|
Changzheng Ri
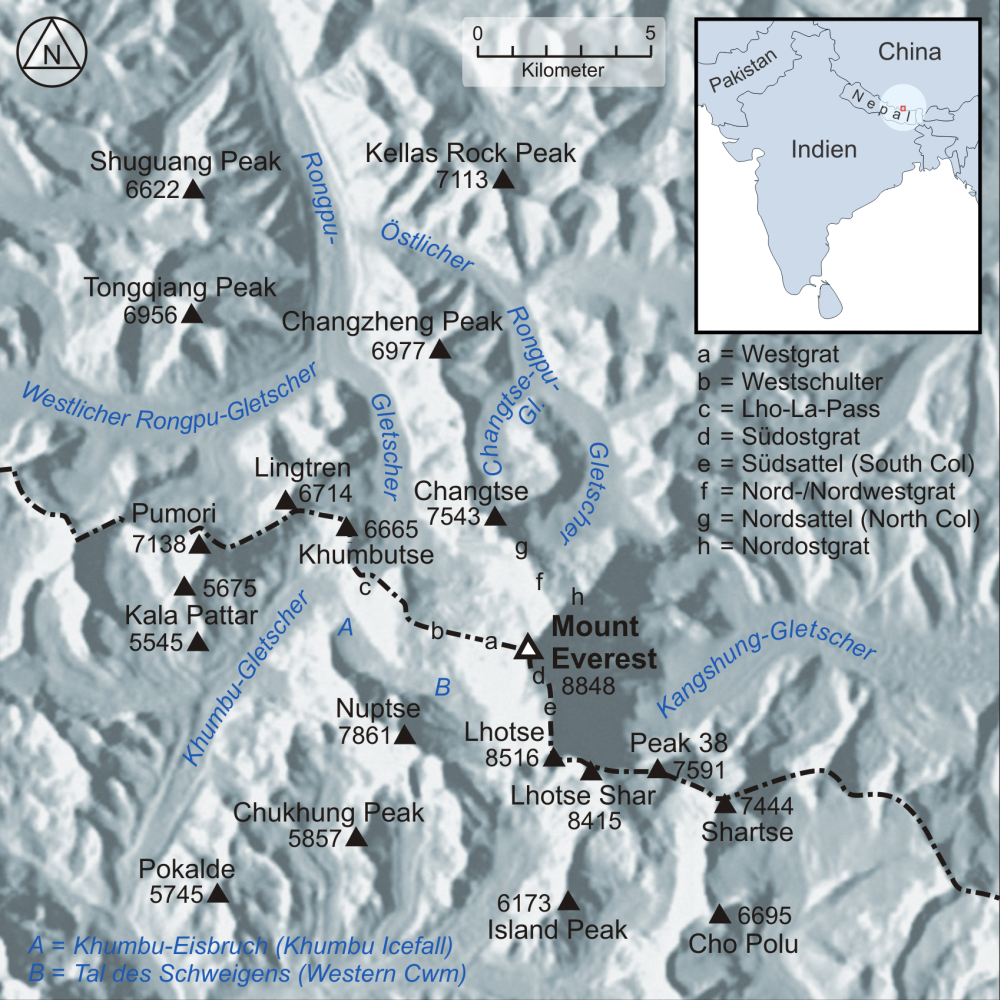
Changzheng Ri () is a mountain in Tibet, China. Description Changzheng Ri is a summit in the Himalayas of Tibet. It is situated north of Changtse and north of Mount Everest in Qomolangma National Nature Preserve. Precipitation runoff from the mountain's slopes drains to the Rong River which is a tributary of the Arun River. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 1,366 metres (4,481 ft) above the Rongbuk Glacier in . The first ski descent from the peak was made in 2003 by Jimmy Chin. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Changzheng Ri is located in a tundra climate zone with cold, snowy winters, and cool summers. Weather systems are forced upwards by the Himalaya mountains (orographic lift), causing heavy precipitation in the form of rainfall and snowfall. Mid-June through early-August is the monsoon season. The months of April, May, September, and October offer the most favorable weather for viewing or climbing this peak. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at its summit. Its height was most recently measured in 2020 by Chinese and Nepali authorities as . Mount Everest attracts many climbers, including highly experienced mountaineers. There are two main climbing routes, one approaching the summit from the southeast in Nepal (known as the standard route) and the other from the north in Tibet. While not posing substantial technical climbing challenges on the standard route, Everest presents dangers such as altitude sickness, weather, and wind, as well as hazards from avalanches and the Khumbu Icefall. As of May 2024, 340 people have died on Everest. Over 200 bodies remain on the mountain and have not been removed due to the dangerous conditions. Climbers typically ascend only part of Mount Eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rongbuk Glacier
The Rongbuk Glacier () is located in the Himalaya of southern Tibet. Two large tributary glaciers, the East Rongbuk Glacier and the West Rongbuk Glacier, flow into the main Rongbuk Glacier. It flows north and forms the Rongbuk Valley north of Mount Everest. The famous Rongbuk Monastery is located at the northern end of the Rongbuk valley. Mount Everest is the source of the Rongbuk Glacier and East Rongbuk Glacier. Discovery The English climber George Mallory first explored the main Rongbuk Valley and its glacier while searching for possible routes to the summit of Mount Everest, during the first British Everest reconnaissance expedition of 1921. On the same expedition, Oliver Wheeler first explored the East Rongbuk Glacier. His exploration below the Lhakpa La pass led him on 3 August 1921 to realise that the East Rongbuk Valley provided the key to a viable route to the summit of Everest. A few weeks later, a party consisting of George Mallory, Guy Bullock, and Oliver Wheele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingtren
Lingtren (), , is a mountain in the Mahalangur Himal area of Himalaya, about distant in a direct line from Mount Everest. It lies on the international border between Nepal and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and it was first climbed in 1935. A mountain nearby to the west was originally named Lingtrennup but is now more commonly called Xi Lingchain. Geography A long chain of mountains extends generally somewhat north of west from Mount Everest whose west ridge descends to the col of Lho La () before rising to Khumbutse (). The ridge drops to an unnamed col at and then ascends to Lingtren from where it continues to another unnamed col at and then to Pumori (). Bounded on the north by this chain of mountains is the Western Cwm in Nepal down which the Khumbu Glacier descends to the northwest over the Icefall before it turns sharply southwest. Lingtren lies at the apex of this right-angled bend. North of the mountain chain in Tibet the West Rongbuk Glacier flows east to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khartaphu
Khartaphu (also Kardapu) is a mountain in the Himalayas of Asia at the head of the Tibetan Kharta valley. At above sea level, it is the 102nd highest mountain in the world. The peak is located in Tibet Autonomous Region, China about northeast of Mount Everest. Khartaphu has a moderately significant subpeak, Khartaphu West, also known as Xiangdong, located approximately west of Khartaphu (main) with an elevation of and a prominence In topography, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling ... of . Khartaphu was first climbed by the 1935 British Mount Everest reconnaissance expedition. References Mountains of Tibet Seven-thousanders of the Himalayas {{Tibet-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everest Base Camps
There are two base camps on Mount Everest, on opposite sides of the mountains: South Base Camp is in Nepal at an altitude of (), while North Base Camp is in Tibet at (). The base camps are rudimentary campsites at the base of Mount Everest that are used by mountain climbers during their ascent and descent. They are also visited by hikers. South Base Camp is used when climbing via the southeast ridge, while North Base Camp is used when climbing via the northeast ridge. Supplies are shipped to the South Base Camp by porters, and with the help of animals, usually yaks. The North Base Camp is accessed by a paved road that branches from China National Highway 318. Climbers typically rest at base camp for several days for acclimatization, to reduce the risk of altitude sickness. South Base Camp in Nepal The Everest Base Camp trek on the south side, at an elevation of , is one of the most popular trekking routes in the Himalayas and about 40,000 people per year make the trek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Himalayas
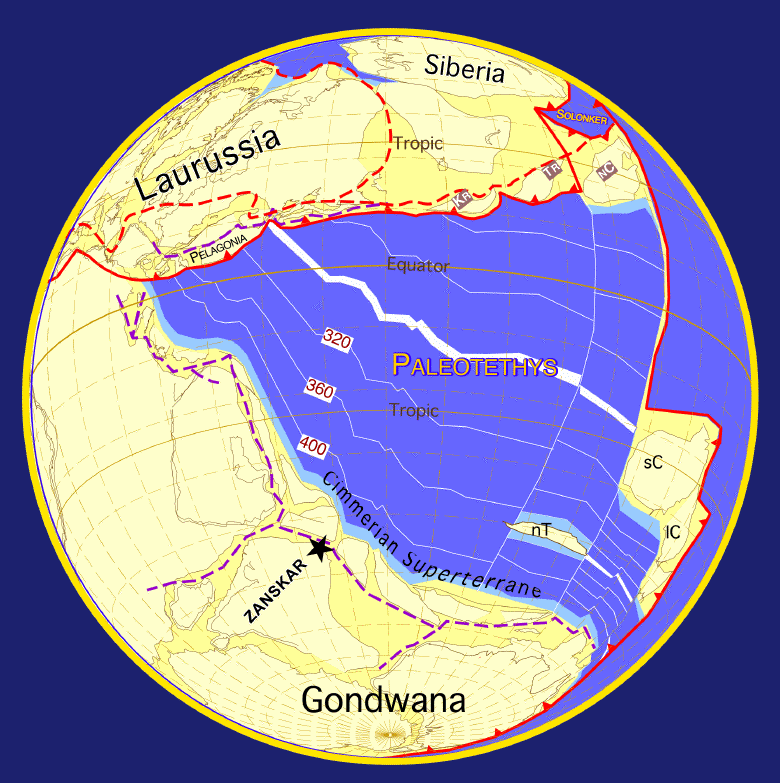
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namcha Barwa syntaxis at the eastern end of the mountain range and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the collision of the continental crust of two tectonic plates, namely, the Indian Plate thrusting into the Eurasian Plate. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the world population, and accounts for a quarter of the global sedimentary budget. Topographically, the belt has many superlatives: the highest rate of uplift (nearly 10 mm/year at Nanga Parbat), the highest relief (8848 m at Mt. Everest Chomolangma), among the highest erosion rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the greatest rivers and the highest concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orographic Lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions, precipitation. Orographic lifting can have a number of effects, including precipitation, rain shadowing, leeward winds, and associated clouds. Precipitation Precipitation induced by orographic lift occurs in many places throughout the world. Examples include: * The Mogollon Rim in central Arizona * The western slope of the Sierra Nevada range in California. * The western slope of the Wasatch Range in Utah. Specifically the Little and Big Cottonwood Canyons. * The mountains near Baja California North – specifically La Bocana to Laguna Hanson. * The windward slopes of Khasi and Jayantia Hills (see Mawsynram) in the state of Meghalaya in India. * The Western Highlands of Yemen, which rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tundra Climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. It is classified as ET according to the Köppen climate classification. It is a climate which at least one month has an average temperature high enough to melt snow (), but no month with an average temperature in excess of . If the climate occurs at high elevations, it is known as alpine climate. Despite the potential diversity of climates in the ''ET'' category involving precipitation, extreme temperatures, and relative wet and dry seasons, this category is rarely subdivided. Rainfall and snowfall are generally slight due to the low vapor pressure of water in the chilly atmosphere, but as a rule potential evapotranspiration is extremely low, allowing soggy terrain of swamps and bogs even in places that get precipitation typical of deserts of lower and middle latitudes. The amount of native tundra biomass depends more on the local temperature than the amount of precipitation. Tundra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jimmy Chin
Jimmy Chin (born October 12, 1973) is an American professional mountain athlete, photographer, skier, film director, and author. Chin has been a professional climber and skier on The North Face Athlete team for over 20 years. In 2006, Chin achieved the first successful American ski descent from the summit of Mount Everest with Kit and Rob DesLauriers. Five years later, Chin, Conrad Anker, and Renan Ozturk captured the first ascent of "Shark's Fin", a granite wall on India's Meru Peak. Chin's work documenting expeditions and climbs has been featured in numerous publications, including ''National Geographic'', ''The New York Times Magazine'', '' Vanity Fair'', ''Outside'' magazine and others. In 2019, Chin was awarded the ''National Geographic'' "Photographer's Photographer Award" by his peers. His first book of photography documenting his career in the mountains, ''There and Back'', became a ''New York Times'' Best Seller in 2021. Chin co-directs with his wife Elizabeth Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Relief
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns. Bathymetry is the study of underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. Importance The understanding of terrain is critical for many reasons: * The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands. * In terms of environmental quality, agriculture, hydrology and other interdisciplinary sciences; understanding the terrain of an area assists the understanding of watershed boundaries, drainage characteristics, drainage systems, groundwater systems, water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |