|
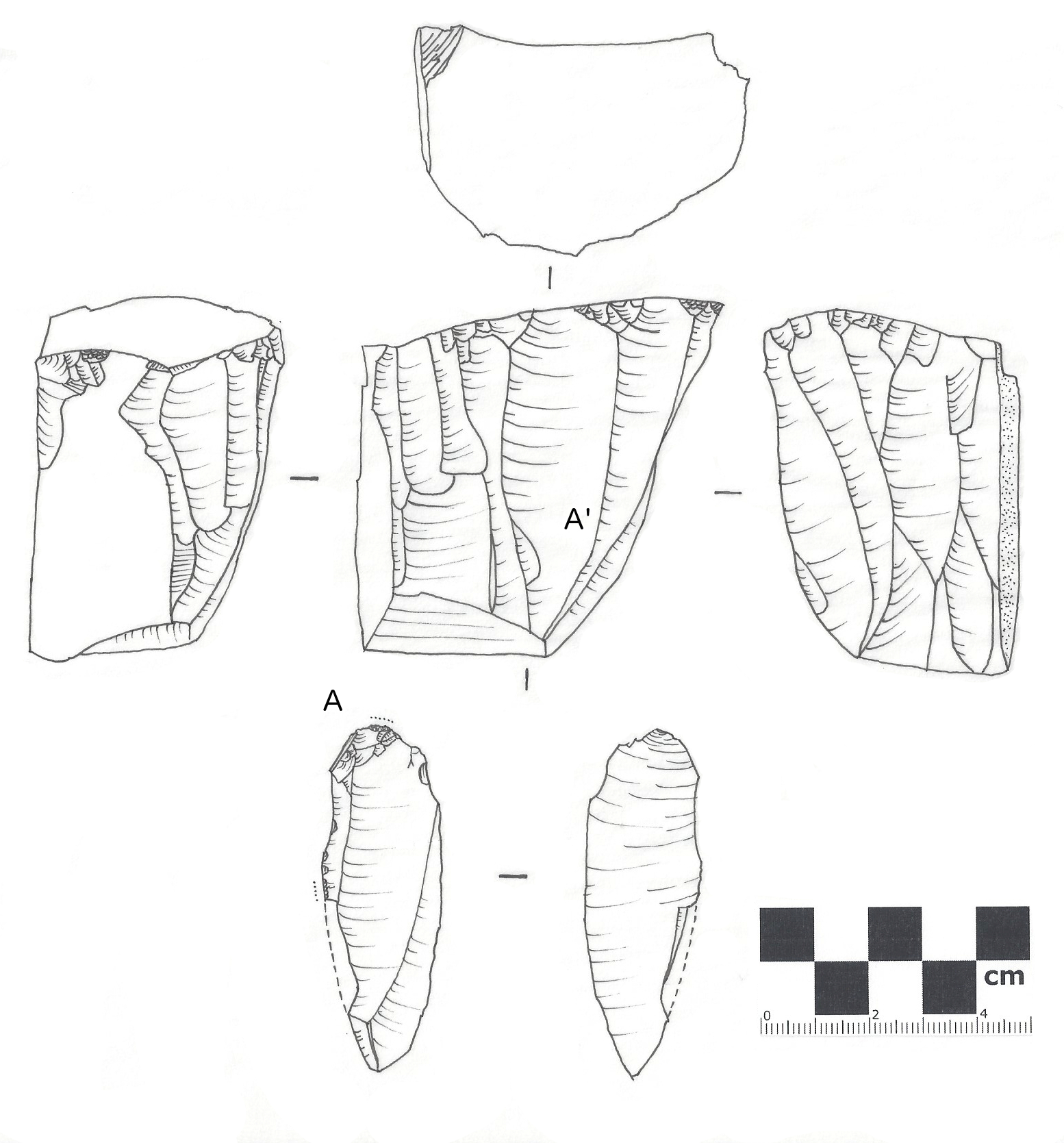
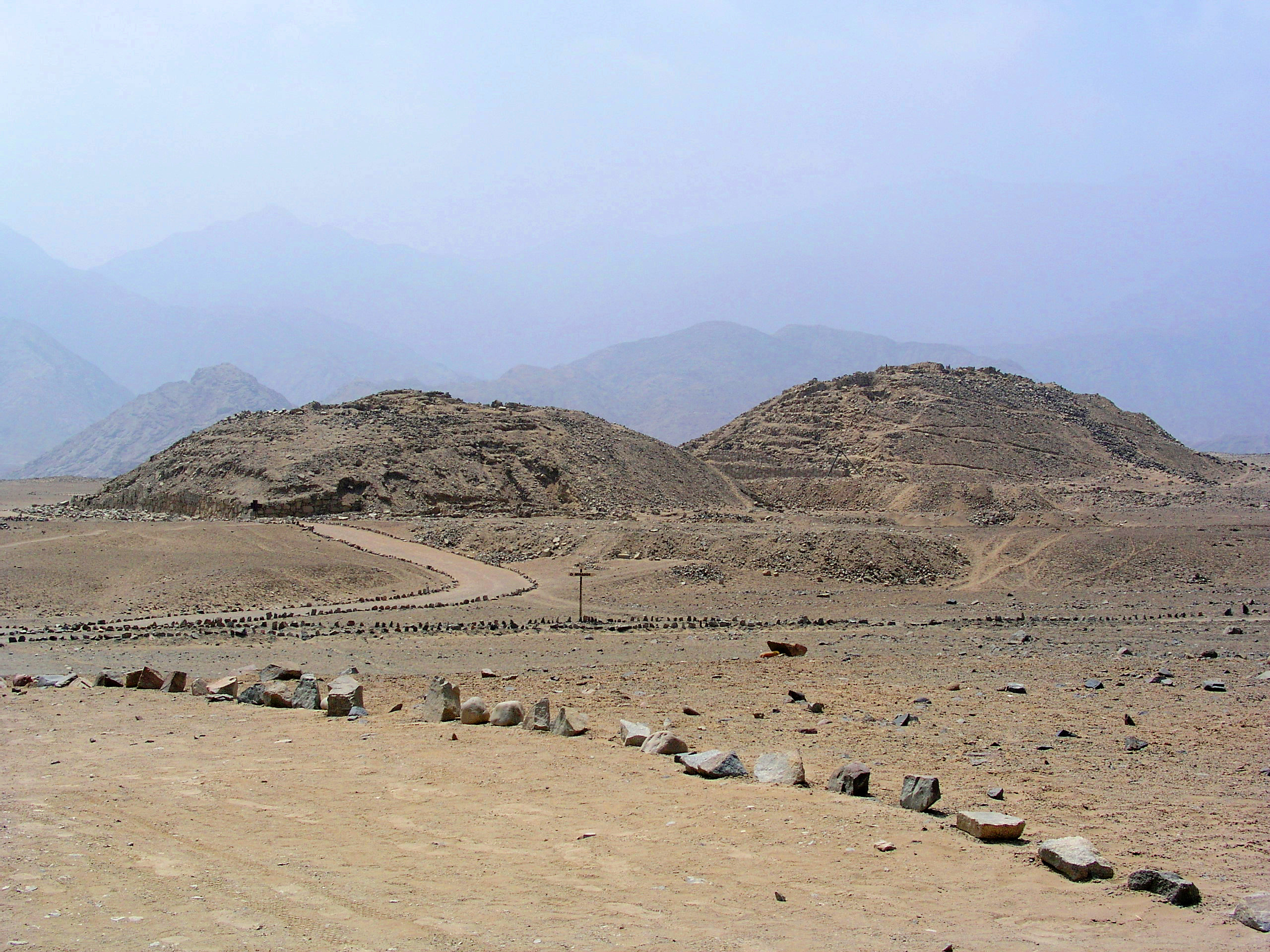
Chivateros
Chivateros is a prehistoric stone tool quarry and associated workshop located near the mouth of the Chillón river in the Ventanilla District, northwest of Lima, Peru. Archaeological site Excavations were led in 1963 and 1966 by archaeologists Thomas C. Patterson and Edward P. Lanning, who noticed three cultural assemblages in the Chillón valley and uncovered large quantities of debris of lithic artifact production, initially interpreted as lithic instruments (hand axes, spearheads, scrapers, etc.). In an area of coastal lomas Lomas (Spanish for "hills"), also called fog oases and mist oases, are areas of fog-watered vegetation in the coastal desert of Peru and northern Chile. About 100 lomas near the Pacific Ocean are identified between 5°S and 30°S latitude, a nort ... (areas of fog-watered vegetation), excavations revealed a lithic flake industry as early as the Late Pleistocene, dating between 9,000 and 11,000 years ago. Wood fragments helped define a ''Chivateros I' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventanilla District
Ventanilla is a district of the Constitutional Province of Callao in Peru, and one of the seven districts that comprise the port city of Callao. Covering more than half of the province's territory, it is Callao's largest district. The current mayor of Ventanilla is Pedro Carmelo Spadaro. It was officially established as a district on January 28, 1969. The first stone for the building of Ventanilla was placed on September 24, 1960, in what is now the Central Church of Ventanilla San Pedro Nolasco. Geography The district has a total land area of 73.52 km2. Its administrative center is located 71 meters above sea level. Ventanilla is located in the northern part of the province. Ventanilla is made up of eight urban zones and more than 160 neighborhoods (''barrios''). Boundaries * North: Santa Rosa and Ancón (both in the Lima Province) * East: Puente Piedra (Lima Province) and Mi Peru (Callao). * South: Downtown Callao, and San Martín de Porres (Lima Province) * West: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean Preceramic
The Andean preceramic refers to the early period of human occupation in the Andean area of South America that preceded the introduction of ceramics. This period is also called pre-ceramic or aceramic. Earliest human occupations The earliest humans that came to South America are known as Paleo-Indians. This period is generally known as the Lithic stage. After this came the period that is widely known as Archaic, although there are also some different classifications of this period. The precise classification is complicated because somewhat different terminologies tend to be used for North America and Mesoamerica. The Andean preceramic period would include cultures that belong to Lithic and Archaic stages. Preceramic in Peru The Zaña Valley in northern Peru contains the earliest known canals in South America. These were small stone-lined canals which drew water from streams in the Andes Mountains region. These canals may have been built as early as 4700 BC. A great deal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter-gatherers
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, honey, or anything safe to eat, and/or by hunting game (pursuing and/or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish), roughly as most animal omnivores do. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who did not change were displaced or conquered by farming or pastoralist gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chillón River
The Chillón River is a river located in western Peru. Its waters are produced by the melting of ice in the glaciers of the Andes, and its mouth is located in the Pacific Ocean coast of the Callao Region. Its volume gets higher during the summer months (December to March). The river's valley is very fertile. It has been inhabited by varying indigenous cultures for more than ten thousand years, as shown by archeological Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ... evidence. The 4,000-year-old ruins known as El Paraíso are located 40 kilometres north-east of Lima in the Chillón River Valley. A temple at the site is believed to be about 5,000 years old, if the date is confirmed it would be among the oldest sites in the world, comparable to the ancient city of Caral, a coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of the country, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Together with the seaside city of Callao, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area. With a population of more than 9.7 million in its urban area and more than 10.7 million in its metropolitan area, Lima is one of the largest cities in the Americas. Lima was named by natives in the agricultural region known by native Peruvians as ''Limaq''. It became the capital and most important city in the Viceroyalty of Peru. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru (República del Perú). Around one-third of the national population now lives in its metropolitan area. The city of Lima is considered to be the political, cultural, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assemblage (archaeology)
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomas
Lomas (Spanish for "hills"), also called fog oases and mist oases, are areas of fog-watered vegetation in the coastal desert of Peru and northern Chile. About 100 lomas near the Pacific Ocean are identified between 5°S and 30°S latitude, a north–south distance of about . Lomas range in size from a small vegetated area to more than and their flora includes many endemic species. Apart from river valleys and the lomas the coastal desert is almost without vegetation. Scholars have described individual lomas as "an island of vegetation in a virtual ocean of desert." In a nearly rainless desert, the lomas owe their existence to the moist dense fog and mist which rolls in from the Pacific. The fog is called garúa in Peru and Camanchaca in Chile. Environment According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, the coastal desert of Peru and the Atacama desert of Chile feature a rare desert climate, that is abbreviated "BWn" on climate maps with the n denoting frequent fog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of Peru
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_Guamán_Poma%2C_1616.jpg)