|
Chaicayán Group
Chaicayán Group is a group of poorly defined sedimentary rock strata found in the Taitao Peninsula on the west coast of Patagonia. The most common rock types are siltstone and sandstone. Conglomerates occur but are less common. Study of fossils and uranium–lead dating of detrital zircons indicates a Miocene age, at least for the upper sequences. The Chaicayán Group was deposited likely due to a marine transgression that drowned much of Patagonia and Central Chile in the Late Oligocene and Miocene. The group is intruded by porphyritic stocks and sills of Pliocene age. See also * Geology of Chile * Ayacara Formation * La Cascada Formation La Cascada Formation a sedimentary formation near Futaleufú in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. Lithologies vary from sandstone, siltstone and conglomerate. The sediment that now forms the rock deposited during the Oligocene and ... * Puduhuapi Formation * Vargas Formation References {{Geology of Chile Geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic Unit
A stratigraphic unit is a volume of rock of identifiable origin and relative age range that is defined by the distinctive and dominant, easily mapped and recognizable petrographic, lithologic or paleontologic features ( facies) that characterize it. Units must be ''mappable'' and ''distinct'' from one another, but the contact need not be particularly distinct. For instance, a unit may be defined by terms such as "when the sandstone component exceeds 75%". Lithostratigraphic units Sequences of sedimentary and volcanic rocks are subdivided on the basis of their shared or associated lithology. Formally identified lithostratigraphic units are structured in a hierarchy of lithostratigraphic rank, higher rank units generally comprising two or more units of lower rank. Going from smaller to larger in rank, the main lithostratigraphic ranks are bed, member, formation, group and supergroup. Formal names of lithostratigraphic units are assigned by geological surveys. Units of form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detrital Zircon Geochronology
Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of geochronology, analyzing the age of zircons deposited within a specific sedimentary rock, sedimentary unit by examining their inherent radioisotopes, most commonly the uranium–lead dating, uranium–lead ratio. Zircon is a common Accessory mineral, accessory or trace mineral constituent of most granite and felsic igneous rocks. Due to its hardness, durability and chemical inertness, zircon persists in sedimentary deposits and is a common constituent of most sands. Zircons contain trace amounts of uranium and thorium and can be dated using several modern analytical techniques. Detrital zircon geochronology has become increasingly popular in geological studies from the 2000s mainly due to the advancement in radiometric dating techniques. Detrital zircon age data can be used to constrain the maximum depositional age, determine provenance (geology), provenance, and reconstruct the tectonic setting on a regional scale. Detrital zirco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Groups Of South America
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vargas Formation
The Vargas Formation is a sedimentary formation on the left bank of Palena River in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. The formation is made of black shale and sandstone that deposited in the Late Oligocene or Early Miocene epoch some 26 million years ago. The formation has contact across a fault plane with granitoids of Cretaceous age of the North Patagonian Batholith. The exposures of Vargas Formation are small and its fossils poorly preserved. Gastropods, bivalves, echinoderms, and planktic foraminifer fossils have been found in the formation. Hans Steffen was the first to investigate Vargas Formation with his research being published in 1944. See also * Geology of Chile * Chaicayán Group * Ayacara Formation * La Cascada Formation La Cascada Formation a sedimentary formation near Futaleufú in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. Lithologies vary from sandstone, siltstone and conglomerate. The sediment that now forms the rock deposited dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puduhuapi Formation
The Puduhuapi Formation is a sedimentary formation whose only known outcrops are on Puduhuapi Island of the Chiloé Archipelago, west of Chaitén in western Patagonia, Chile. Lithologies vary from sandstone and siltstone to conglomerate. The sediment that now forms the rock deposited during the Miocene no earlier than 23 million years ago. See also * Geology of Chile * Chaicayán Group * Ayacara Formation * La Cascada Formation * Vargas Formation The Vargas Formation is a sedimentary formation on the left bank of Palena River in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. The formation is made of black shale and sandstone that deposited in the Late Oligocene or Early Miocene epoch som ... References {{Geology of Chile Geologic formations of Chile Miocene Series of South America Neogene Chile Sandstone formations Siltstone formations Conglomerate formations of Chile Geology of Los Lagos Region Mapuche language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Cascada Formation
La Cascada Formation a sedimentary formation near Futaleufú in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. Lithologies vary from sandstone, siltstone and conglomerate. The sediment that now forms the rock deposited during the Oligocene and Early Miocene epoch in shallow marine environment. The formation contain fossils of bivalves and gastropods. The formation unconformably overlies sedimentary rock of Jurassic age, Cretaceous sedimentary rocks of Divisadero Group and Cretaceous granite plutons. Further south in Aysén Region The Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region (, , '), often shortened to Aysén Region or Aisén,Examples of name usage1, official regional government site refers to the region as "Región de Aysén"., Chile's official meteorological ..., the Guadal Formation is a geologically equivalent formation. See also * Geology of Chile * Chaicayán Group * Ayacara Formation * Puduhuapi Formation * Vargas Formation References { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayacara Formation
The Ayacara Formation is a sedimentary formation made up of interbedded sand and siltstone cropping out around Hornopirén and Ayacara Peninsula in western Los Lagos Region, Chile. Less common rocks are tuff and conglomerate. The formation dates to the Early and Middle Miocene (no earlier than 21.8–17.6 million years ago) when it deposited during a marine transgression. See also * Geology of Chile * Chaicayán Group * La Cascada Formation * Puduhuapi Formation * Vargas Formation The Vargas Formation is a sedimentary formation on the left bank of Palena River in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. The formation is made of black shale and sandstone that deposited in the Late Oligocene or Early Miocene epoch som ... References {{Geology of Chile Geologic formations of Chile Miocene Series of South America Aquitanian (stage) Burdigalian Langhian Serravallian Neogene Chile Sandstone formations Siltstone formations Conglomerate formations of Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Chile
The geology of Chile is a characterized by processes linked to subduction, such as volcanism, earthquakes, and orogeny. The building blocks of Chile's geology were assembled during the Paleozoic Era when Chile was the southwestern margin of the supercontinent Gondwana. In the Jurassic, Gondwana began to split, and the ongoing period of crustal deformation and mountain building known as the Andean orogeny began. In the Late Cenozoic, Chile definitely separated from Antarctica, and the Andes experienced a significant rise accompanied by a cooling climate and the onset of glaciations. The subduction interactions shaped four main morphostructures of Chile: the Andes, the Intermediate Depression, the Coast Range, and the Peru–Chile Trench off the coast. Since Chile is on an active continental margin, it has many volcanoes. Almost the entire country is subject to earthquakes arising from strains in the Nazca and Antarctic plates or shallow strike-slip faults. Northern Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
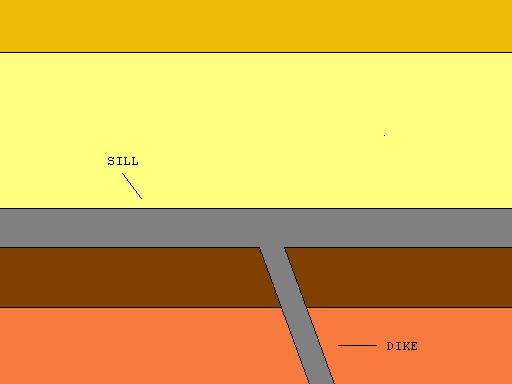
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that it does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex. and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Formation Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock (geology)
In geology, a stock is an igneous Intrusion (geology), intrusion that has a surface exposure of less than ,Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, p. 513. . differing from batholiths only in being smaller. A stock has a Intrusive rock#Related terms, discordant relationship with the rocks that it intrudes. Many stocks are cupola (geology), cupolas of hidden batholiths. Some circular or elliptical stocks may be volcanic plugs, which fill the vents of now extinct volcanoes. A boss is a small stock. Examples * the Alta and Clayton Peak stocks (composed of granodiorite), near Park City, Utah * the Hellroaring Creek and Salal Creek Pluton, Salal Creek stocks (of granite-granodiorite and quartz monzonite, respectively) in British Columbia, Canada * the Céret stock (of gabbro and diorite) in Pyrénées-Orientales, France * the Parashi stock (of tonalite) in La Guajira Department, Colombia * stocks of syenite in the Caldera de Tejeda on Gran Canar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyritic
Porphyritic is an adjective used in geology to describe igneous rocks with a distinct difference in the size of mineral crystals, with the larger crystals known as phenocrysts. Both extrusive and intrusive rocks can be porphyritic, meaning all types of igneous rocks can display some degree of porphyritic texture. Most porphyritic rocks have bimodal size ranges, meaning the rock is composed of two distinct sizes of crystal. In extrusive rocks, the phenocrysts are surrounded by a fine-grained (aphanitic) matrix or groundmass of volcanic glass or non-visible crystals, commonly seen in porphyritic basalt. Porphyritic intrusive rocks have a matrix with individual crystals easily distinguished with the eye, but one group of crystals appearing clearly much bigger than the rest, as in a porphyritic granite. The term comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning " purple". Purple was the color of royalty, and the "imperial porphyry" was a deep purple igneous rock with large crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |