|
Chromium Hydride
Chromium hydrides are compounds of chromium and hydrogen, and possibly other elements. Intermetallic compounds with not-quite-stoichometric quantities of hydrogen exist, as well as highly reactive molecules. When present at low concentrations, hydrogen and certain other elements alloyed with chromium act as softening agents that enables the movement of dislocations that otherwise not occur in the crystal lattices of chromium atoms. The hydrogen in typical chromium hydride alloys may contribute only a few hundred parts per million in weight at ambient temperatures. Varying the amount of hydrogen and other alloying elements, and their form in the chromium hydride either as solute elements, or as precipitated phases, expedites the movement of dislocations in chromium, and thus controls qualities such as the hardness (materials science), hardness, ductility, and tensile strength of the resulting chromium hydride. Material properties Even in the narrow range of concentrations that m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties that differ from those of the pure elements from which they are made. The vast majority of metals used for commercial purposes are alloyed to improve their properties or behavior, such as increased strength, hardness or corrosion resistance. Metals may also be alloyed to reduce their overall cost, for instance alloys of gold and Copper(II) sulfate, copper. A typical example of an alloy is SAE 304 stainless steel, 304 grade stainless steel which is commonly used for kitchen utensils, pans, knives and forks. Sometime also known as 18/8, it as an alloy consisting broadly of 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The chromium and nickel alloying elements add strength and hardness to the majority iron element, but their main function is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NiAs
Nias (, Nias: ''Tanö Niha'') is an island located off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago () of which the island is the centre, but also includes the Batu Islands to the southeast and the small Hinako Islands to the west. Geography Nias Island covers an area of (including the Batu Islands to the south and minor offshore islands). It is mostly a lowland area rising to around above sea level. There were 756,338 inhabitants on the island (including the Batu Islands and minor offshore islands) at the 2010 Census;Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. at the 2015 Intermediate Census this had risen to 798,506 and the 2020 Census documented a total of 880,550.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. The official estimate as of mid-2024 was 946,746; it is officially projected to be 962,819 in mid 2025.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 28 February 2025, ''Provinsi Sumatera Utara Dalam Angka 2025'' (Katalog-BPS 1102001.12) It is located in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
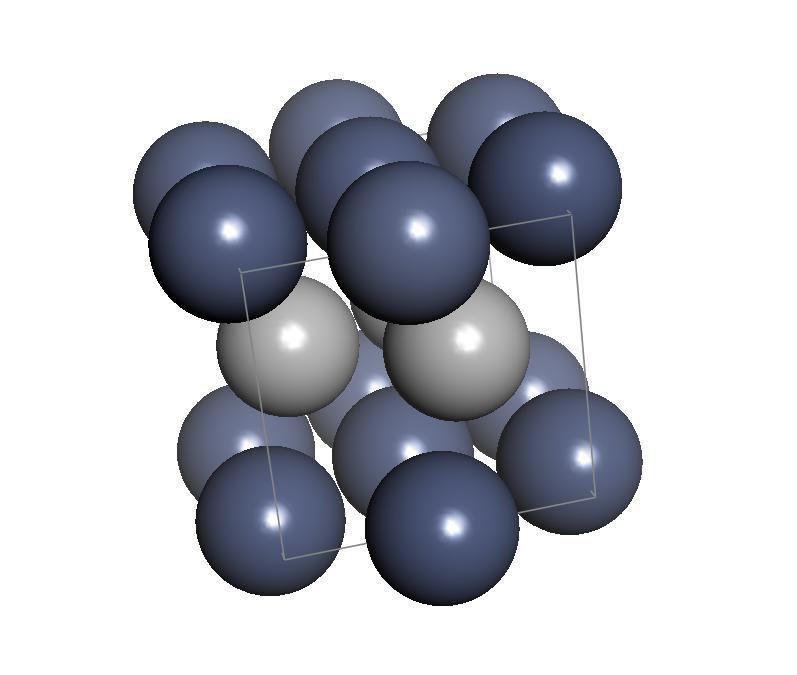
Chromium(I) Hydride
Chromium(I) hydride, systematically named chromium hydride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (also written as or CrH). It occurs naturally in some kinds of stars where it has been detected by its spectrum. However, molecular chromium(I) hydride with the formula CrH has been isolated in solid gas matrices. The molecular hydride is very reactive. As such the compound is not well characterised, although many of its properties have been calculated via computational chemistry. Molecular forms A. G. Gaydon first created CrH gas with an electric arc between chromium electrodes in a hydrogen air flame. CrH can be formed by the reaction of chromium metal vapour, created by an electrical discharge in the presence of hydrogen. The electric discharge breaks up the H2 molecules into reactive H atoms. So the reaction then proceeds as Cr(g) + H → CrH. Another method to make CrH is to react chromium carbonyl (Cr(CO)6) vapour with atomic hydrogen generated by an electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation (chemistry), passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation. Spain, Spanish-Mexico, Mexican scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called "brown lead". Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it "vanadium" after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent, as a rubber additive, and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese is commonly found in labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloying Elements
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties that differ from those of the pure elements from which they are made. The vast majority of metals used for commercial purposes are alloyed to improve their properties or behavior, such as increased strength, hardness or corrosion resistance. Metals may also be alloyed to reduce their overall cost, for instance alloys of gold and copper. A typical example of an alloy is 304 grade stainless steel which is commonly used for kitchen utensils, pans, knives and forks. Sometime also known as 18/8, it as an alloy consisting broadly of 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The chromium and nickel alloying elements add strength and hardness to the majority iron element, but their main function is to make it resistant to rust/corrosion. In an al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It forms colorless crystals. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon. Preparation Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction. Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium Chloride
Chromium chloride may refer to: * Chromium(II) chloride, also known as chromous chloride * Chromium(III) chloride, also known as chromic chloride or chromium trichloride * Chromium(IV) chloride, unstable {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium Sesquioxide
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite. Structure and properties has the corundum structure, consisting of a hexagonal close packed array of oxide anions with two thirds of the octahedral holes occupied by chromium. Similar to corundum, is a hard, brittle material (Mohs hardness 8 to 8.5). It is antiferromagnetic up to , the Néel temperature. It is not readily attacked by acids. Occurrence occurs naturally as the mineral eskolaite, which is found in chromium-rich tremolite skarns, metaquartzites, and chlorite veins. Eskolaite is also a rare component of chondrite meteorites. The mineral is named after Finnish geologist Pentti Eskola. Production The Parisians Pannetier and Binet first prepared the transparent hydrated form of in 1838 via a secret process, sold as a pigment. It is derived from the mineral chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |