|
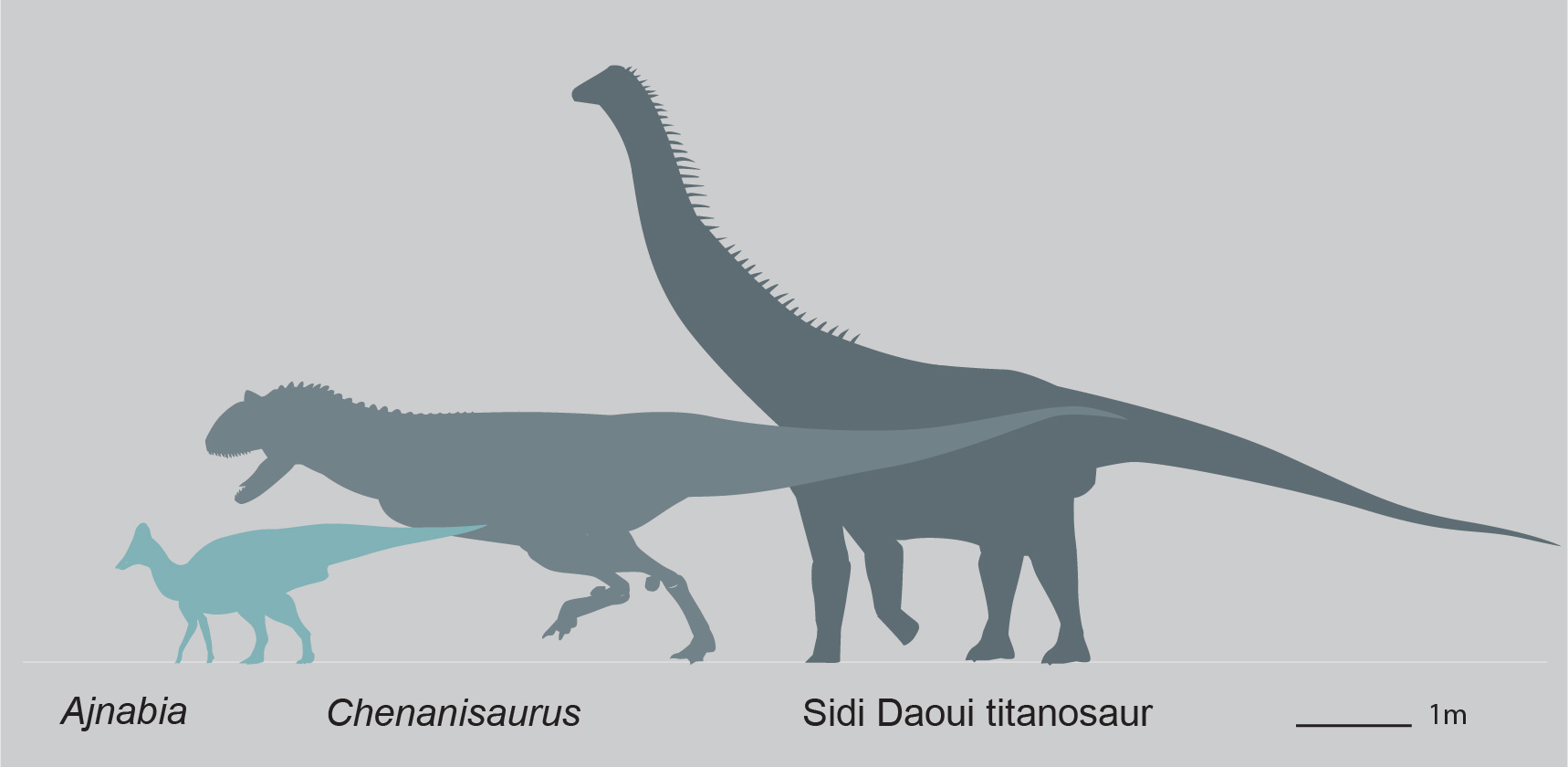
Chenanisaurus Barbaricus
''Chenanisaurus'' is a genus of predatory abelisaurid dinosaur, with a single known species ''C. barbaricus''. It comes from the upper Maastrichtian phosphates of the Ouled Abdoun Basin in Morocco, North Africa. The animal is known from a holotype, consisting of a partial jaw bone, and several isolated teeth found in the same beds. ''Chenanisaurus'' is one of the largest members of the Abelisauridae, and one of the last, being a contemporary of the North American ''Tyrannosaurus''. It would have been among the dinosaur species wiped out by the Chicxulub asteroid impact and the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass extinction that followed. Description ''Chenanisaurus'' is quite a large abelisaurid, measuring , based on measurements of the holotype dentary. Its size is comparable to that of large abelisaurids such as '' Carnotaurus'' and '' Pycnonemosaurus''. Nicholas R. Longrich and colleagues, the describers of ''Chenanisaurus'', identified distinctive features distinguishing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
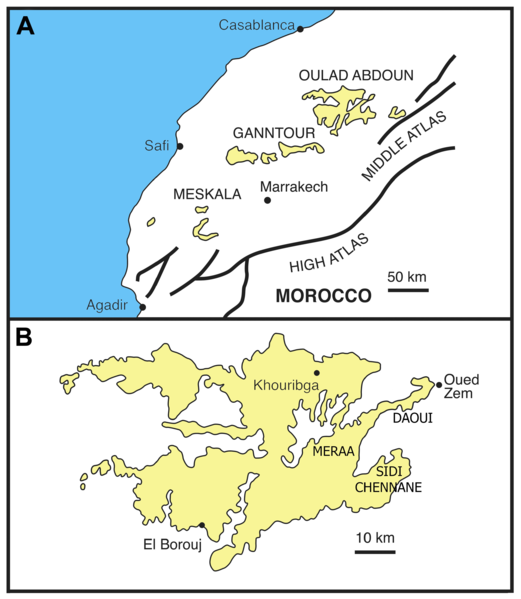
Ouled Abdoun Basin
The Oulad Abdoun Basin (also known as the Ouled Abdoun Basin or Khouribga Basin) is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous ( Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years. Geography The Oulad Abdoun is located west of the Atlas Mountains, near the city of Khouribga. The Oulad Abdoun phosphate deposits encompass some , an area of . The Oulad Abdoun is the largest and northernmost of Morocco's major phosphate basins, which from northeast to southwest, include the Ganntour, Meskala, and Oued Eddahab (Laayoune-Baa) basins. Paleobiota The Oulad Abdoun Basin stretches from late Cretaceous to the Eocene, and contains abundant marine vertebrate fossils, including sharks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratosaurs Phylogenetics-2018 Delcourt
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with ''Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, ''Saltriovenator'', dates to the earliest part of the Jurassic, around 199 million years ago. According to the majority of the latest research, Ceratosauria includes three major clades: Ceratosauridae, Noasauridae, and Abelisauridae, found primarily (though not exclusively) in the Southern Hemisphere. Originally, Ceratosauria included the above dinosaurs plus the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic Coelophysoidea and Dilophosauridae, implying a much earlier divergence of ceratosaurs from other theropods. However, most recent studies have shown that coelophysoids and dilophosaurids do not form a natural group with other ceratosaurs, and are excluded from this group. Ceratosauria derives its names from the type species, ''Ceratosaurus nasicornis'', described by O.C. Marsh in 1884. A m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelisaurids
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are found on the modern continents of Africa and South America, as well as on the Indian subcontinent and the island of Madagascar. Isolated teeth were found in the Late Jurassic of Portugal, and the Late Cretaceous genera ''Tarascosaurus'' and ''Arcovenator'' have been described in France. Abelisaurids first appear in the fossil record of the early middle Jurassic period, and at least two genera (the Moroccan '' Chenanisaurus'' and the Madagascan ''Majungasaurus'') survived until the end of the Mesozoic era 66 million years ago. Like most theropods, abelisaurids were carnivorous bipeds. They were characterized by stocky hind limbs and extensive ornamentation of the skull bones, with grooves and pits. In many abelisaurids, such as ''Carnotaurus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 In Archosaur Paleontology
The year 2017 in archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology is the scientific study of those animals, especially as they existed before the Holocene Epoch began about 11,700 years ago. The year 2017 in paleontology included various significant developments regarding archosaurs. This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that have been described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in the year 2017. General research * A study on the evolution of forelimb anatomy, musculature and joint ranges of motion from early archosaurs to sauropodomorph dinosaurs based on data from ''Mussaurus patagonicus'' and extant freshwater crocodile is published by Otero ''et al.'' (2017). Pseudosuchians Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Ceratosaur Research
This timeline of ceratosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ceratosaurs, a group of relatively primitive, often horned, predatory theropod dinosaurs that became the apex predators of the southern hemisphere during the Late Cretaceous. The nature and taxonomic composition of the Ceratosauria has been controversial since the group was first distinguished in the late 19th century. In 1884 Othniel Charles Marsh described the new genus and species ''Ceratosaurus nasicornis'' from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of the western United States. He felt that it belonged in a new family that he called the Ceratosauridae. He created the new taxon Ceratosauria to include both the Ceratosauridae and the ostrich-like ornithomimids. The idea of the Ceratosauria was soon contested, however. Later that same decade both Lydekker and Marsh's hated rival Edward Drinker Cope argued that the taxon was invalid. The idea of the Ceratos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajnabia
''Ajnabia'' (meaning "stranger" or "foreigner") is a genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Morocco. It is the first definitive hadrosaur from Africa, and is thought to be related to European dinosaurs like '' Arenysaurus''. The discovery of ''Ajnabia'' came as a surprise to the paleontologists who found it, because Africa was isolated by water from the rest of the world during the Cretaceous, such that hadrosaurs were assumed to have been unable to reach the continent. The animal is relatively small; assuming it represents an adult it would be one of the smallest if not the smallest known hadrosaurids. Discovery and naming Ajnabia was recovered from the Late Maastrichtian strata of the phosphate mines at Sidi Chennane, in Khouribga Province, Morocco. Recovered elements include most of the left maxilla and part of the right, and a fragment of the right dentary. The name Ajnabia derives from the Arabic ''ajnabi'', meaning "stranger" or "foreign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanosauria
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thriving at the time of the extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous. This group includes some of the largest land animals known to have ever existed, such as ''Patagotitan''—estimated at long with a weight of —and the comparably-sized ''Argentinosaurus'' and ''Puertasaurus'' from the same region. The group's name alludes to the mythological Titans of ancient Greek mythology, via the type genus (now considered a ''nomen dubium)'' '' Titanosaurus''. Together with the brachiosaurids and relatives, titanosaurs make up the larger sauropod clade Titanosauriformes. Titanosaurs have long been a poorly-known group, and the relationships between titanosaur species are still not well-understood. Description Titanosauria have the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenanisaurus Shoreline
''Chenanisaurus'' is a genus of predatory abelisaurid dinosaur, with a single known species ''C. barbaricus''. It comes from the upper Maastrichtian phosphates of the Ouled Abdoun Basin in Morocco, North Africa. The animal is known from a holotype, consisting of a partial jaw bone, and several isolated teeth found in the same beds. ''Chenanisaurus'' is one of the largest members of the Abelisauridae, and one of the last, being a contemporary of the North American ''Tyrannosaurus''. It would have been among the dinosaur species wiped out by the Chicxulub asteroid impact and the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass extinction that followed. Description ''Chenanisaurus'' is quite a large abelisaurid, measuring , based on measurements of the holotype dentary. Its size is comparable to that of large abelisaurids such as ''Carnotaurus'' and ''Pycnonemosaurus''. Nicholas R. Longrich and colleagues, the describers of ''Chenanisaurus'', identified distinctive features distinguishing the anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnotaurinae
Carnotaurinae is a subfamily of the theropod dinosaur family Abelisauridae. It includes the dinosaurs ''Aucasaurus'' (from Argentina), ''Carnotaurus'' (from Argentina). The group was first proposed by American paleontologist Paul Sereno in 1998, defined as a clade containing all abelisaurids more closely related to ''Carnotaurus'' than to ''Majungasaurus''. Classification *Subfamily Carnotaurinae **Brachyrostra ***'' Ekrixinatosaurus'' (Argentina) ***'' Elemgasem'' (Argentina) ***'' Guemesia'' (Argentina) ***'' Ilokelesia'' (Argentina) ***'' Skorpiovenator'' (Argentina) ***''Thanos'' (Brazil) ***Furileusauria ****?'' Niebla'' (Argentina) ****'' Llukalkan'' (Argentina) ****'' Viavenator'' (Argentina) ****'' Pycnonemosaurus'' (Brazil) ****'' Quilmesaurus'' (Argentina) ****Carnotaurini *****''Carnotaurus'' (Argentina) ***** Abelisaurinae ******''Aucasaurus'' (Argentina) ******'' Abelisaurus'' (Argentina) Phylogeny In 2008, Canale ''et al.'' published a phylogenetic analysis focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelisaurinae
Carnotaurini is a tribe of the theropod dinosaur family Abelisauridae from the Late Cretaceous period of Patagonia. It includes the dinosaurs ''Carnotaurus sastrei''; the type species, ''Aucasaurus garridoi'', and ''Abelisaurus comahuensis''. This group was first proposed by paleontologists Rodolfo Coria, Luis Chiappe, and Lowell Dingus in 2002, being defined as a clade containing "''Carnotaurus sastrei'', ''Aucasaurus garridoi'', their most recent common ancestor, and all of its decendants." Description Anatomical description and geological distribution Carnotaurins were relatively lightly built but large theropods, ranging in size from 6.1-7.8 m (20-25.6 ft) and 1400–2000 kg (1.6-2.3 tons) in weight. Their geographical distribution lied in South America, as all three species have been found in various formations in Argentina, being the Anacleto Formation of the Rio Colorado Subgroup in the Neuquén Basin and possibly the Sir Fernandez field of the Allen Formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |