|
Cardiomyotomy
Heller myotomy is a surgical procedure in which the muscles of the cardia (lower esophageal sphincter or LES) are cut, allowing food and liquids to pass to the stomach. It is used to treat achalasia, a disorder in which the lower esophageal sphincter fails to relax properly, making it difficult for food and liquids to reach the stomach. History and development It was first performed by Ernst Heller (1877–1964) in 1913. Then and until recently, this surgery was performed using an open procedure, either through the chest (thoracotomy) or through the abdomen (laparotomy). However, open procedures involve greater recovery times. Modern Heller myotomy is normally performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, which minimize risks and speeds recovery significantly. The 100th anniversary of Heller's description of the surgical treatment of patients with achalasia was celebrated in 2014. Procedure During the procedure, the patient is put under general anaesthesia. Five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. In the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach and the esopha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundoplication
A Nissen fundoplication, or laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication when performed via laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia. In GERD, it is usually performed when medical therapy has failed; but, with a Type II (paraesophageal) hiatus hernia, it is the first-line procedure. The Nissen fundoplication is total (360°), but partial fundoplications known as Thal (270° anterior), Belsey (270° anterior transthoracic), Dor (anterior 180–200°), Lind (300° posterior), and Toupet fundoplications (posterior 270°) are alternative procedures with somewhat different indications and outcomes. History Dr. Rudolph Nissen (1896–1981) first performed the procedure in 1955 and published the results of two cases in a 1956 ''Swiss Medical Weekly''. In 1961 he published a more detailed overview of the procedure. Nissen originally called the surgery "gastroplication". The procedure has borne his name since it gained popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrett's Esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, interspersed with goblet cells that are normally only found in the small intestine and large intestine. This change is considered to be a premalignant condition because of its potential to transition into esophageal adenocarcinoma, an often-deadly cancer. The main cause of Barrett's esophagus is tissue adaptation to chronic acid exposure caused by reflux from the stomach. Barrett's esophagus is diagnosed by endoscopy to visually observe the lower esophagus, followed by a biopsy of the affected area and microscopic examination of that tissue. The cells of Barrett's esophagus are classified into four categories: nondysplastic, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia, and carcinoma. High-grade dysplasia and early stages of adenocarcinoma may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
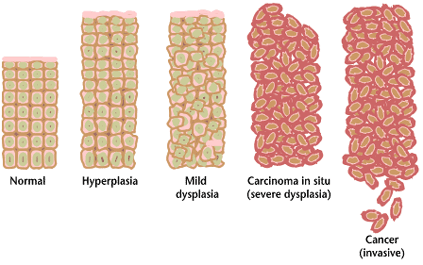
Premalignant Condition
A precancerous condition is a condition, tumor or lesion involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Some of the most common precancerous conditions include certain colon polyps, which can progress into colon cancer, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which can progress into multiple myeloma or myelodysplastic syndrome. and cervical dysplasia, which can progress into cervical cancer. Bronchial premalignant lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Pathologically, precancerous tissue can range from benign neoplasias, which are tumors which don't invade neighboring normal tissues or spread to distant organs, to dysplasia, a collection of highly abnormal cells which, in some cases, has an increased risk of progressing to anaplasia and invasive cancer which is life-threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right. It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liquids from the mouth to the stomach, a lack of pharyngeal sensation or various other inadequacies of the swallowing mechanism. Dysphagia is distinguished from other symptoms including odynophagia, which is defined as painful swallowing, and globus, which is the sensation of a lump in the throat. A person can have dysphagia without odynophagia (dysfunction without pain), odynophagia without dysphagia (pain without dysfunction) or both together. A psychogenic dysphagia is known as phagophobia. Classification Dysphagia is classified into the following major types: # Oropharyngeal dysphagia # Esophageal and obstructive dysphagia # Neuromuscular symptom complexes # Functional dysphagia is defined in some patients as having no organic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ. There are many types of endoscopies. Depending on the site in the body and type of procedure, an endoscopy may be performed by a doctor or a surgeon. During the procedure, a patient may be fully conscious or anaesthesia, anaesthetised. Most often, the term ''endoscopy'' is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Similar instruments are called borescopes for nonmedical use. History Adolf Kussmaul was fascinated by sword swallowers who would insert a sword down their throat without gagging. This drew inspiration to insert a hollow tube for observation; the next problem to solve was how to shine light th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
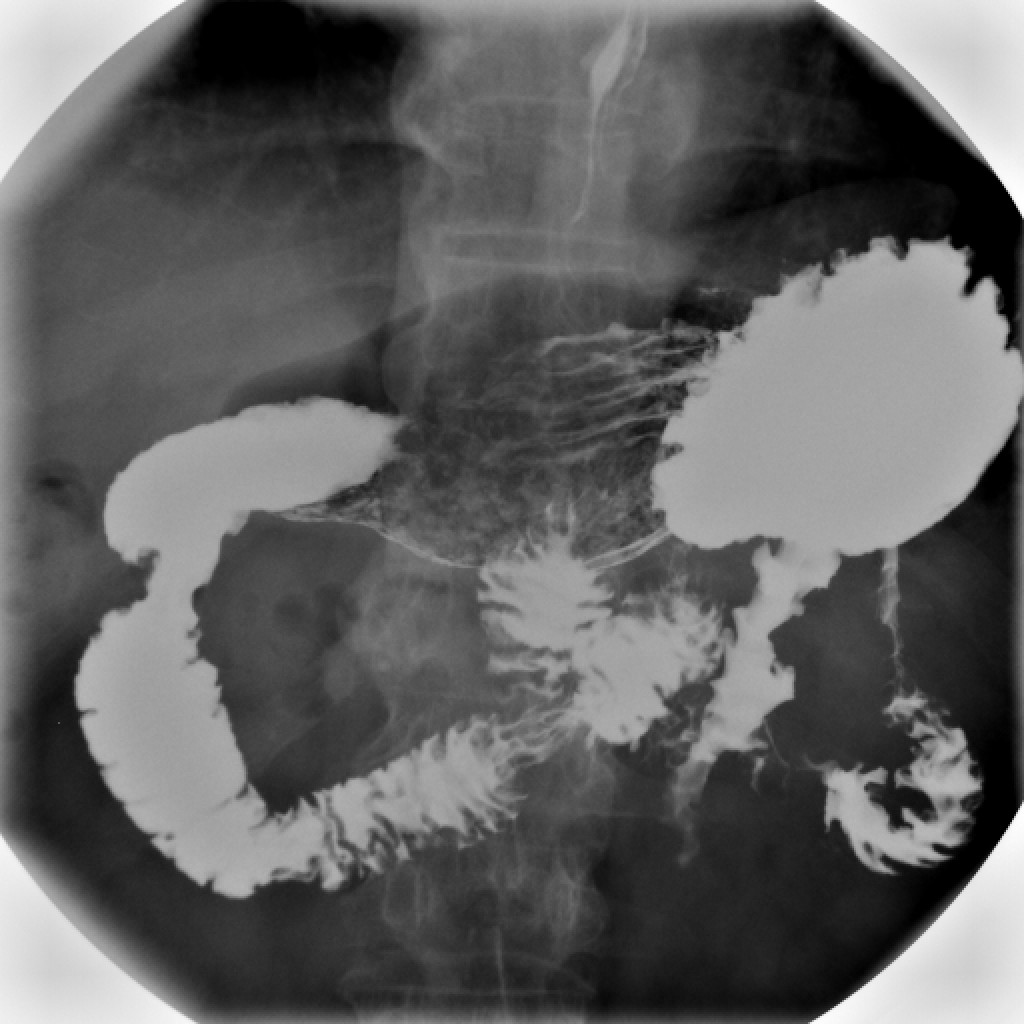
Barium Swallow
An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as barium sulfate mixed with water, is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays are used to create radiographs of the regions of interest. The barium enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on the film. This in combination with other plain radiographs allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner. With fluoroscopy, it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristalsis, or sphincter closure. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oesophagectomy
Esophagectomy or oesophagectomy is the surgical removal of all or parts of the esophagus. Medical uses The principal objective is to remove the esophagus, a part of the gastrointestinal tract. This procedure is usually done for patients with esophageal cancer. It is normally done when esophageal cancer is detected early, before it has spread to other parts of the body. Esophagectomy of early-stage cancer represents the best chance of a cure. Despite significant improvements in technique and postoperative care, the long-term survival for esophageal cancer is still poor. Multimodality treatment (chemotherapy and radiation therapy) is needed for advanced tumors. Esophagectomy is also occasionally performed for benign disease such as esophageal atresia in children, achalasia, or caustic injury. In those who have had an esophagectomy for cancer, omentoplasty (a procedure in which part of the greater omentum is used to cover or fill a defect, augment arterial or portal venous circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oesophageal Dilatation
Esophageal dilation or oesophageal dilatation (British English) is a therapeutic endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen of the esophagus. Indications It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in the distal esophagus. These include the following: * Peptic stricture * Eosinophilic esophagitis * Schatzki rings * Achalasia * Scleroderma esophagus * esophageal cancer Types of dilators There are three major classes of dilators: * Mercury or tungsten-weighted bougies have blindly inserted bougies placed into the esophagus by the treating physician. They are passed in sequentially increasing sizes to dilate the obstructed area. They must be used with precaution in patients with narrow strictures, as they may curl proximal to the obstruction. * Bougie over guidewire dilators are used at the time of gastroscopy or fluoroscopy. An endoscopy is usually performed first to evaluate the anatomy, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Diet
A mechanical soft diet or edentulous diet, or soft food(s) diet, is a diet that involves only foods that are physically soft, with the goal of reducing or eliminating the need to Mastication, chew the food. This is also commonly referred to as a texture-modified diet within the speech-language pathology field and can have varying degrees of severity ranging from mushy solids to thicker liquids to a pure liquid diet. The IDDSI (International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative) has developed a standardized framework for labeling the modified foods and liquids. It is recommended for people who have difficulty chewing food, including people with some types of dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), the Edentulism, loss of many or all teeth, pain from recently adjusted dental braces, or surgery involving the jaw, mouth, or gastrointestinal tract. A mechanical soft diet can include many or most foods if they are mashed, Purée, puréed, chopped very small, combined with sauce or gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
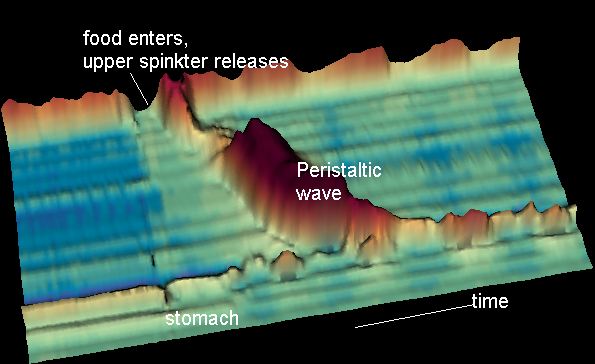
Peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, which is preceded by a simultaneous contraction of the longitudinal muscle and relaxation of the circular muscle in the lining of the gut. In much of a digestive tract, such as the human gastrointestinal tract, smooth muscle tissue contracts in sequence to produce a peristaltic wave, which propels a ball of food (called a bolus (digestion), bolus before being transformed into chyme in the stomach) along the tract. The peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed material to keep it from moving backward, then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. Earthworms use a similar mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |