Cebrenia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cebrenia was an ancient country in the  The location of Cebrenia was described by
The location of Cebrenia was described by 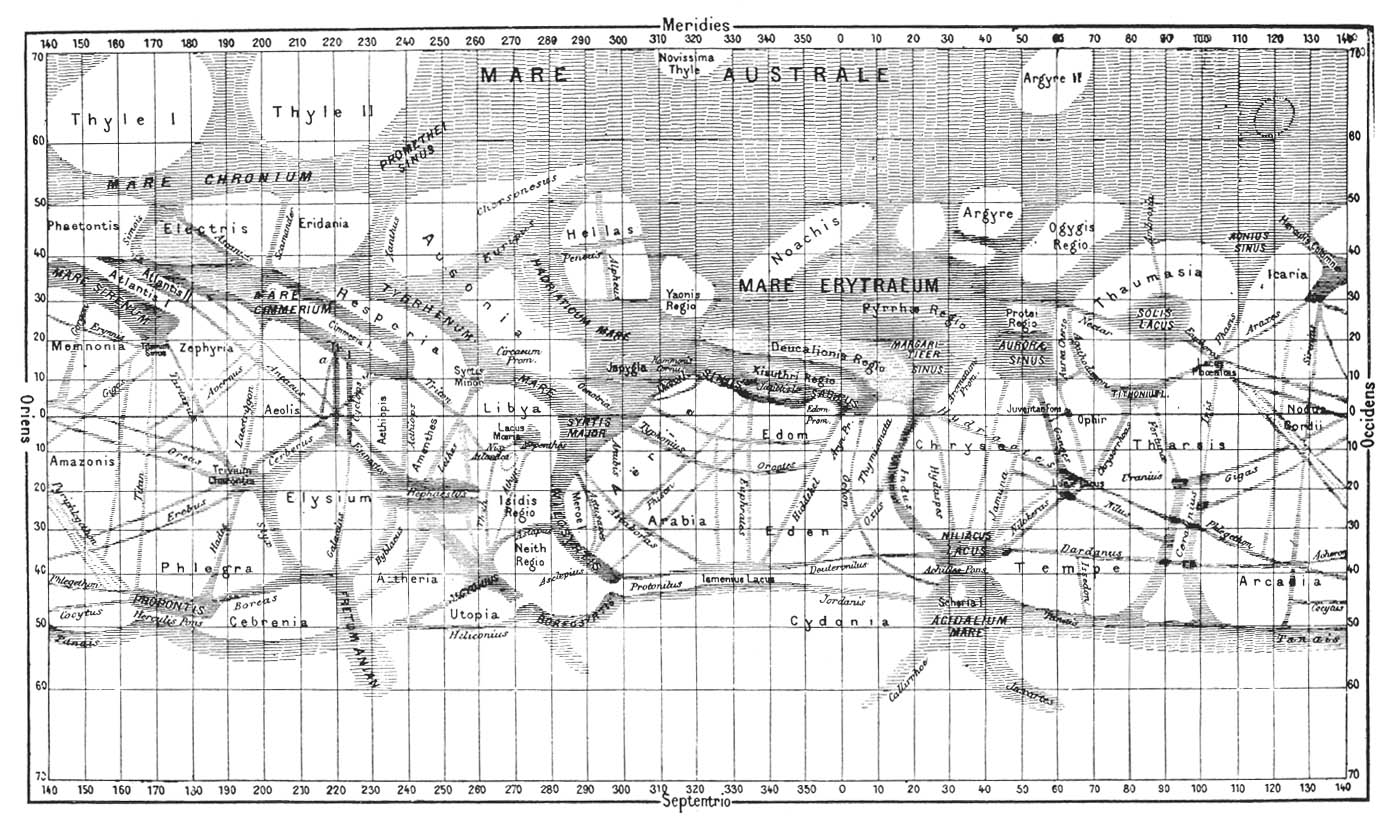 When the 19th century astronomer
When the 19th century astronomer
Troad
The Troad ( or ; , ''Troáda'') or Troas (; , ''Trōiás'' or , ''Trōïás'') is a historical region in northwestern Anatolia. It corresponds with the Biga Peninsula ( Turkish: ''Biga Yarımadası'') in the Çanakkale Province of modern Tur ...
, the hinterland of Troy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destina ...
, beside the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey th ...
in what is now Turkey.
 The location of Cebrenia was described by
The location of Cebrenia was described by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
(c. 64 BCE–24 CE) in section 13.1.33 of his ''Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
'':
Above them he coastal cities near Troylies the plain of Troy, extending as far asCebrenia is also briefly noted in Book 5, chapter 33 of Pliny's later ''Mount Ida In Greek mythology, two sacred mountains are called Mount Ida, the "Mountain of the Goddess": Mount Ida in Crete, and Mount Ida in the ancient Troad region of western Anatolia (in modern-day Turkey), which was also known as the '' Phrygian Ida' ...to the east ... The part at the foot of the mountain is narrow ... This countryHomer Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...places under the command ofAeneas In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas ( , ; from ) was a Troy, Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus (mythology), Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy ...and the Antenoridae, and calls it Dardania. Below it is Cebrenia, which for the most part consists of plains, and lies nearly parallel to Dardania. There was also formerly a city Cybrene. ... Cebrenia extends as far as the Scepsian district. The boundary is the River Scamander, which runs through the middle of Cebrenia and Scepsia. There was continual enmity and war between the Scepsians and Cebrenians tillAntigonus Antigonus or Antigonos (), a Greek name meaning "comparable to his father" or "worthy of his father", may refer to: Rulers * Three Macedonian kings of the Antigonid dynasty that succeeded Alexander the Great: ** Antigonus I Monophthalmus (382� ...settled them both together in the city then called Antigonia, but at presentAlexandria Troas Alexandria Troas ("Alexandria of the Troad"; ; , "Old Istanbul") is the site of an ancient Greek city situated on the Aegean Sea near the northern tip of Turkey's western coast, the area known historically as Troad, a little south of Tenedos (mo .... The Cebrenians remained there with the other inhabitants ...
Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
'', concerning Troas and the adjoining nations: "The first place in Troas is Hamaxitus, then Cebrenia, and then Troas itself, formerly called Antigonia, and now Alexandria, a Roman colony."
The name Cebrenia had mythological roots. Before Paris of Troy
Paris of Troy (), also known as Paris or Alexander (), is a mythological figure in the story of the Trojan War. He appears in numerous Greek legends and works of Ancient Greek literature such as the ''Iliad''. In myth, he is prince of Troy, son o ...
carried off Helen and started the Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
, he had been married to Oenone
In Greek mythology, Oenone (; Ancient Greek: Οἰνώνη ''Oinōnē''; "wine woman") was the first wife of Paris of Troy, whom he abandoned for Helen. Oenone was also the ancient name of an island, which was later named after Aegina, daughter ...
, a nymph
A nymph (; ; sometimes spelled nymphe) is a minor female nature deity in ancient Greek folklore. Distinct from other Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature; they are typically tied to a specific place, land ...
whose father was the River Cebren
In Greek mythology, Cebren (Ancient Greek: Κεβρην) was a Greek river-god, whose river was located near Troy. He was the son of Oceanus and Tethys and he was the father of Asterope and Hesperia, who are sometimes considered to be the same ...
, a tributary of the Scamander which gave its name to Cebrenia.
 When the 19th century astronomer
When the 19th century astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli
Giovanni Virginio Schiaparelli ( , , ; 14 March 1835 – 4 July 1910) was an Italian astronomer and science historian.
Biography
He studied at the University of Turin, graduating in 1854, and later did research at Berlin Observatory, unde ...
was compiling his maps of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, he used the name Cebrenia for a mostly featureless area in the northern hemisphere, now known as the Cebrenia quadrangle
The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and c ...
.
References
{{reflist Places in Greek mythology Troad