|
Chinchilla AI
Chinchilla is a family of large language models developed by the research team at DeepMind, presented in March 2022. It is named "chinchilla" because it is a further development over a previous model family named Gopher. Both model families were trained in order to investigate the scaling laws of large language models. It claimed to outperform GPT-3. It considerably simplifies downstream utilization because it requires much less computer power for inference and fine-tuning. Based on the training of previously employed language models, it has been determined that if one doubles the model size, one must also have twice the number of training tokens. This hypothesis has been used to train Chinchilla by DeepMind DeepMind Technologies is a British artificial intelligence subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and research laboratory founded in 2010. DeepMind was List of mergers and acquisitions by Google, acquired by Google in 2014 and became a wholly owned subsid .... Similar to Gopher in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Language Model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model consisting of a neural network with many parameters (typically billions of weights or more), trained on large quantities of unlabelled text using self-supervised learning. LLMs emerged around 2018 and perform well at a wide variety of tasks. This has shifted the focus of natural language processing research away from the previous paradigm of training specialized supervised models for specific tasks. Properties Though the term ''large language model'' has no formal definition, it often refers to deep learning models having a parameter count on the order of billions or more. LLMs are general purpose models which excel at a wide range of tasks, as opposed to being trained for one specific task (such as sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, or mathematical reasoning). The skill with which they accomplish tasks, and the range of tasks at which they are capable, seems to be a function of the amount of resources (data, parameter-si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeepMind
DeepMind Technologies is a British artificial intelligence subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and research laboratory founded in 2010. DeepMind was acquired by Google in 2014 and became a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc, after Google's restructuring in 2015. The company is based in London, with research centres in Canada, France, and the United States. DeepMind has created a neural network that learns how to play video games in a fashion similar to that of humans, as well as a Neural Turing machine, or a neural network that may be able to access an external memory like a conventional Turing machine, resulting in a computer that mimics the short-term memory of the human brain. DeepMind made headlines in 2016 after its AlphaGo program beat a human professional Go player Lee Sedol, a world champion, in a five-game match, which was the subject of a documentary film. A more general program, AlphaZero, beat the most powerful programs playing go, chess and shogi (Japanese chess) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinchilla
Chinchillas are either of two species ('' Chinchilla chinchilla'' and '' Chinchilla lanigera'') of crepuscular rodents of the parvorder Caviomorpha. They are slightly larger and more robust than ground squirrels, and are native to the Andes mountains in South America. They live in colonies called " herds" at high elevations up to . Historically, chinchillas lived in an area that included parts of Bolivia, Peru, Argentina, and Chile, but today, colonies in the wild are known only in Chile. Along with their relatives, viscachas, they make up the family Chinchillidae. They are also related to the chinchilla rat. The chinchilla has the densest fur of all mammals that live on land. In the water, the sea otter has a denser coat. The chinchilla is named after the Chincha people of the Andes, who once wore its dense, velvet-like fur. By the end of the 19th century, chinchillas had become quite rare after being hunted for their ultra-soft fur. Most chinchillas currently used by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
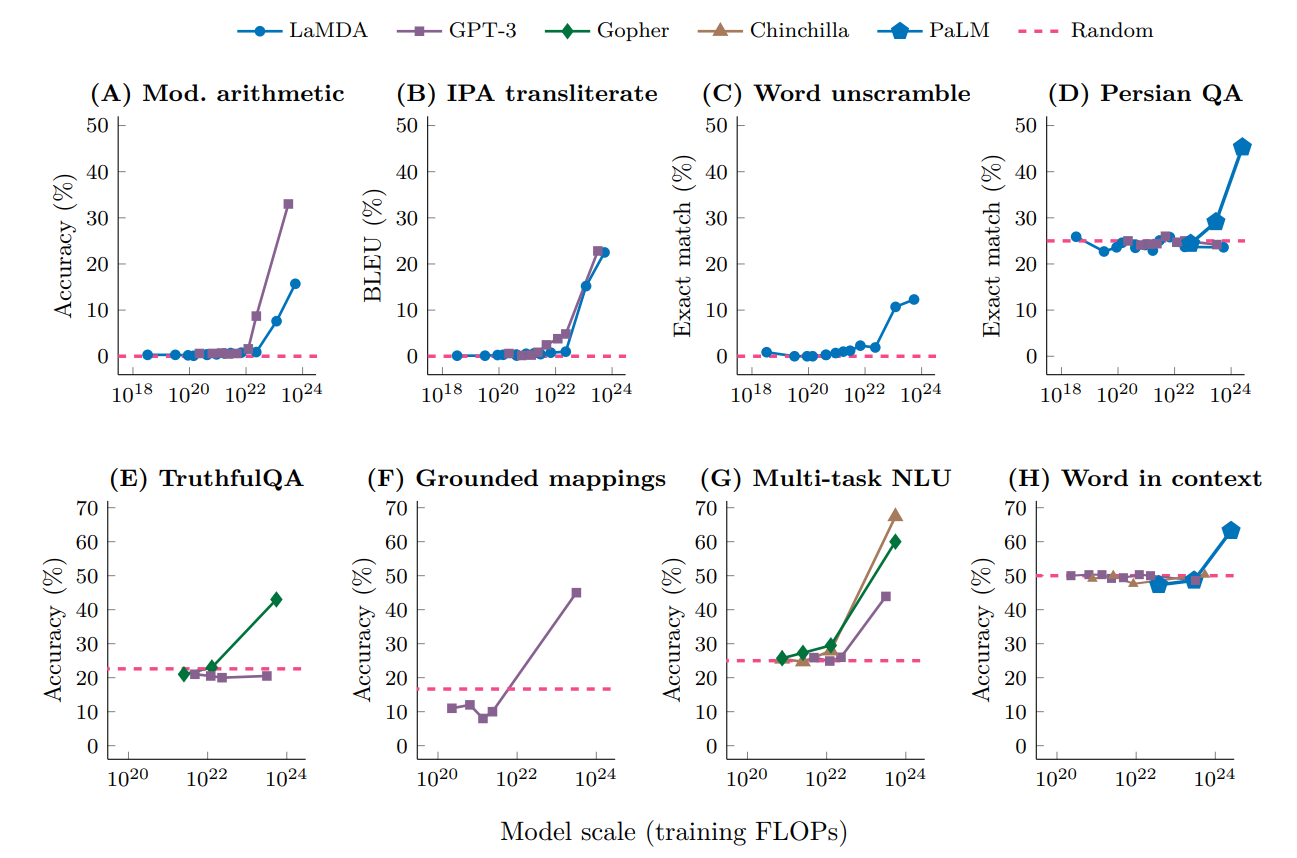
Neural Scaling Law
In machine learning, a neural scaling law is an empirical scaling law that describes how neural network performance changes as key factors are scaled up or down. These factors typically include the number of parameters, training dataset size, and training cost. Introduction In general, a neural model can be characterized by 4 parameters: size of the model, size of the training dataset, cost of training, error rate after training. Each of these four variables can be precisely defined into a real number, and they are empirically found to be related by simple statistical laws, called "scaling laws". These are usually written as N, D, C, L (number of parameters, dataset size, computing cost, loss). Size of the model In most cases, the size of the model is simply the number of parameters. However, one complication arises with the use of sparse models, such as mixture-of-expert models. In sparse models, during every inference, only a fraction of the parameters are used. In compariso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPT-3
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) is an autoregressive language model that uses deep learning to produce human-like text. Given an initial text as prompt, it will produce text that continues the prompt. The architecture is a standard transformer network (with a few engineering tweaks) with the unprecedented size of 2048-token-long context and 175 billion parameters (requiring 800 GB of storage). The training method is "generative pretraining", meaning that it is trained to predict what the next token is. The model demonstrated strong few-shot learning on many text-based tasks. It is the third-generation language prediction model in the GPT-n series (and the successor to GPT-2) created by OpenAI, a San Francisco-based artificial intelligence research laboratory. GPT-3, which was introduced in May 2020, and was in beta testing as of July 2020, is part of a trend in natural language processing (NLP) systems of pre-trained language representations. The quality of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding
In artificial intelligence, Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) is a benchmark for evaluating the capabilities of large language models. Benchmark It consists of about 16,000 multiple-choice questions spanning 57 academic subjects including mathematics, philosophy, law, and medicine. It is one of the most commonly used benchmarks for comparing the capabilities of large language models, with over 100 million downloads as of July 2024. The MMLU was released by Dan Hendrycks and a team of researchers in 2020 and was designed to be more challenging than then-existing benchmarks such as General Language Understanding Evaluation (GLUE) on which new language models were achieving better-than-human accuracy. At the time of the MMLU's release, most existing language models performed around the level of random chance (25%), with the best performing GPT-3 model achieving 43.9% accuracy. The developers of the MMLU estimate that human domain-experts achieve around 89.8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
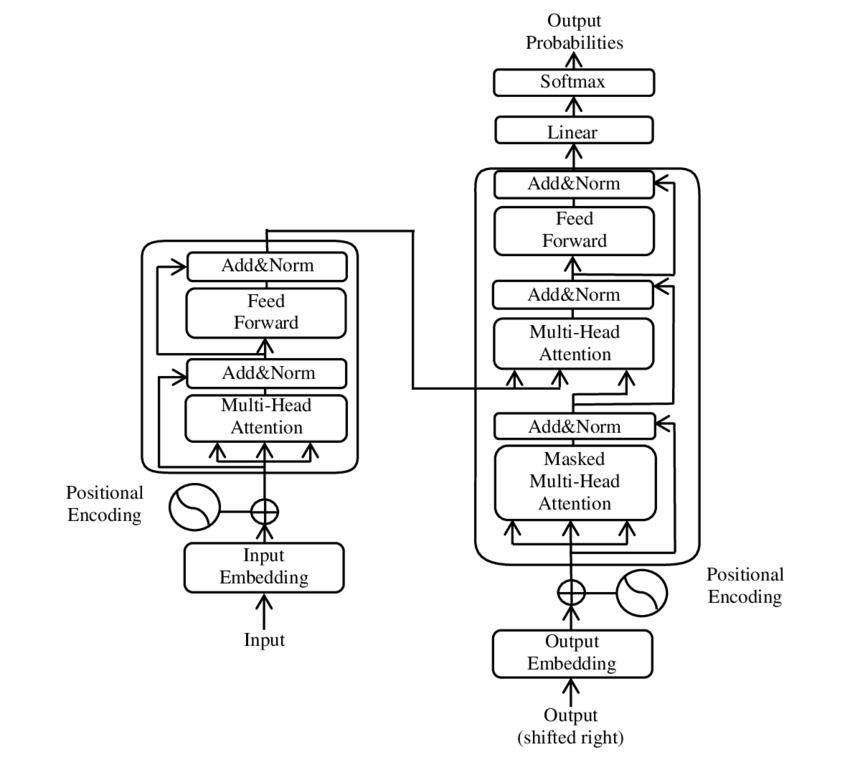
Transformer (machine Learning Model)
A transformer is a deep learning model that adopts the mechanism of self-attention, differentially weighting the significance of each part of the input data. It is used primarily in the fields of natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision (CV). Like recurrent neural networks (RNNs), transformers are designed to process sequential input data, such as natural language, with applications towards tasks such as translation and text summarization. However, unlike RNNs, transformers process the entire input all at once. The attention mechanism provides context for any position in the input sequence. For example, if the input data is a natural language sentence, the transformer does not have to process one word at a time. This allows for more parallelization than RNNs and therefore reduces training times. Transformers were introduced in 2017 by a team at Google Brain and are increasingly the model of choice for NLP problems, replacing RNN models such as long short-term me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPT-2
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2 (GPT-2) is an open-source artificial intelligence created by OpenAI in February 2019. GPT-2 translates text, answers questions, summarizes passages, and generates text output on a level that, while sometimes indistinguishable from that of humans, can become repetitive or nonsensical when generating long passages. It is a general-purpose learner; it was not specifically trained to do any of these tasks, and its ability to perform them is an extension of its general ability to accurately synthesize the next item in an arbitrary sequence. GPT-2 was created as a "direct scale-up" of OpenAI's 2018 GPT model, with a ten-fold increase in both its parameter count and the size of its training dataset. The GPT architecture implements a deep neural network, specifically a transformer model, which uses attention in place of previous recurrence- and convolution-based architectures. Attention mechanisms allow the model to selectively focus on segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RMSNorm
In machine learning, normalization is a statistical technique with various applications. There are mainly two forms of normalization, data normalization and activation normalization. Data normalization, or feature scaling, is a general technique in statistics, and it includes methods that rescale input data so that they have well-behaved range, mean, variance, and other statistical properties. Activation normalization is specific to deep learning, and it includes methods that rescale the activation of hidden neurons inside a neural network. Normalization is often used for faster training convergence, less sensitivity to variations in input data, less overfitting, and better generalization to unseen data. They are often theoretically justified as reducing covariance shift, smoother optimization landscapes, increasing regularization, though they are mainly justified by empirical success. Batch normalization Batch normalization (BatchNorm) operates on the activations of a layer for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Optimizer
Stochastic gradient descent (often abbreviated SGD) is an iterative method for optimizing an objective function with suitable smoothness properties (e.g. differentiable or subdifferentiable). It can be regarded as a stochastic approximation of gradient descent optimization, since it replaces the actual gradient (calculated from the entire data set) by an estimate thereof (calculated from a randomly selected subset of the data). Especially in high-dimensional optimization problems this reduces the very high computational burden, achieving faster iterations in trade for a lower convergence rate. While the basic idea behind stochastic approximation can be traced back to the Robbins–Monro algorithm of the 1950s, stochastic gradient descent has become an important optimization method in machine learning. Background Both statistical estimation and machine learning consider the problem of minimizing an objective function that has the form of a sum: : Q(w) = \frac\sum_^n Q_i(w), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |