Ajnabia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Ajnabia'' (meaning "stranger" or "foreigner") is a genus of
 The holotype specimen, MHNM KHG 222, was recovered from the phosphates of the
The holotype specimen, MHNM KHG 222, was recovered from the phosphates of the
Ajnabia odysseus- the first duckbill dinosaur from Africa- by Nick Longrich
Duckbilled dinosaurs crossed oceans to reach Africa, fossil reveals
lambeosaurine
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', '' Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini ('' ...
hadrosaur
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which inclu ...
from the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
(Maastrichtian) of Morocco. It is the first definitive hadrosaur from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and is thought to be related to European dinosaurs like '' Arenysaurus''. The discovery of ''Ajnabia'' came as a surprise to the paleontologists who found it, because Africa was isolated by water from the rest of the world during the Cretaceous, such that hadrosaurs were assumed to have been unable to reach the continent. The animal is relatively small; assuming it represents an adult it would be one of the smallest if not the smallest known hadrosaurids.
Discovery and naming
Ajnabia was recovered from the Late Maastrichtian strata of the phosphate mines at Sidi Chennane, in Khouribga Province, Morocco. Recovered elements include most of the left maxilla and part of the right, and a fragment of the right dentary. The name Ajnabia derives from the Arabic ''ajnabi'', meaning "stranger" or "foreigner", referring to the animal as part of a dinosaur lineage that immigrated to Africa from elsewhere. Thetype
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
and only species is ''A. odysseus'', referring to the Greek hero and legendary sea voyager Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odys ...
.
Palaeoecology
 The holotype specimen, MHNM KHG 222, was recovered from the phosphates of the
The holotype specimen, MHNM KHG 222, was recovered from the phosphates of the Ouled Abdoun Basin
The Oulad Abdoun Basin (also known as the Ouled Abdoun Basin or Khouribga Basin) is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and a ...
of north-central Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
. The phosphates are a nearshore marine environment, dominated by sharks, fish, mosasaurs
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the ...
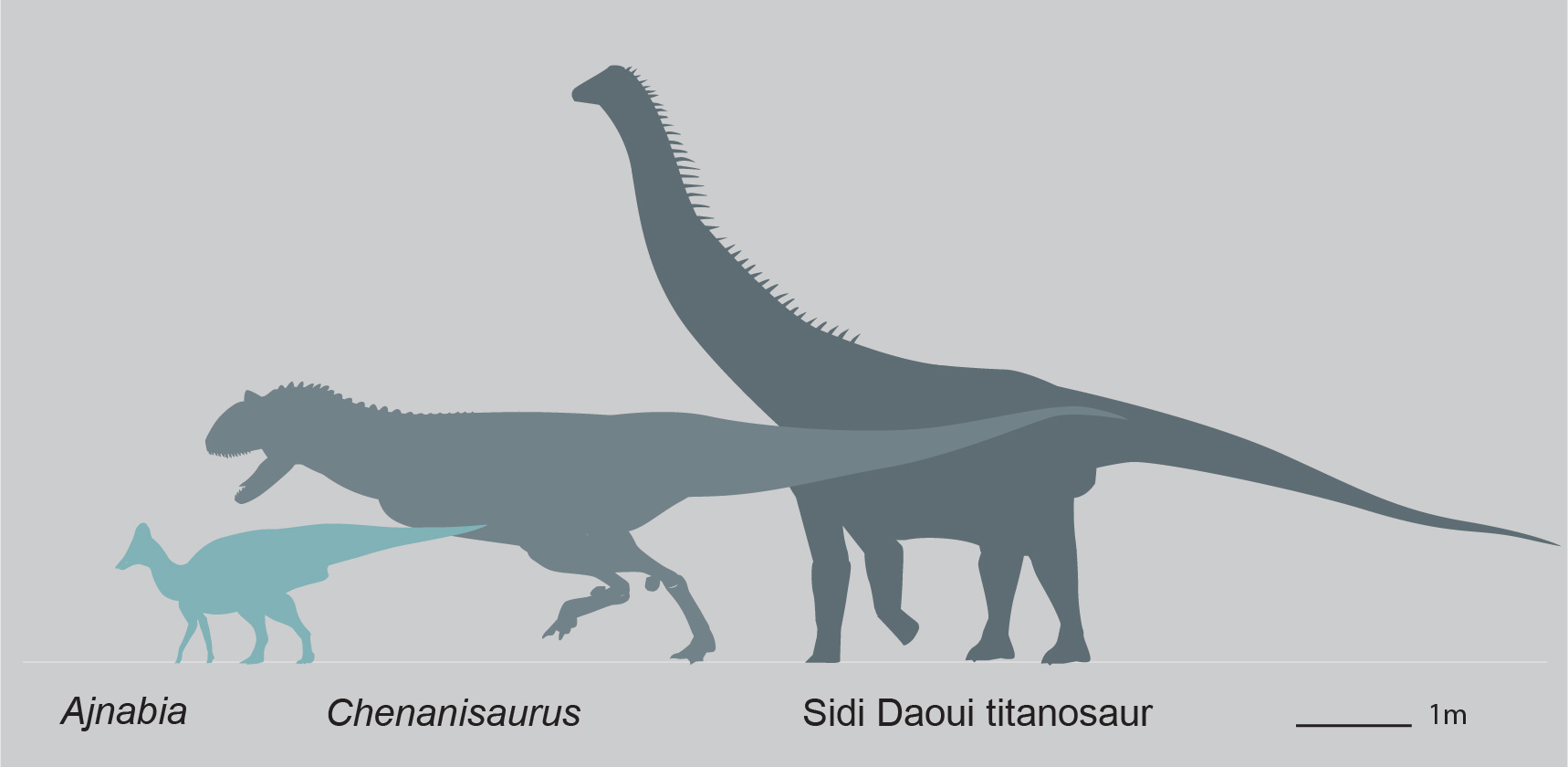
and other marine reptiles. Rare dinosaurs are present here, however, including the large abelisaurid ''Chenanisaurus barbaricus
''Chenanisaurus'' is a genus of predatory abelisaurid dinosaur, with a single known species ''C. barbaricus''. It comes from the upper Maastrichtian phosphates of the Ouled Abdoun Basin in Morocco, North Africa. The animal is known from a ho ...
'' and an unnamed titanosaurian. These dinosaurs would have lived in the very latest Cretaceous (Late Maastrichtian) approximately 1 million years before the K-Pg boundary and the Chicxulub asteroid impact that wiped out the dinosaurs. They therefore provide insights into the diversity of Africa just before the dinosaurs became extinct.
Palaeobiogeography
Phylogenetic analysis suggests that ''Ajnabia'' is a member of theLambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', '' Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Cor ...
, and specifically a member of the Arenysaurini
Arenysaurini is a proposed tribe of primitive lambeosaurine hadrosaurs. It is composed of genera found in Europe and North Africa during the end of the Cretaceous period, and has been suggested to unite all lambeosaurs from the former continent i ...
, a clade otherwise known only from Europe. Based on the relationships of ''Ajnabia'' to other dinosaurs, and reconstructions of Late Cretaceous continents and seas, it was proposed that dispersal of Lambeosaurinae into North Africa most likely occurred via oceanic dispersal
Oceanic dispersal is a type of biological dispersal that occurs when terrestrial organisms transfer from one land mass to another by way of a sea crossing. Island hopping is the crossing of an ocean by a series of shorter journeys between isla ...
, with hadrosaurs swimming or drifting between Europe and North Africa.
External links
Ajnabia odysseus- the first duckbill dinosaur from Africa- by Nick Longrich
Duckbilled dinosaurs crossed oceans to reach Africa, fossil reveals
References
Cretaceous Morocco Fossil taxa described in 2020 Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Africa Lambeosaurines Maastrichtian genus first appearances Maastrichtian genus extinctions Ornithischian genera {{Ornithopod-stub