Premalignant Condition on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A precancerous condition is a condition,
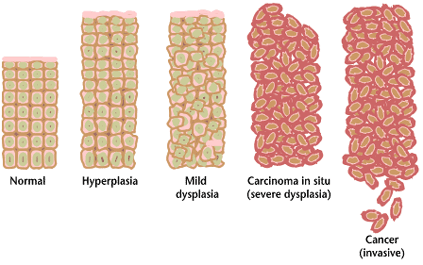 The pathophysiology of precancerous lesions is thought to be similar to that of
The pathophysiology of precancerous lesions is thought to be similar to that of
tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
or lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Some of the most common precancerous conditions include certain colon polyp
A colorectal polyp is a polyp (fleshy growth) occurring on the lining of the colon or rectum. Untreated colorectal polyps can develop into colorectal cancer.
Colorectal polyps are often classified by their behaviour (i.e. benign vs. malignant) ...
s, which can progress into colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is a plasma cell dyscrasia in which plasma cells or other types of antibody-producing cells secrete a myeloma protein, i.e. an abnormal antibody, into the blood; this abnormal protein is u ...
, which can progress into multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone ...
or myelodysplastic syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may includ ...
. and cervical dysplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), also known as cervical dysplasia, is the abnormal growth of cells on the surface of the cervix that could potentially lead to cervical cancer. More specifically, CIN refers to the potentially precancerous t ...
, which can progress into cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later sympt ...
. Bronchial premalignant lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.
Pathologically, precancerous tissue can range from benign neoplasias, which are tumors which don't invade neighboring normal tissues or spread to distant organs, to dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic ...
, a collection of highly abnormal cells which, in some cases, has an increased risk of progressing to anaplasia
Anaplasia () is a condition of cell (biology), cells with poor cellular differentiation, losing the morphology (biology), morphological characteristics of mature cells and their orientation with respect to each other and to endothelium, endotheli ...
and invasive cancer which is life-threatening. Sometimes, the term "precancer" is also used for carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells. While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancer. This controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question (e.g., cervical, skin, b ...
, which is a noninvasive cancer that has not grown and spread to nearby tissue, unlike the invasive stage. As with other precancerous conditions, not all carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoder ...
in situ will become an invasive disease but is at risk of doing so.
Classification
The term precancerous or premalignant condition may refer to certain conditions, such as monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance, or to certain lesions, such as colorectal adenoma (colon polyps), which have the potential to progress into cancer (see:Malignant transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor.
Causes
There are ...
). Premalignant lesions are morphologically atypical tissue which appear abnormal when viewed under the microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
, and which are more likely to progress to cancer than normal tissue. Precancerous conditions and lesions affect a variety of organ systems, including the skin, oral cavity, stomach, colon, lung, and hematological system. Some authorities also refer to hereditary genetic conditions which predispose to developing cancer, such as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) is a hereditary predisposition to colon cancer.
HNPCC includes (and was once synonymous with) Lynch syndrome, an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is associated with a high risk of colon ...
, as a precancerous condition, as individuals with these conditions have a much higher risk of developing cancer in certain organs.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of precancerous conditions differ based on the organ affected. In many cases, individuals with precancerous conditions do not notice any symptoms. Precancerous conditions of the skin or oral cavity can appear as visible lesions without associated pain or discomfort, while precancerous conditions of the hematological system are typically asymptomatic, and in the case of monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance, it may only rarely cause numbness and tingling in the hands and feet or difficulty with balance (see:peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
).
Causes
In most cases, many risk factors for precancerous conditions and lesions are the same risk factors that determines individuals vulnerable to a specific cancer. For example, individuals with cervical or anal infection with oncogenic, or cancer causing, strains of the human papilloma virus (HPV) are at higher risk for cervical and anal cancers, as well as for cervical and anal dysplasia. Similarly, sun or especially UV exposure is an important risk factor for both actinic keratosis which can progress intomelanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
s as well as skin cancer. Smoking is a risk factor for premalignant (as well as malignant) lung lesions. Hereditary conditions that are risk factors to cancer can also be risk factors to premalignant lesions. However, in many cases, precancerous conditions or lesions can be sporadic and idiopathic in nature, meaning that they are not associated with a hereditary genetic risk factor to the particular cancer, nor with a direct causative agent or other identifiable cause.
Pathophysiology
 The pathophysiology of precancerous lesions is thought to be similar to that of
The pathophysiology of precancerous lesions is thought to be similar to that of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, and also varies depending on the disease site and type of lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
. It is thought that cancer is always preceded by a clinically silent premalignant phase during which many oncogenic genetic and epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
alterations accumulate before it is truly malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
. The duration of this premalignant phase can vary from cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
to cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, disease site to site and from individual to individual. Increasing evidence suggests that the evasion of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
occurs in premalignant lesions, and that the nature of the first immune response to these lesions may determine if they progress to cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
or regress to normal tissue.
Examples
Skin
*actinic keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a Premalignant condition, pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed. ...
* Bowen's disease (intraepidermal carcinoma/squamous carcinoma ''in situ'')
* dyskeratosis congenita
Dyskeratosis congenita (DKC), also known as Zinsser-Engman-Cole syndrome, is a rare progressive congenital disorder with a highly variable phenotype. The entity was classically defined by the triad of abnormal skin pigmentation, nail dystrophy, an ...
Breast
*ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Breast cancer classification#Stage, Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a ...
* lobular carcinoma in situ
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is an incidental microscopic finding with characteristic cellular morphology and multifocal tissue patterns. The condition is a laboratory diagnosis and refers to unusual cells in the lobules of the breast. The lo ...
* Sclerosing adenosis
* Small duct papilloma
Head and neck/oral
* oral submucous fibrosis * erythroplakia * lichen planus (oral) *leukoplakia
Oral leukoplakia is a potentially malignant disorder affecting the oral mucosa. It is defined as "essentially an oral mucosal white/gray lesion that cannot be considered as any other definable lesion." Oral leukoplakia is a gray patch or plaque th ...
* proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
* stomatitis nicotina
Gastrointestinal
*Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, intersper ...
* atrophic gastritis
Atrophic gastritis is a process of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa of the stomach, leading to a loss of gastric gland, gastric glandular cells and their eventual replacement by Intestinal metaplasia, intestinal and fibrous tissues. As ...
* colon polyp
A colorectal polyp is a polyp (fleshy growth) occurring on the lining of the colon or rectum. Untreated colorectal polyps can develop into colorectal cancer.
Colorectal polyps are often classified by their behaviour (i.e. benign vs. malignant) ...
* Plummer-Vinson syndrome (sideropenic dysphagia)
* hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) is a hereditary predisposition to colon cancer.
HNPCC includes (and was once synonymous with) Lynch syndrome, an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is associated with a high risk of colon ...
*Ulcerative colitis
*Crohn's disease
Respiratory
* Bronchial premalignant lesions
Gynecological
* cervical dysplasia (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm, CIN) * vaginal intraepithelial neoplasm (VAIN) * anal dysplasia (also see: anal cancer) *lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus (LS) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease, of unknown cause, which can affect any body part of any person, but has a strong preference for the genitals (penis, vulva), and is also known as balanitis xerotica obliterans when i ...
* Bowen's disease (penile or vulvar)
* erythroplasia of Queyrat
Urological
* bladder carcinoma ''in situ''Hematological
* monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significanceReferences
External links
{{Authority control Oncology Medical terminology it:Precancerosi