originally used for the top-trim level Belvederes. The word "wikt:belvedere, belvedere" is Italian for "beautiful sight" or "fair view." Chrysler also had the Belvidere Assembly Plant in Belvidere, Illinois, which began vehicle production in 1965. However, the Plymouth Belvedere was never assembled there. During the 1950s and 1960s Chrysler Canada built the Belvedere for Commonwea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, Petrochemical, petrochemical plants, Oil refinery, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement There are three primary classifications of heat exchangers accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Heat Exchanger
A regenerative heat exchanger, or more commonly a regenerator, is a type of heat exchanger where heat from the hot fluid is intermittently stored in a thermal storage medium before it is transferred to the cold fluid. To accomplish this the hot fluid is brought into contact with the heat storage medium, then the fluid is displaced with the cold fluid, which absorbs the heat. In regenerative heat exchangers, the fluid on either side of the heat exchanger can be the same fluid. The fluid may go through an external processing step, and then it is flowed back through the heat exchanger in the opposite direction for further processing. Usually the application will use this process cyclically or repetitively. Regenerative heating was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution when it was used in the hot blast process on blast furnaces. It was later used in glass melting furnaces and steel making, to increase the efficiency of open hearth furnaces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rover Company
The Rover Company Limited was a British car manufacturing company originally founded in 1878, beginning car manufacturing in 1904. It primarily operated from its base in Solihull, Warwickshire. Rover also manufactured the Land Rover series from 1948 onwards, and created the Range Rover in 1970, which went on to become its most successful and profitable product. Land Rover eventually became a separate company and brand in its own right. Rover was bought by Leyland Motors in 1967, which had already acquired Triumph Motor Company, Standard-Triumph seven years earlier. Initially, Rover maintained a level of autonomy within the Leyland conglomerate, but by 1978, Leyland – by then British Leyland (BL) – had run into severe financial difficulties and had been Nationalization, nationalized by the Government of the United Kingdom, British Government. Most of the assets of the former Rover Company were moved into a new BL subsidiary named ''Land Rover Ltd'' whilst the Rover (marque), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing four automobile brands: Chevrolet, Buick, GMC (marque), GMC, and Cadillac, each a separate division of GM. By total sales, it has continuously been the largest automaker in the United States, and was the List of manufacturers by motor vehicle production, largest in the world for 77 years before losing the top spot to Toyota in 2008. General Motors operates manufacturing plants in eight countries. In addition to its four core brands, GM also holds interests in Chinese brands Baojun and SAIC-GM-Wuling, Wuling via SAIC-GM-Wuling, SAIC-GM-Wuling Automobile. GM further owns GM Defense, a namesake defense vehicles division which produces military vehicles for the United States government and military, the vehicle safety, security, and information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is introduced, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sam B
''Dead Island'' is a 2011 action role-playing game developed by Techland and published by Deep Silver. Released for Linux, Microsoft Windows, OS X, PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360, the game is centered on the challenge of surviving a zombie-infested open world with an important emphasis on melee combat. The plot focuses on four playable survivors trying to survive and escape off the fictional island of Banoi. The game was announced at the 2006 Electronic Entertainment Expo, but delayed until 2011. The game's cinematic announcement trailer was met with controversy over its depiction of a dead child. However reception was nonetheless positive, with praise going towards the emotional impact, animation and story, with the trailer being held as one of the best in any medium. The game was released in 2011. September for North America/Europe and in October for Japan. Despite the pre-release acclaim, the game received generally lukewarm reviews. While praised for its atmosphere, gameplay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bud Mann
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be specialized to develop flowers or short shoots or may have the potential for general shoot development. The term bud is also used in zoology, where it refers to an outgrowth from the body which can develop into a new individual. Overview The buds of many woody plants, especially in temperate or cold climates, are protected by a covering of modified leaves called ''scales'' which tightly enclose the more delicate parts of the bud. Many bud scales are covered by a gummy substance which serves as added protection. When the bud develops, the scales may enlarge somewhat but usually just drop off, leaving a series of horizontally-elongated scars on the surface of the growing stem. By means of these scars one can determine the age of any young branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Huebner
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Leonard Ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |