Detrital Zircon Geochronology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of analyzing the age of
Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of analyzing the age of

Geochronology and Isotopes Data Portal
Sediments Geochronological dating methods Zircon
 Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of analyzing the age of
Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of analyzing the age of zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of th ...
s deposited within a specific sedimentary unit by examining their inherent radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s, most commonly the uranium–lead ratio. Zircon is a common accessory or trace mineral constituent of most granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
and felsic
In geology, felsic is a grammatical modifier, modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted ...
igneous rocks. Due to its hardness, durability and chemical inertness, zircon persists in sedimentary deposits and is a common constituent of most sands. Zircons contain trace amounts of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
and thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
and can be dated using several modern analytical techniques.
Detrital zircon geochronology has become increasingly popular in geological studies from the 2000s mainly due to the advancement in radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to Chronological dating, date materials such as Rock (geology), rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurity, impurities were selectively incorporat ...
techniques. Detrital zircon age data can be used to constrain the maximum depositional age, determine provenance
Provenance () is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art, but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including archaeology, p ...
, and reconstruct the tectonic setting on a regional scale.
Detrital zircon
Origin
Detrital zircons are part of thesediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
derived from weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals (as well as wood and artificial materials) through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms. It occurs '' in situ'' (on-site, with little or no move ...
and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
of pre-existing rocks. Since zircons are heavy and highly resistant at Earth's surface, many zircons are transported, deposited and preserved as detrital zircon grains in sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s.
Properties
Detrital zircons usually retain similar properties as their parentigneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
s, such as age, rough size and mineral chemistry. However, the composition of detrital zircons is not entirely controlled by the crystallization of the zircon mineral. In fact, many of them are modified by later processes in the sedimentary cycle. Depending on the degree of physical sorting
Sorting refers to ordering data in an increasing or decreasing manner according to some linear relationship among the data items.
# ordering: arranging items in a sequence ordered by some criterion;
# categorizing: grouping items with similar p ...
, mechanical abrasion and dissolution, a detrital zircon grain may lose some of its inherent features and gain some over-printed properties like rounded shape and smaller size. On a larger scale, two or more tribes of detrital zircons from different origins may deposit within the same sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock They form when long-term subsidence ...
. This give rise to a natural complexity of associating detrital zircon populations and their sources.
Zircon is a strong tool for uranium-lead age determination because of its inherent properties:Gehrels, G. (12 August 2010). UThPb analytical methods for Zircon. ''Arizona LaserChron Center''. Retrieved 10 November 2016, from https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B9ezu34P5h8eMzkyMGFlNjgtMDU0Zi00MTQyLTliZDMtODU2NGE0MDQ2NGU2/view?hl=en.
# Zircon contains high amount of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
for machine recognition, commonly 100–1000 ppm.
# Zircon has a low amount of lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
during crystallization, in parts per trillion. Thus, lead found in zircon can be assumed as daughter nuclei from parent uranium.
# Zircon crystals grow between 600 and 1100 °C, while lead is retained within the crystal structure below 800 °C (see Closure temperature
In radiometric dating, closure temperature or blocking temperature refers to the temperature of a system, such as a mineral, at the time given by its radiometric date. In physical terms, the closure temperature is the temperature at which a syste ...
). So once zircon has cooled below 800 °C it retains all the lead from the radioactive decay. Therefore, U-Pb age can be treated as the age of crystallization, if the mineral/sample itself has not undergone high temperature metamorphism after formation.
# Zircon commonly crystallizes in felsic
In geology, felsic is a grammatical modifier, modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted ...
igneous rocks, with greater than 60% silica (SiO2) content. These rocks are generally less dense and more buoyant. They sit high in the Earth's (continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
), and have good preservation potential.
# Zircon is physically and chemically resistant, so it is more likely to be preserved in the sedimentary cycle.
# Zircon contains other elements which gives supplementary information, such as hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element; it has symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dm ...
(Hf), uranium/thorium (U/Th) ratio.
Sample collection
There are no set rules for sample selection in detrital zircon geochronology studies. The objective and scale of the research project govern the type and number of samples taken. In some cases, the sedimentary rock type and depositional setting can significantly affect the result. Examples include: * Matured quartz arenite within Vlamy Formation yield older and more diverse ages given by well-rounded detrital zircons, which may correlate to multiple sedimentary reworking events. On the contrary, Harmony Formation in the same region has younger and homogenous ages given byeuhedral
Euhedral and anhedral are terms used to describe opposite properties in the formation of crystals. Euhedral (also known as idiomorphic or automorphic) crystals
are those that are well-formed, with sharp, easily recognised faces. The opposite i ...
detrital zircons. These two formations illustrate the possibility of relating sedimentary maturity with resulting zircon ages, meaning that rounded and well-sorted sedimentary rocks (e.g. siltstone and mudstone) may have older and more diverse ages.
* Turbidites in Harts Pass Formation contain homogenous detrital zircons ages. On the other hand, fluvial Winthrop Formation in another strata of the same basin has various detrital zircon age populations. Comparing the vertical detrital zircon distribution within these two formations, one can expect a narrower age population of detrital zircons from rocks which are rapidly deposited, such as turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic Deposition (geology), deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.
Sequencing
...
s. Rocks that are gradually deposited (e.g. marine mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
), however, have a greater chance and time to incorporate zircon sediments from different localities.
Detrital zircon extraction
After rock samples are collected, they are cleaned, chipped, crushed and milled through standardized procedures. Then, detrital zircons are separated from the fine rock powder by three different ways, namely gravity separation using water, magnetic separation, and gravity separation using heavy liquid. In the process, grains are also sieved according to their size. The commonly used grain size for detrital zircon provenance analysis is 63–125 μm, which is equivalent to fine sand grain size.Type of detrital zircon analysis
There are two main types of detrital zircon analysis: qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis. The biggest advantage of qualitative analysis is being able to uncover all possible origin of the sedimentary unit, whereas quantitative analysis should allow meaningful comparison of proportions in the sample.Qualitative analysis
Qualitative approach examines all the available detrital zircons individually regardless of their abundance among all grains. This approach is usually conducted with high precisionthermal ionization mass spectrometry
Thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS), also known as surface ionization, is a highly sensitive isotope mass spectrometry characterization technique. The isotopic ratios of radionuclides are used to get an accurate measurement for the elemen ...
(TIMS) and sometimes secondary ion mass spectrometry
Secondary-ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) is a technique used to analyze the composition of solid surfaces and thin films by sputtering the surface of the specimen with a focused primary ion beam and collecting and analyzing ejected secondary ions ...
(SIMS). Optical examination and classification of detrital zircon grains are commonly included in qualitative studies through back-scatter electrons (BSE) or cathodoluminescence
Cathodoluminescence is an optical and electromagnetic phenomenon in which electrons impacting on a luminescent material such as a phosphor, cause the emission of photons which may have wavelengths in the visible spectrum. A familiar example i ...
(CL) imagery, despite the relationship between the age and optical classification of detrital zircon grains is not always reliable.
Quantitative analysis
Quantitative approach requires large number of grain analyses within a sample rock in order to represent the overall detrital zircon population statistically (i.e. the total number of analyses should achieve an appropriate level of confidence). Because of the large sample size, secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) and laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry ( LA-ICPMS) are used instead of thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS). In this case, BSE and CL imagery are applied to select the best spot on a zircon grain for acquiring reliable age.Methods
Different methods in detrital zircon analysis yield different results. Generally, researchers would include the methods/ analytical instruments they used within their studies. There are generally three categories, which are the instrument(s) used for zircon analysis, their calibration standards and instrument(s) used for zircon imagery. Details are listed in Table 1.Detrital zircon data
Depending on the detrital zircon study, there should be different variables included for analysis. There are two main types of data, analyzed zircon data (quantifiable data and imagery/descriptive data), and sample (where they extract the zircon grains) data. Details are listed in Table 2.Filtering detrital zircon data
All data acquired first-hand should be cleansed before using to avoid error, normally by computer.By U-Pb age discordance
Before applying detrital zircon ages, they should be evaluated and screened accordingly. In most cases, data are compared with U-Pb Concordia graphically. For a large dataset, however, data with high U-Pb age discordance (>10 – 30%) are filtered out numerically. The acceptable discordance level is often adjusted with the age of the detrital zircon since older population should experience higher chances of alteration and project higher discordance.Gehrels, G. (2011). Detrital zircon U‐Pb geochronology: Current methods and new opportunities. ''Tectonics of sedimentary basins: recent advances'', 45–62. (SeeUranium–lead dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routi ...
)
By choosing the best age
Because of the intrinsic uncertainties within the three yield U-Pb ages (207Pb/235U, 206Pb/238U and 207Pb/206Pb), the age at ~1.4 Ga has the poorest resolution. An overall consensus for age with higher accuracy is to adopt: * 207Pb/206Pb for ages older than 0.8 – 1.0 Ga * 206Pb/238U for ages younger than 0.8 – 1.0 GaBy data clustering
Given the possibility of concordant yet incorrect detrital zircon U-Pb ages associated with lead loss or inclusion of older components, some scientists apply data selection through clustering and comparing the ages. Three or more data overlapping within ±2σ uncertainty would be classified as a valid age population of a particular source origin.By age uncertainty (±σ)
There are no set limit for age uncertainty and the cut-off value varies with different precision requirement. Although excluding data with huge age uncertainty would enhance the overall zircon grain age accuracy, over elimination may lower overall research reliability (decrease in size of the database). The best practice would be to filter accordingly, i.e. setting the cut-off error to eliminate reasonable portion of the dataset (say <5% of the total ages available)By applied analytical methods
Depending on the required analytical accuracy, researchers may filter data via their analytical instruments. Generally, researchers use only the data fromsensitive high-resolution ion microprobe
The sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe (also sensitive high mass-resolution ion microprobe or SHRIMP) is a large-diameter, double-focusing secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) sector instrument that was produced by Australian Scientific ...
(SHRIMP), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a type of mass spectrometry that uses an inductively coupled plasma to ionize the sample. It atomizes the sample and creates atomic and small polyatomic ions, which are then detected. It i ...
(LA-ICPMS) and thermal ionization mass spectrometry
Thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS), also known as surface ionization, is a highly sensitive isotope mass spectrometry characterization technique. The isotopic ratios of radionuclides are used to get an accurate measurement for the elemen ...
(TIMS) because of their high precision (1–2%, 1–2% and 0.1% respectively) in spot analysis. An older analytical technique, lead-lead evaporation, is no longer used since it cannot determine the U-Pb concordance of the age data.
By spot nature
Apart from analytical methods, researchers would isolate core or rim ages for analysis. Normally, core ages would be used as crystallization age as they are first generated and least disturbed part in zircon grains. On the other hand, rim ages can be used to track peakmetamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated ...
as they are first in contact with certain temperature and pressure condition. Researchers may utilize these different spot natures to reconstruct the geological history of a basin.
Application of detrital zircon ages
Maximum depositional age
Some of the most important information we can get from detrital zircon ages is the maximum depositional age of the referring sedimentary unit. The sedimentary unit cannot be older than the youngest age of the analyzed detrital zircons because the zircon should have existed before the rock formation. This provides useful age information to rock strata where fossils are unavailable, such as the terrestrial successions during Precambrian or pre-Devonian times. Practically, maximum depositional age is averaged from a cluster of youngest age data or the peak in age probability because the youngest U-Pb age within a sample is almost always younger with uncertainty.Tectonic studies
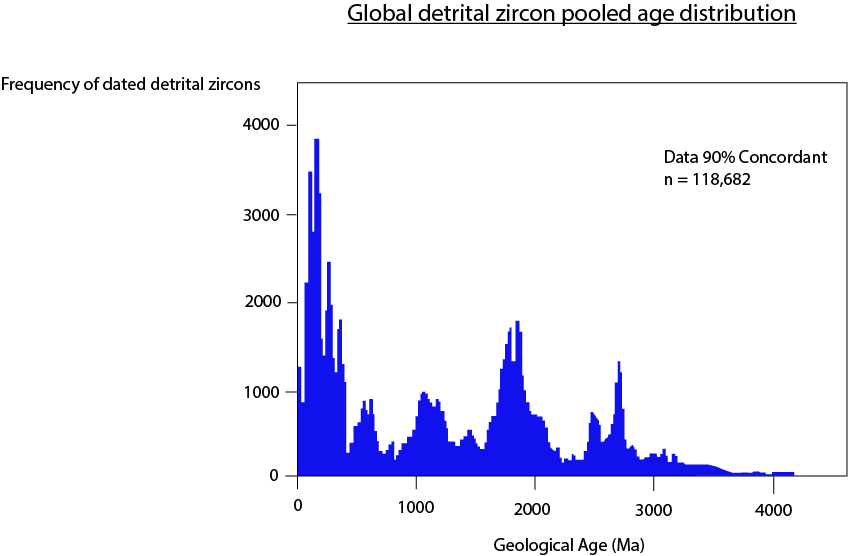
Using detrital zircon age abundance
In a global scale, detrital zircon age abundance can be used as a tool to infer significant tectonic events in the past. In Earth's history, the abundance of magmatic age peaks during periods ofsupercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
assembly. This is because supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
provides a major crustal envelop selectively preserve the felsic magmatic rocks, resulting from partial melts. Thus, many detrital zircons originate from these igneous provence, resulting similar age peak records. For instance, the peak at about 0.6–0.7 Ga and 2.7 Ga (Figure 6) may correlate the break-up of Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). wer ...
and supercontinent Kenorland
Kenorland is a hypothetical Neoarchean supercontinent. If it existed, it would have been one of the earliest known supercontinents on Earth. It is thought to have formed during the Neoarchaean Era c. 2.72 billion years ago (2.72 Ga) by the acc ...
respectively.
Using difference between detrital zircons crystallisation ages and their corresponding maximum depositional age
Apart from the detrital zircon age abundance, difference between detrital zircons crystallisation ages (CA) and their corresponding maximum depositional age (DA) can be plotted incumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x.
Ever ...
to correlate particular tectonic regime in the past. The effect of different tectonic settings on the difference between CA and DA is illustrated in Figure 7 and summarized in Table. 3.

References
{{Reflist, 30emExternal links
Geochronology and Isotopes Data Portal
Sediments Geochronological dating methods Zircon