|
Chromium(II) Bromide
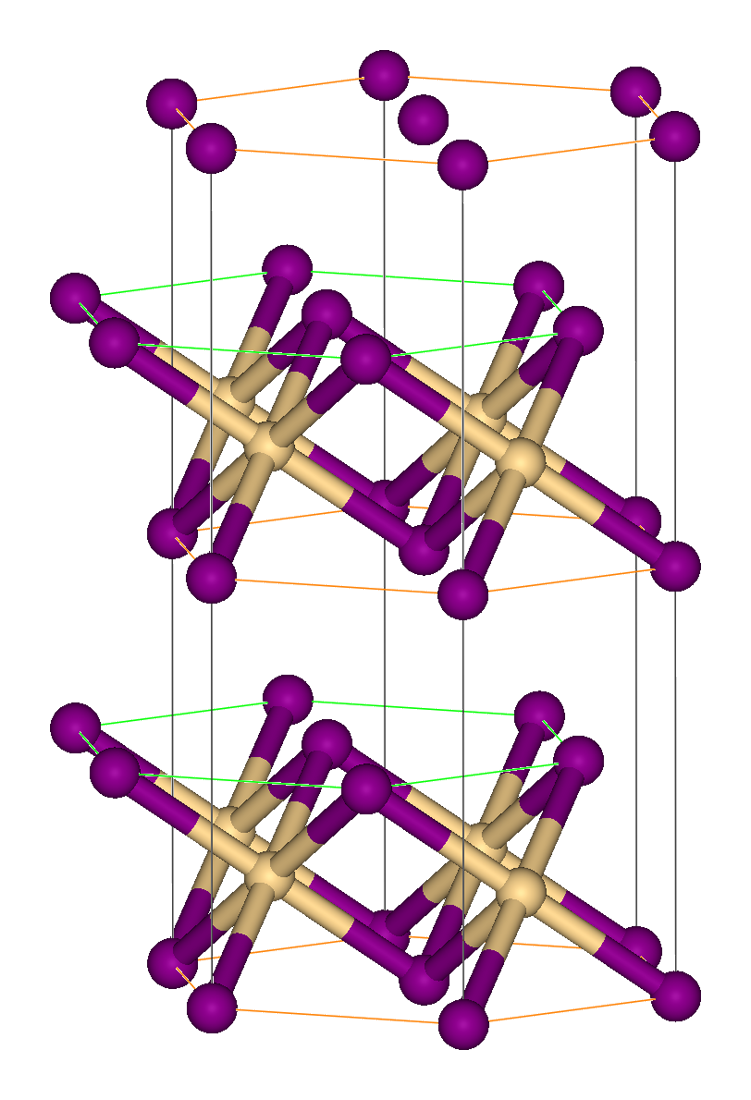
Chromium(II) bromide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrBr2. Like many metal dihalides, CrBr2 adopts the "cadmium iodide structure" motif, i.e., it features sheets of octahedral Cr(II) centers interconnected by bridging bromide ligands. It is a white solid that dissolves in water to give blue solutions that are readily oxidized by air. Synthesis and reactions It can be prepared by reduction of chromium(III) bromide with hydrogen gas for 6–10 hours at 350-400 °C, cogenerating hydrogen bromide Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room tempe ...: :2CrBr3 + H2 → 2CrBr2 + 2HBr Treatment of chromium powder with concentrated hydrobromic acid gives a blue hydrated chromium(II) bromide, which can be converted to a related acetonitrile complex. :Cr + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon ( graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Iodide
Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects. Preparation Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid. Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine. Crystal structure In cadmium iodide the iodide anions form a hexagonal close packed arrangement while the cadmium cations fill all of the octahedral sites in alternate layers. The resultant structure consists of a layered lattice. This same basic structure is found in many other salts and minerals. Cadmium iodide is mostly ionically bonded but with partial covalent character. Cadmium iodide's crystal structure is the prototype on which the crystal structures many other compounds can be conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridging Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a bridging ligand is a ligand that connects two or more atoms, usually metal ions. The ligand may be atomic or polyatomic. Virtually all complex organic compounds can serve as bridging ligands, so the term is usually restricted to small ligands such as pseudohalides or to ligands that are specifically designed to link two metals. In naming a complex wherein a single atom bridges two metals, the bridging ligand is preceded by the Greek letter mu, μ, with a subscript number denoting the number of metals bound to the bridging ligand. μ2 is often denoted simply as μ. When describing coordination complexes care should be taken not to confuse μ with η ('eta'), which relates to hapticity. Ligands that are not bridging are called terminal ligands. List of bridging ligands Virtually all ligands are known to bridge, with the exception of amines and ammonia. Common bridging ligands include most of the common anions. Many simple organic ligands form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(III) Bromide
Chromium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrBr3. It is a dark colored solid that appears green in transmitted light but red with reflected light. It is used as a precursor to catalysts for the oligomerization of ethylene. Synthesis The compound is prepared in a tube furnace by the reaction of bromine vapor and chromium powder at 1000 °C. It is purified by extracting with absolute diethyl ether to remove any CrBr2, and is subsequently washed with absolute diethyl ether and absolute ethanol. Analogous to the behavior of related chromium(III) halides, the tribromide dissolves in water to give CrBr3(H2O)3 only upon the addition of catalytic amounts of a reducing agent, which generates CrBr2. The reducing agent generates chromous bromide on the surface of the solid, which dissolves and re-oxidizes to Cr(III). Reactions Chromium(III) bromide is reduced by hydrogen gas at 350-400 °C to give chromium(II) bromide Chromium(II) bromide is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bromide
Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C. Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached. Hydrogen bromide, and its aqueous solution, are commonly used reagents in the preparation of bromide compounds. Reactions Organic chemistry Hydrogen bromide and hydrobromic acid are important reagents in the production of organobromine compounds.Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Butterworth-Heineman: Oxford, Great Britain; 1997; pp. 809–812.Vollhardt, K. P. C.; Schore, N. E. Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function; 4th Ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY; 2003. In a fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrobromic Acid
Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid has a p''K''a of −9, making it a stronger acid than hydrochloric acid, but not as strong as hydroiodic acid. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known. Uses Hydrobromic acid is mainly used for the production of inorganic bromides, especially the bromides of zinc, calcium, and sodium. It is a useful reagent for generating organobromine compounds. Certain ethers are cleaved with HBr. It also catalyzes alkylation reactions and the extraction of certain ores. Industrially significant organic compounds prepared from hydrobromic acid include allyl bromide, tetrabromobis(phenol), and bromoacetic acid. HBr almost uniquely participates in anti-Markovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes. The resulting 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile Complex
Transition metal nitrile complexes are coordination compounds containing nitrile ligands. Because nitriles are weakly basic, the nitrile ligands in these complexes are often labile. Scope of nitriles Typical nitrile ligands are acetonitrile, propionitrile, and benzonitrile. The structures of u(NH3)5(NCPh)sup>n+ have been determined for the 2+ and 3+ oxidation states. Upon oxidation the Ru-NH3 distances contract and the Ru-NCPh distances elongate, consistent with amines serving as pure-sigma donor ligands and nitriles functioning as pi-acceptors. Synthesis and reactions Acetonitrile, propionitrile and benzonitrile are also popular solvents. Because nitrile solvents have high dielectric constants, cationic complexes containing a nitrile ligand are often soluble in a solution of that nitrile. Some complexes can be prepared by dissolving an anhydrous metal salt in the nitrile. In other cases, a suspension of the metal is oxidized with a solution of NOBF4 in the nitrile: :Ni + 6 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(II) Compounds
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal. Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored. Industrial production of chromium proceeds from chromite ore (mostly FeCr2O4) to produce fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromides
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm. Natural occurrence Bromide is present in typical seawater (35 PSU) with a concentration of around 65 mg/L, which is about 0.2% of all dissolved salts. Seafood and deep sea plants generally have higher levels than land-derived foods. Bromargyrite—natural, crystalline silver bromide—is the most common bromide mineral known but is still very rare. In addition to silver, bromine is also in minerals combined with mercury and copper. Formation and rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
copper(I)_hexafluorophosphate.png)
