|
Cebrenia
Cebrenia was an ancient country in the Troad, the hinterland of Troy, beside the Dardanelles in what is now Turkey. The location of Cebrenia was described by Strabo (c. 64 BCE–24 CE) in section 13.1.33 of his ''Geography'': Above them he coastal cities near Troylies the plain of Troy, extending as far as Mount Ida to the east ... The part at the foot of the mountain is narrow ... This country Homer places under the command of Aeneas and the Antenoridae, and calls it Dardania. Below it is Cebrenia, which for the most part consists of plains, and lies nearly parallel to Dardania. There was also formerly a city Cybrene. ... Cebrenia extends as far as the Scepsian district. The boundary is the River Scamander, which runs through the middle of Cebrenia and Scepsia. There was continual enmity and war between the Scepsians and Cebrenians till Antigonus settled them both together in the city then called Antigonia, but at present Alexandria Troas. The Cebrenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebrenia Quadrangle
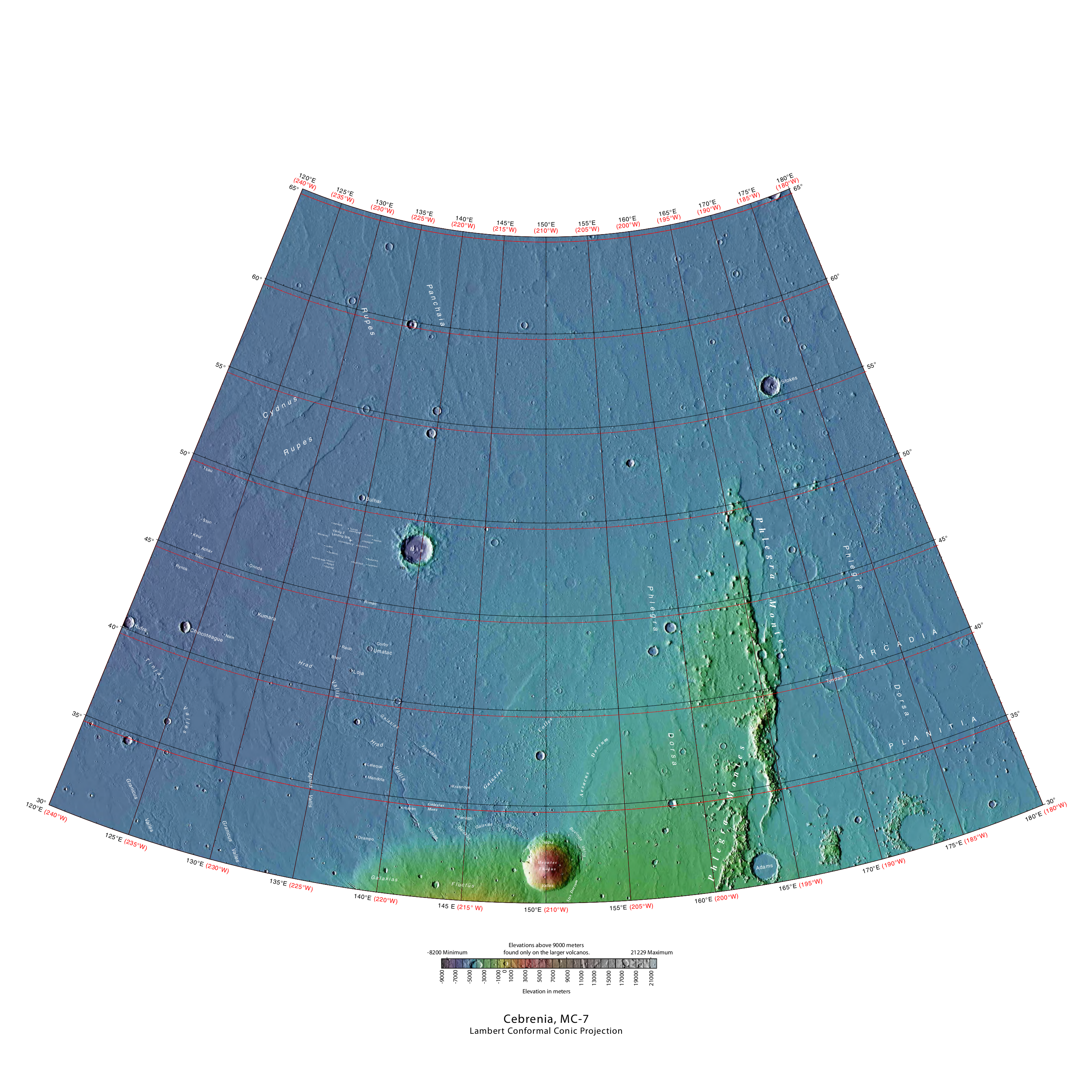
The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars’ eastern hemisphere and covers 120° to 180° east longitude (180° to 240° west longitude) and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Cebrenia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-7 (Mars Chart-7). It includes part of Utopia Planitia and Arcadia Planitia. The southern and northern borders of the Cebrenia quadrangle are approximately and wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about (slightly less than the length of Greenland). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars’ surface area. Origin of name Cebrenia is a telescopic albedo feature centered on 50° N and 150° E on Mars. The feature is named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troad
The Troad ( or ; el, Τρωάδα, ''Troáda'') or Troas (; grc, Τρῳάς, ''Trōiás'' or , ''Trōïás'') is a historical region in northwestern Anatolia. It corresponds with the Biga Peninsula (Turkish: ''Biga Yarımadası'') in the Çanakkale province of modern Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander ( Karamenderes) and the Simois, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. Mount Ida, called by Homer "many-fountain" (πολυπίδαξ), sourced several rivers, including Rhesos, Heptaporos, Caresus, Rhodios, Granicus (Granikos), Aesepus, Skamandros and Simoeis liad 12.18 ff these rivers were deified as a source of life by the Greeks, who depicted them on their coins as river-gods reclining by a stream and holding a reed. History The Troad gets its name from the Hittites' name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria Troas
Alexandria Troas ("Alexandria of the Troad"; el, Αλεξάνδρεια Τρωάς; tr, Eski Stambul) is the site of an ancient Greek city situated on the Aegean Sea near the northern tip of Turkey's western coast, the area known historically as Troad, a little south of Tenedos (modern Bozcaada). It is located southeast of modern Dalyan, a village in the Ezine district of Çanakkale Province. The site sprawls over an estimated ; among the few structures remaining today are a ruined bath, an odeon, a theatre, gymnasium complex John Freely (2003). ''The Aegean Coast of Turkey''. Redhouse Press, Istanbul, pp.3-8. and a recently uncovered stadion. The circuit of the old walls can still be traced. History Hellenistic According to Strabo, this site was first called Sigeia (Σιγία); around 306 BC Antigonus refounded the city as the much-expanded Antigonia Troas by settling the people of five other towns in Sigeia,Jona Lendering (2006)Alexandria in Troas(from Livius.org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a large impact feature. Days and seasons on Mars are comparable to those of Earth, as the planets have a similar rotation period a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Schiaparelli
Giovanni Virginio Schiaparelli ( , also , ; 14 March 1835 – 4 July 1910) was an Italian astronomer and science historian. Biography He studied at the University of Turin, graduating in 1854, and later did research at Berlin Observatory, under Encke. In 1859–1860 he worked in Pulkovo Observatory near St Petersburg, and then worked for over forty years at Brera Observatory in Milan. He was also a senator of the Kingdom of Italy, a member of the Accademia dei Lincei, the Accademia delle Scienze di Torino and the Regio Istituto Lombardo, and is particularly known for his studies of Mars. Mars Among Schiaparelli's contributions are his telescopic observations of Mars. In his initial observations, he named the " seas" and "continents" of Mars. During the planet's "great opposition" of 1877, he observed a dense network of linear structures on the surface of Mars, which he called in Italian, meaning "channels", but the term was mistranslated into English as "canals" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Map Mars
Giovanni may refer to: * Giovanni (name), an Italian male given name and surname * Giovanni (meteorology), a Web interface for users to analyze NASA's gridded data * ''Don Giovanni'', a 1787 opera by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, based on the legend of Don Juan * Giovanni (Pokémon), boss of Team Rocket in the fictional world of Pokémon * Giovanni (World of Darkness), a group of vampires in ''Vampire: The Masquerade/World of Darkness'' roleplay and video game * "Giovanni", a song by Band-Maid from the 2021 album ''Unseen World'' * ''Giovanni's Island'', a 2014 Japanese anime drama film * ''Giovanni's Room'', a 1956 novel by James Baldwin * Via Giovanni, places in Rome See also * * *Geovani *Giovanni Battista *San Giovanni (other) *San Giovanni Battista (other) San Giovanni Battista is the Italian translation of Saint John the Baptist. It may also refer to: Italian churches * San Giovanni Battista, Highway A11, a church in Florence, Italy * San Giovanni Battista, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebren
Cebren was a Greek river-god,Aaron J. Atsma, "Cebren: River god of Troad in Anatolia", Theoi Project , http://www.theoi.com/Potamos/PotamosKebren.html whose river was located near Troy. He was the son of Oceanus and Tethys and he was the father of Asterope, Hesperia, who are sometimes considered to be the same person, and Oenone In Greek mythology, Oenone (; Ancient Greek: Οἰνώνη ''Oinōnē''; "wine woman") was the first wife of Paris of Troy, whom he abandoned for Helen. Oenone was also the ancient name of an island, which was later named after Aegina, daughter .... The city Cebrene (also spelled Kebrene or Kevrin) was named for Cebren. References Potamoi {{Greek-deity-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are typically tied to a specific place or landform, and are usually depicted as maidens. They were not necessarily immortal, but lived much longer than human beings. They are often divided into various broad subgroups, such as the Meliae (ash tree nymphs), the Dryads (oak tree nymphs), the Naiads (freshwater nymphs), the Nereids (sea nymphs), and the Oreads (mountain nymphs). Nymphs are often featured in classic works of art, literature, mythology, and fiction. Since the Middle Ages, nymphs have been sometimes popularly associated or even confused with fairies. Etymology The Greek word has the primary meaning of "young woman; bride, young wife" but is not usually associated with deities in particular. Yet the etymology of the noun rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oenone
In Greek mythology, Oenone (; Ancient Greek: Οἰνώνη ''Oinōnē''; "wine woman") was the first wife of Paris of Troy, whom he abandoned for Helen. Oenone was also the ancient name of an island, which was later named after Aegina, daughter of the river god Asopus. Biography Oenone was a mountain nymph (an oread) on Mount Ida in Phrygia, a mountain associated with the Mother Goddess Cybele and the Titaness Rhea. Her gift of prophecy was learned from Rhea.Apollodorus, 3.12.6 Her father was either the river-gods, Cebren or Oeneus. Her name links her to the gift of wine. Mythology Paris, son of the king Priam and the queen Hecuba, fell in love with Oenone when he was a shepherd on the slopes of Mount Ida, having been exposed in infancy (owing to a prophecy that he would be the means of the destruction of the city of Troy) and rescued by the herdsman Agelaus. The couple married, and Oenone gave birth to a son, Corythus. When Paris later abandoned her to return to Troy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has been narrated through many works of Greek literature, most notably Homer's ''Iliad''. The core of the ''Iliad'' (Books II – XXIII) describes a period of four days and two nights in the tenth year of the decade-long siege of Troy; the '' Odyssey'' describes the journey home of Odysseus, one of the war's heroes. Other parts of the war are described in a cycle of epic poems, which have survived through fragments. Episodes from the war provided material for Greek tragedy and other works of Greek literature, and for Roman poets including Virgil and Ovid. The ancient Greeks believed that Troy was located near the Dardanelles and that the Trojan War was a historical event of the 13th or 12th century BC, but by the mid-19th century AD, both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Of Troy
Helen of Troy, Helen, Helena, (Ancient Greek: Ἑλένη ''Helénē'', ) also known as beautiful Helen, Helen of Argos, or Helen of Sparta, was a figure in Greek mythology said to have been the most beautiful woman in the world. She was believed to have been the daughter of Zeus and Leda, and was the sister of Clytemnestra, Castor and Pollux, Philonoe, Phoebe and Timandra. She was married to King Menelaus of Sparta "who became by her the father of Hermione, and, according to others, of Nicostratus also." The usual tradition is that after the goddess Aphrodite promised her to Paris in the Judgement of Paris, she was seduced by him and carried off to Troy. This resulted in the Trojan War when the Achaeans set out to reclaim her. Another ancient tradition, told by Stesichorus, tells of how "not she, but her wraith only, had passed to Troy, while she was borne by the Gods to the land of Egypt, and there remained until the day when her lord Menelaus, turning aside on the hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris (mythology)
Paris ( grc, Πάρις), also known as Alexander (, ''Aléxandros''), the son of King Priam and Queen Hecuba of Troy, is a mythological nobleman that appears in a number of Greek legends. Of these appearances, probably the best known was the elopement with Helen, queen of Sparta, this being one of the immediate causes of the Trojan War. Later in the war, he fatally wounds Achilles in the heel with an arrow as foretold by Achilles's mother, Thetis. The name ''Paris'' is probably of Luwian origin, and comparable to '' Pari-zitis'', attested as a Hittite scribe's name. The name Paris is etymologically unrelated to the name of the French city of Paris, which derives its name from a Gaulish tribe called the Parisii. Description Paris was described by the chronicler Malalas in his account of the ''Chronography'' as " well-grown, sturdy, white, good nose, good eyes, black pupils, black hair, incipient beard, long-faced, heavy eyebrows, big mouth, charming, eloquent, agile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




