|
Celeron M
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessors targeted at low-cost personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023. The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, 1998, and was based on the Pentium II. Celeron-branded processors released from 2009 to 2023 are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed compared to flagship Intel CPU lines, such as the Pentium or Core brands. They often have less cache or intentionally disabled advanced features, with variable impact on performance. While some Celeron designs have achieved strong performance for their segment, the majority of the Celeron line has exhibited noticeably degraded performance. This has been the primary justification for the higher cost of other Intel CPU brands versus the Celeron range. In September 2022, Intel announced that the Celeron brand, along with Pentium, were to be replaced with the new "Intel Processor" branding for l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented. Intel reverted to the traditional socket interface with the release of Socket 370 in 1999. General With the introduction of the Pentium II CPU, the need for greater access for testing had made the transition from socket to slot necessary. Previously with the Pentium Pro, Intel had combined processor and cache dies in the same Socket 8 package. These were connected by a full-speed bus, resulting in significant performance benefits. Unfortunately, this method required that the two components be bonded together early in the production process, before testing was possible. As a result, a single, tiny flaw in either die made it necessary to discard the entire assembly, causing low production yield and high cost. Intel subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket P
The Intel Socket P (mPGA478MN) is the mobile processor socket replacement for Core microarchitecture chips such as Core 2 Duo. It launched on May 9, 2007, as part of the Santa Rosa platform with the Merom and Penryn processors. Technical specifications The front-side bus (FSB) of CPUs that install in Socket P can run at 400, 533, 667, 800, or 1066 MT/s. By adapting the multiplier the frequency of the CPU can throttle up or down to save power, given that all Socket P CPUs support EIST, except for Celeron that do not support EIST. Socket P has 478 pins, but is not electrically pin-compatible with Socket M or Socket 478. Socket P is also known as a 478-pin Micro FCPGA or μFCPGA-478. On the plastic grid is printed mPGA478MN. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
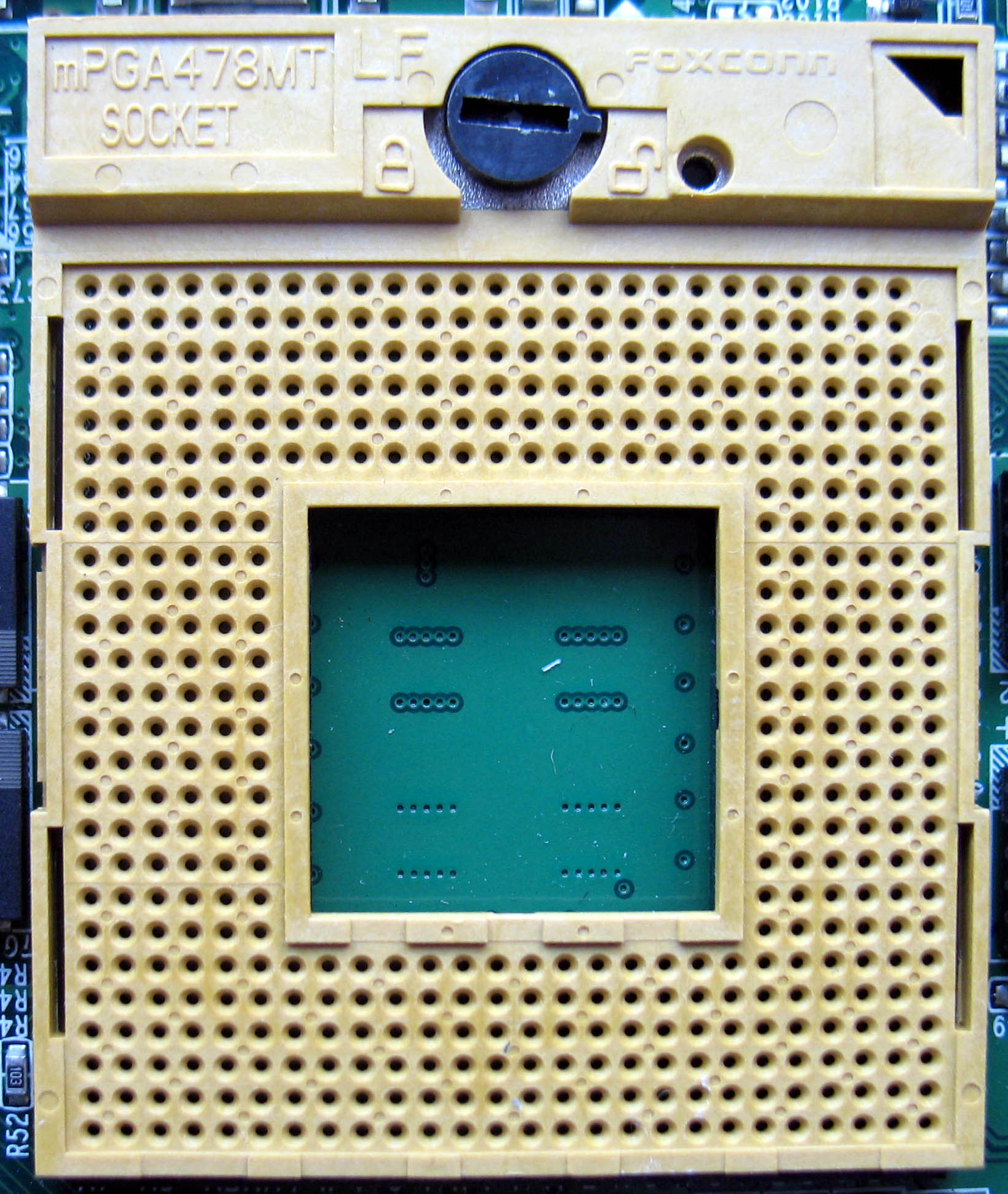
Socket M
Socket M (mPGA478MT) is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006 for the Intel Core line of mobile processors. Technical specifications Socket M is used in all Intel Core products, as well as the Core-derived Dual-Core Xeon codenamed Sossaman. It was also used in the first generation of the mobile version of Intel's Core 2 Duo, specifically, the T5x00 and T7x00 Merom lines (referred to as Napa Refresh), though that line switched to Socket P (Santa Rosa) in 2007. It typically uses the Intel 945PM/945GM chipsets which support up to 667 MHz FSB and the Intel PM965/GM965 which allows 800 MHz FSB support, though the Socket M, PM965/GM965 combination is less common. The "Sossaman" Xeons use the E7520 chipset. Relation to other sockets Socket M is pin-compatible with desktop socket mPGA478A but it is not electrically compatible. Socket M is not pin-compatible with the older desktop Socket 478 (mPGA478B) or the newer mobile Socket P (mPGA478MN) by location of one pin; it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 479
Socket 479 (mPGA479M) is a CPU socket used by some Intel microprocessors. It is primarily known as the socket used by Pentium M and Celeron M mobile processors normally found in laptops, however the socket has also been used with Tualatin (microprocessor), Tualatin-M Mobile Celeron and Pentium III processors years before it. The official naming by Intel is μFCPGA and μPGA479M. Technical specifications Socket 479 has 479 pin holes. Pentium M processors in PGA package have 479 pins that plug into this zero insertion force socket. Only 478 pins are electrically connected (B2 is reserved and "depopulated on the Micro-FCPGA package"). Although mechanically similar, Socket 478 has one pin fewer, making it impossible to use a Pentium M processor in a Socket 478 board. For this reason, some manufacturers like Asus have made drop-in boards (e.g. CT-479) which allow the use of Socket 479 processors in Socket 478 boards. Conversely, it is impossible to use any Socket 478 desktop Celeron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 495
Socket 495, also known as μPGA2, is a CPU socket used for the Intel Pentium III and Celeron mobile processors. This socket was also used in Microsoft's Xbox console for the List of Intel Pentium_III processors#"Coppermine-128" (180 nm), Xbox CPU, albeit in a ball grid array, BGA (ball grid array) format. It replaces Socket 615 (μPGA1), which was used in Pentium II and early Celeron mobile processors. Technical specifications This socket is a 495 pin CPU socket designed to house any processor in the Socket 495 package. The socket has a 1.27mm pitch and is designed to support a heatsink. See also * List of Intel processors * List of Intel Celeron processors References {{Intelsock Intel CPU sockets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1700
LGA 1700 (Socket V) is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket, compatible with Intel Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ... desktop processors Alder Lake and Raptor Lake, which was first released in November 2021. LGA 1700 is designed as a replacement for LGA 1200 (known as ''Socket H5'') and it has 1700 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. Compared to its predecessor, it has 500 more pins, which required a major change in socket and processor sizes; it is 7.5 mm longer. It is the first major change in Intel's LGA desktop CPU socket size since the introduction of LGA 775 in 2004, especially for consumer-grade CPU sockets. The larger size also required a change in the heatsink fastening holes configuration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1200
LGA 1200, also known as Socket H5, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket, socket, compatible with Intel desktop Central processing unit, processors Comet Lake (10th gen) and Rocket Lake (11th-gen) desktop CPUs, which was released in April 2020. LGA 1200 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1151 (known as ''Socket H4''). LGA 1200 is a land grid array mount with 1200 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. It uses a modified design of LGA 1151, with 49 more pins on it, improving power delivery and offering support for future incremental I/O features. Pin 1 position remains the same as it was in previous generation processors, but it has shifted socket keying to left (previously it was right), making Comet Lake processors incompatible both electrically and mechanically with previous chips. ASRock, Asus, Biostar, Gigabyte Technology, Gigabyte and Micro-Star International, MSI have confirmed their motherboards based on the Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1151
LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, is a type of zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket for Intel desktop processors which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1150 (known as ''Socket H3''). LGA 1151 has 1151 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator, i.e. a voltage regulator which integrated on the CPU's die, introduced with Haswell and Broadwell, has again been moved to the motherboard. Most motherboards for the first revision of the socket support solely DDR4 memory, a lesser number support DDR3(L) memory, and the least number have slots for both DDR4 or DDR3(L) but only one memory type can be installed. Some have UniDIMM support, enabling either type of memory to be placed in the same DIMM, rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
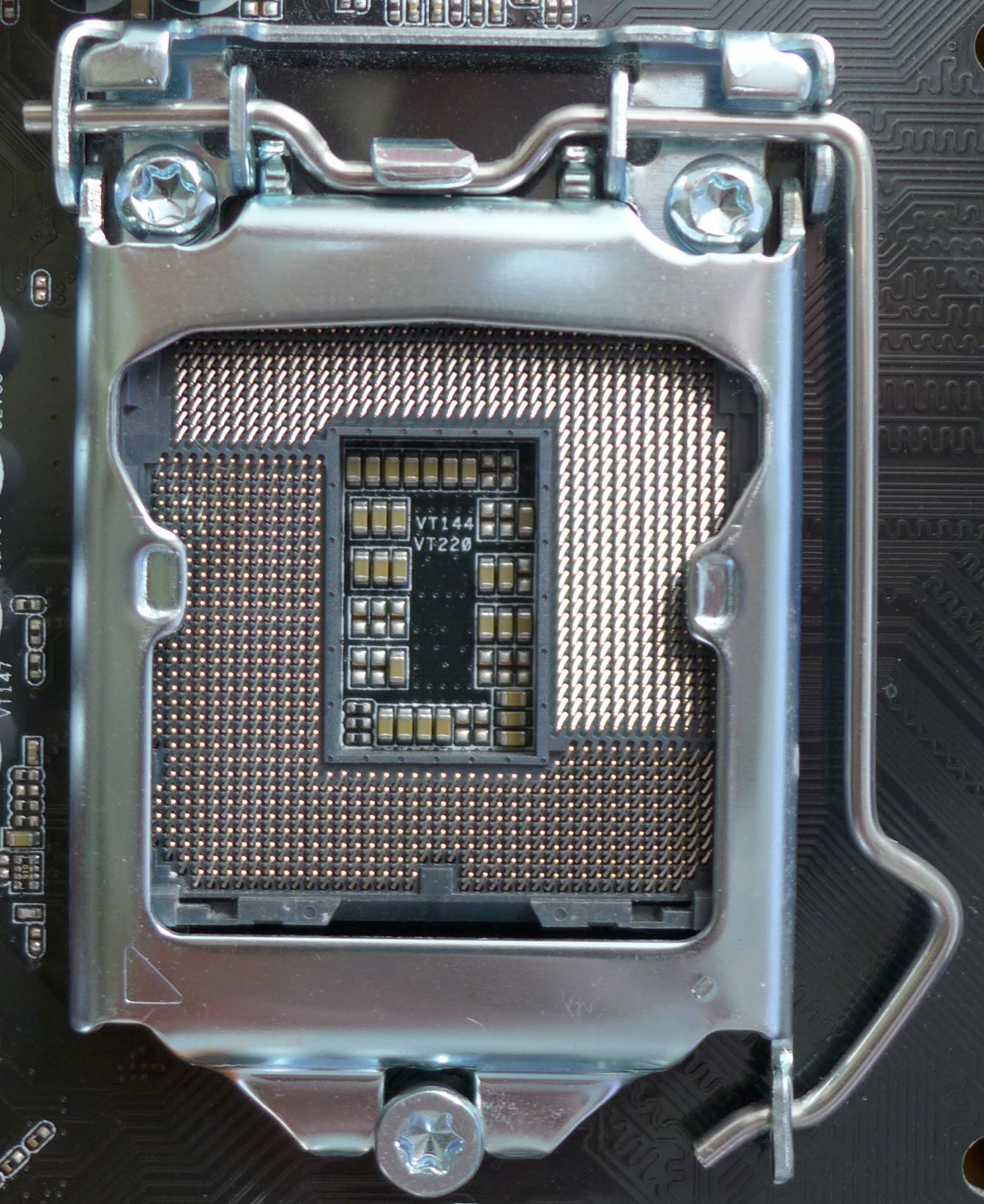
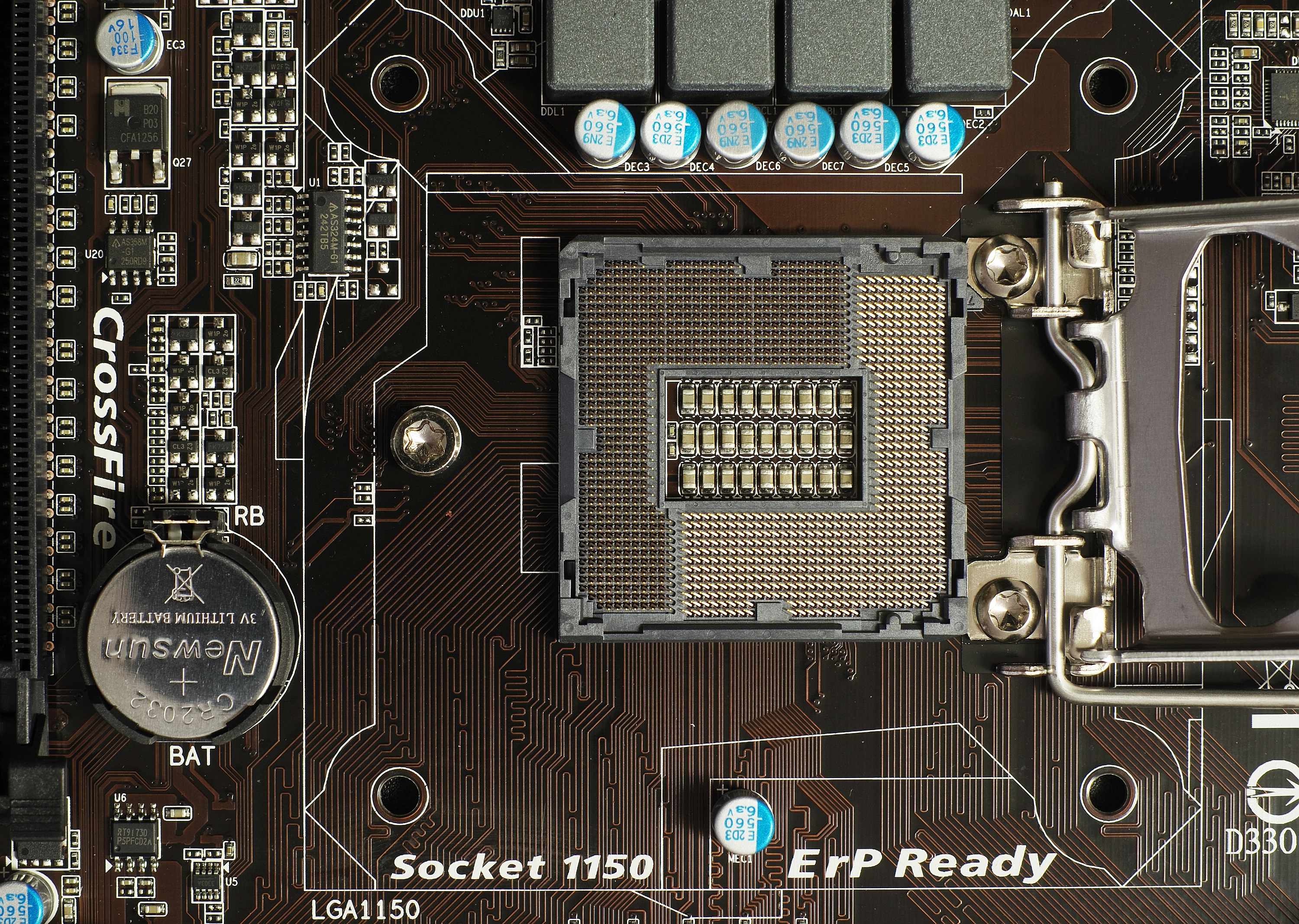
LGA 1150
LGA 1150, also known as Socket H3, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for CPUs built on the Haswell microarchitecture. This socket is also used by the Haswell's successor, Broadwell microarchitecture. It is the successor of LGA 1155 and was itself succeeded by LGA 1151 in 2015. Most motherboards with the LGA 1150 socket support varying video outputs (VGA, DVI or HDMI depending on the model) and Intel Clear Video Technology. Full support of Windows on LGA 1150 platform starts on Windows 7. Official Windows XP support is limited to selected CPUs, chipsets and only for embedded and industrial systems. Intel's Platform Controller Hub (PCH) for the LGA 1150 CPUs is codenamed Lynx Point. Intel Xeon processors for socket LGA 1150 use the Intel C222, C224, and C226 chipsets. Heatsink The 4 holes for fastening the heatsink to the motherboard are placed in a square with a lateral length of 75 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1155
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for their CPUs based on the Sandy Bridge (second generation core) and Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (third generation) microarchitectures. Introduced in 2011, it is the successor of LGA 1156 (known as ''Socket H'') and was itself succeeded by LGA 1150 in 2013. Along with selected variations of LGA 2011 socket, it was the last Intel socket to fully support Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008. LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The pins are arranged in a 40×40 array with a 24×16 central void and additional 61 omitted pins (two adjoining the central void, six in each of the four corners, and 35 in groups around the perimeter), yielding the 1600 − 384 − 61 = 1155 pin count. Processors for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1156
LGA 1156 (land grid array 1156), also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. The last processors supporting the LGA 1156 ceased production in 2011. It was succeeded by the mutually incompatible socket LGA 1155. LGA 1156, along with LGA 1366, were designed to replace LGA 775. Whereas LGA 775 processors connect to a northbridge using the Front Side Bus, LGA 1156 processors integrate the features traditionally located on a northbridge within the processor itself. The LGA 1156 socket allows the following connections to be made from the processor to the rest of the system: * PCI-Express 2.0 ×16 for communication with a graphics card. Some processors allow this connection to be divided into two ×8 lanes to connect two graphics cards. Some motherboard manufacturers use Nvidia's NF200 chip to allow even more graphics cards to be used. * DMI for communication with the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). This consists of a PCI-Express 2.0 ×4 connection. * FDI for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |