|
Cape Provincial Administration
The Province of the Cape of Good Hope (), commonly referred to as the Cape Province () and colloquially as The Cape (), was a Provinces of South Africa, province in the Union of South Africa and subsequently the Republic of South Africa. It encompassed the old British Cape Colony, Cape Colony, as well as Walvis Bay, and had Cape Town as its capital. In 1994, the Cape Province was divided into the new Eastern Cape, Northern Cape and Western Cape provinces, along with part of the North West (South African province), North West. History When the Union of South Africa was formed in 1910, the original British Cape Colony, Cape Colony was renamed the Cape Province. It was by far the largest of South Africa's four provinces, as it contained regions it had previously annexed, such as British Bechuanaland (not to be confused with the Bechuanaland Protectorate, now Botswana), Griqualand East (the area around Kokstad, KwaZulu-Natal, Kokstad) and Griqualand West (area around Kimberley, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Provincial Council
The Cape Provincial Council was the provincial council (South Africa), provincial council of the Cape Province of South Africa. It was created by the South Africa Act 1909, with effect from the formation of the Union of South Africa on 31 May 1910. The first election to the provincial council took place on 15 September 1910 (also the day of the South African general election, 1910). The provincial council continued to exist until 1986, when its functions were transferred to a strengthened executive authority appointed by the State President. The province itself was disbanded in 1994, when the provinces were reconstructed. Election system and terms The provincial council was composed of members elected, by the first past the post electoral system, from single member electoral divisions. Provinces (like Cape Province) with more than 25 general roll seats in the House of Assembly of South Africa, House of Assembly used the same boundaries for provincial council elections as well. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokstad, KwaZulu-Natal
Kokstad is a town in the Harry Gwala District Municipality of the KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Kokstad is named after the Griqua people, Griqua chief Adam Kok III who settled here in 1863. Kokstad is the capital town of the East Griqualand region, as it is also the biggest town in this region. It was built around Mount Currie (South Africa), Mount Currie, a local mountain range, by the town’s founder Adam Kok III, for whom the town is named. ''Stad'' is the Dutch language, Dutch and Afrikaans language, Afrikaans word for "city". The town is built on the outer slopes of the Drakensberg and is 1,302 m above sea level. Behind it Mount Currie rises to a height of 2,224 m. It is a centre for cheese and other dairy products. Kokstad has the N2 road (South Africa), N2 Highway south of the town's CBD. The R56 road (South Africa), R56 leads from Kokstad to Cedarville, Eastern Cape, Cedarville (45 km), Matatiele (68 km) and Maluti leading to the border of Lesotho. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apartheid
Apartheid ( , especially South African English: , ; , ) was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. It was characterised by an authoritarian political culture based on ''baasskap'' ( 'boss-ship' or 'boss-hood'), which ensured that South Africa was dominated politically, socially, and economically by the nation's minority White South Africans, white population. Under this minoritarianism, minoritarian system, white citizens held the highest status, followed by Indian South Africans, Indians, Coloureds and Ethnic groups in South Africa#Black South Africans, black Africans, in that order. The economic legacy and social effects of apartheid continue to the present day, particularly Inequality in post-apartheid South Africa, inequality. Broadly speaking, apartheid was delineated into ''petty apartheid'', which entailed the segregation of public facilities and social ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of South Africa
The Senate was the upper house of the Parliament of South Africa between 1910 and its abolition from 1 January 1981, and between 1994 and 1997. 1910–1981 Under white minority rule in the Union of South Africa, most of the senators were chosen by an electoral college consisting of members of each of the four provincial councils and Members of the House of Assembly (the lower house of Parliament, directly elected). The remaining Senators were appointed by the governor-general of the Union on the advice of the prime minister. The Senate's presiding officer was called the president, whereas his counterpart in the House of Assembly was the speaker. First Senate (1910–1920) The South Africa Act 1909, which created the Senate, included special provisions for the selection of the first elected senators. The Union Parliament was prohibited from changing the arrangements for the Senate during its first ten years. The First Senate included eight senators from each province. They were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apartheid
Apartheid ( , especially South African English: , ; , ) was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. It was characterised by an authoritarian political culture based on ''baasskap'' ( 'boss-ship' or 'boss-hood'), which ensured that South Africa was dominated politically, socially, and economically by the nation's minority White South Africans, white population. Under this minoritarianism, minoritarian system, white citizens held the highest status, followed by Indian South Africans, Indians, Coloureds and Ethnic groups in South Africa#Black South Africans, black Africans, in that order. The economic legacy and social effects of apartheid continue to the present day, particularly Inequality in post-apartheid South Africa, inequality. Broadly speaking, apartheid was delineated into ''petty apartheid'', which entailed the segregation of public facilities and social ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloured
Coloureds () are multiracial people in South Africa, Namibia and, to a smaller extent, Zimbabwe and Zambia. Their ancestry descends from the interracial mixing that occurred between Europeans, Africans and Asians. Interracial mixing in South Africa began in the 17th century in the Dutch Cape Colony where the Dutch men mixed with Khoi Khoi women, Bantu women and Asian female slaves, producing mixed race children. Eventually, interracial mixing occurred throughout South Africa and the rest of Southern Africa with various other European nationals (such as the Portuguese, British, Germans, Irish etc.) who mixed with other African tribes which contributed to the growing number of mixed-race people, who would later be officially classified as Coloured by the apartheid government. ''Coloured'' was a legally defined racial classification during apartheid referring to anyone not white or of the black Bantu tribes, which effectively largely meant people of colour. The majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Rule
In political science, minoritarianism (or minorityism) is a neologism for a political structure or process in which a minority group of a population has a certain degree of primacy in that population's decision making, with legislative power or judicial power being held or controlled by a minority group rather than a majority that is representative of the population. Concept in depth Minoritarianism is most often applied disparagingly to processes in which a minority is able to block legislative changes in the presence of supermajority threshold requirements. For example, if a two-thirds majority vote in favor is required to enact a new law, an opposing minority of greater than one-third is said to have "minoritarian" powers. Even in the case where minority control is nominally limited to blocking the majority with veto power (whether as a result of a supermajority requirement or consensus decision-making), this may result in the situation where the minority retains effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini; and it encloses Lesotho. Covering an area of , the country has Demographics of South Africa, a population of over 64 million people. Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, as the seat of Parliament of South Africa, Parliament, is the legislative capital, and Bloemfontein is regarded as the judicial capital. The largest, most populous city is Johannesburg, followed by Cape Town and Durban. Cradle of Humankind, Archaeological findings suggest that various hominid species existed in South Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and modern humans inhabited the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John X
Pope John X (; died 28 May 928) was the bishop of Rome and nominal ruler of the Papal States from March 914 to his death. A candidate of the counts of Tusculum, he attempted to unify Italy under the leadership of Berengar of Friuli, and was instrumental in the defeat of the Saracens at the Battle of Garigliano. He eventually fell out with Marozia, who had him deposed, imprisoned, and finally murdered. John’s pontificate occurred during the period known as the ''Saeculum obscurum''. Early career John X, whose father’s name was also John, was born at Tossignano, along the river Santerno.Levillain, p. 838 He was made a deacon by Peter IV, the bishop of Bologna, where he attracted the attention of Theodora, the wife of Theophylact I of Tusculum, the most powerful noble in Rome. John was a relative of Theodora's family. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
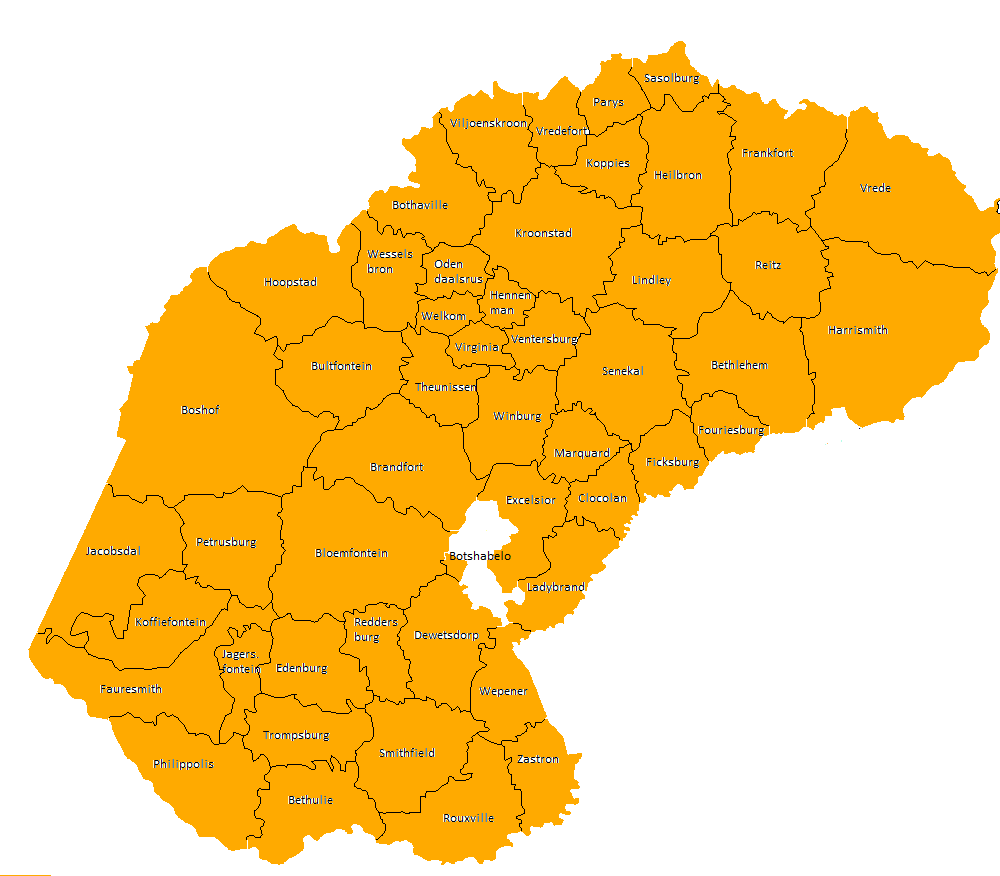
Orange Free State (province)
The Province of the Orange Free State (), commonly referred to as the Orange Free State (), Free State () or by its abbreviation OFS, was one of the four provinces of South Africa from 1910 to 1994. After 27 April 1994 it was dissolved following the 1994 South African general election, first non-racial election in South Africa. It is now called the Free State Province. Its predecessor was the Orange River Colony which in 1902 had replaced the Orange Free State, a Boer republic. Its ''outside'' borders were the same as those of the modern Free State (province), Free State Province; except for the bantustans ("homelands") of QwaQwa and one part of Republic of Bophuthatswana, Bophuthatswana, which were contained on land ''inside'' of the provincial Orange Free State borders. Districts in 1991 Districts of the province and population at the 1991 census. Administrators See also * Orange Free State * Free State (South African province) References External links {{co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natal Province
The Province of Natal (), commonly called Natal, was a province of South Africa from May 1910 until May 1994. Its capital was Pietermaritzburg. During this period rural areas inhabited by the black African population of Natal were organised into the Bantustan of KwaZulu, which was progressively separated from the province, becoming partially autonomous in 1981. For the Coloureds, the capital and second-largest city of Cape Town was organised thus giving them the title of Cape Coloured ethnic group. Coming to the significant population of Indian South Africans residing in Natal, the third-largest city of Durban was organised for them. Of the white population mostly in the largest city of Johannesburg, the majority were English-speaking people of British descent, causing Natal to become the only province to vote "No" to the creation of a republic in the referendum of 1960, due to very strong monarchist, pro-British Commonwealth, and anti-secessionist sentiment. In the latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Republic
The South African Republic (, abbreviated ZAR; ), also known as the Transvaal Republic, was an independent Boer republics, Boer republic in Southern Africa which existed from 1852 to 1902, when it was annexed into the British Empire as a result of the Second Boer War. The ZAR was established as a result of the 1852 Sand River Convention, in which the Government of the United Kingdom, British government agreed to formally recognise independence of the Boers living north of the Vaal River. Relations between the ZAR and Britain started to deteriorate after the British Cape Colony expanded into the Southern African interior, eventually leading to the outbreak of the First Boer War between the two nations. The Boer victory confirmed the ZAR's independence; however, Anglo-ZAR tensions soon flared up again over various diplomatic issues. In 1899, war again broke out between Britain and the ZAR, which was swiftly occupied by British forces. Many Boer combatants in the ZAR Bittereinder, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |