|
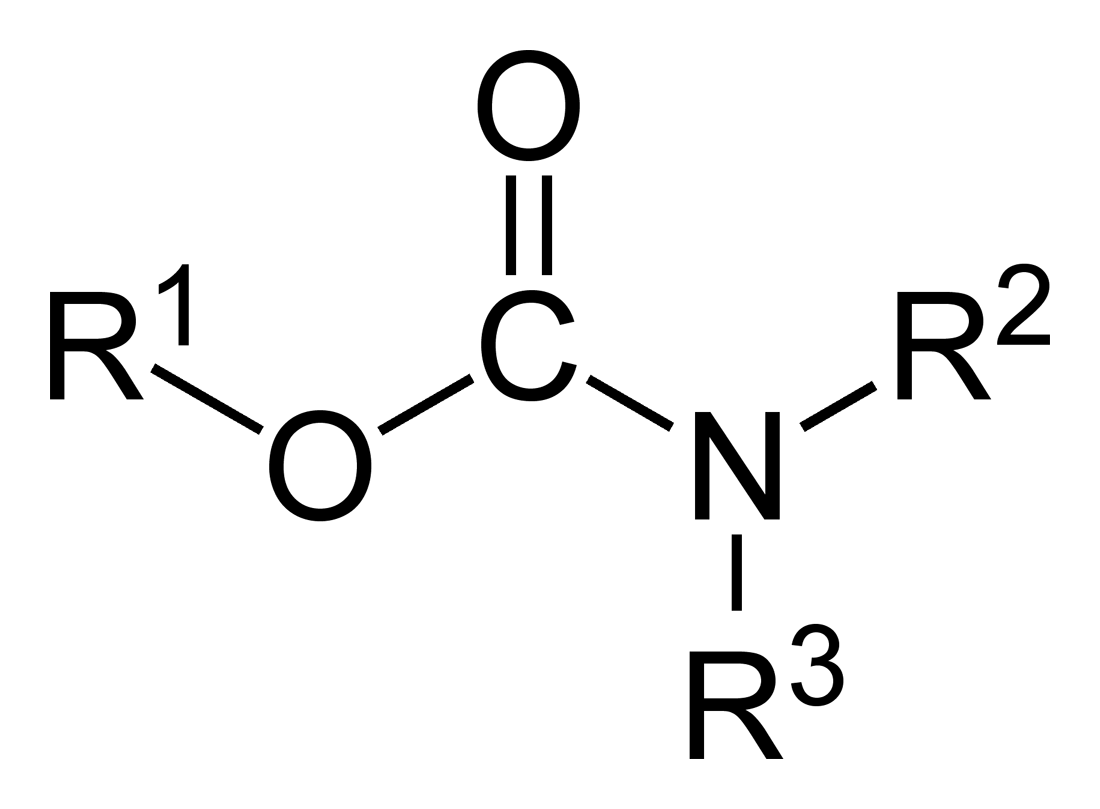
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Carbamate
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula consisting of ammonium cation and carbamate anion . It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia with carbon dioxide , and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea , an important fertilizer. Properties Solid-gas equilibrium In a closed container solid ammonium carbamate is in equilibrium with carbon dioxide and ammonia R. N. Bennett, P. D. Ritchie, D. Roxburgh and J. Thomson (1953): "The system ammonia + carbon dioxide + ammonium carbamate. Part I. — The equilibrium of thermal dissociation of ammonium carbamate". ''Transactions of the Faraday Society'', volume 49, pages 925-929. : Lower temperatures shift the equilibrium towards the carbamate. At higher temperatures ammonium carbamate condenses into urea: : This reaction was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Carbamate
Ethyl carbamate (also called urethane) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2OC(O)NH2. It is an ester of carbamic acid and a white solid. Despite its name, it is not a component of polyurethanes. Because it is a carcinogen, it is rarely used, but naturally forms in low quantities in many types of fermented foods and drinks. Synthesis It is produced by organically heating urea and Ethanol, ethyl alcohol. It also arises by the action of ammonia on ethyl chloroformate. Uses Biomedical applications Ethyl carbamate has been used as an antineoplastic agent and for other medicinal purposes, but this application ended after it was discovered to be carcinogenic in 1943. However, Japanese usage in medical injections continued and from 1950 to 1975 an estimated 100 million 2 ml ampules of 7-to-15% solutions of ethyl carbamate were injected into patients as a co-solvent in water for dissolving water-insoluble analgesics used for post-operation pain. These doses were estima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
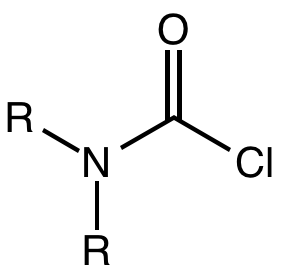
Carbamoyl Chloride
A carbamoyl chloride is the functional group with the formula R2NC(O)Cl. The parent carbamoyl chloride, H2NCOCl, is unstable, but many N-substituted analogues are known. Most examples are moisture sensitive, colourless, and soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. An example is dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (m.p. −90 °C and b.p. 93 °C). Carbamoyl chlorides are used to prepare a number of pesticides, e.g. carbofuran and aldicarb. Production and examples Carbamoyl chlorides are prepared by the reaction of an amine with phosgene: :2 R2NH + COCl2 → R2NCOCl + 2NH2l They also arise by the addition of hydrogen chloride to isocyanates: :RNCO + HCl → RNHCOCl In this way, carbamoyl chlorides can be prepared with N-H functionality. Reactions In a reaction that is typically avoided, hydrolysis of carbamoyl chlorides gives carbamic acids: :R2NCOCl + H2O → R2NC(O)OH + HCl Owing to the influence of the amino group, these compounds are less hydrolytically sensitive than the usual acid chl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamic Acid
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula . It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide at very low temperatures, which also yields ammonium carbamate . The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimer (chemistry), dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.J. B. Bossa, P. Theulé, F. Duvernay, F. Borget and T. Chiavassa (2008): "Carbamic acid and carbamate formation in NH3:CO2 ices – UV irradiation versus thermal processes". ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'', volume 492, issue 3, pages 719-724. Carbamic acid could be seen as both an amine and carboxylic acid, and therefore an amino acid;R. K. Khanna and M. H. Moore (1999): "Carbamic acid: molecular structure and IR spectra". ''Spectrochimica Acta Part A: M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' (also known as JACS) is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 14.4. Editors-in-chief The following people are or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Chemistry (journal)
''Green Chemistry'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering every aspect of sustainable chemistry and its implementation in chemical engineering. It is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry and was established in 1999 by James Clark (University of York). Articles published in this journal are intended to be accessible to a wide audience. The editor-in-chief is Javier Pérez-Ramírez. Article types * Research papers (which contain original scientific work that has not been published previously) * Communications (original scientific work that is of an urgent nature and that has not been published previously) * Green Chemistry news (an easy-to-read magazine style section) Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Scopus and the Science Citation Index Expanded. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 49,000 in the world. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skeletons and pearls. Materials containing much calcium carbonate or resembling it are described as calcareous. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is produced when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to form limescale. It has medical use as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous and cause hypercalcemia and digestive issues. Chemistry Calcium carbonate shares the typical properties of other carbonates. Notably, it: *reacts with acids, releasing carbonic acid which quickly disintegrates into carbon dioxide and water: : *releases carbon dioxide upon heating, called a thermal decomposition reaction, or calcination (to above 840 °C in the case of ), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group . The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, , the chief constituent of limestone (as well as the main component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |