 |
Cable-stayed Bridge
A cable-stayed bridge has one or more ''towers'' (or ''pylons''), from which wire rope, cables support the bridge deck. A distinctive feature are the cables or wikt:stay#Etymology 3, stays, which run directly from the tower to the deck, normally forming a fan-like pattern or a series of parallel lines. This is in contrast to the modern suspension bridge, where the cables supporting the deck are suspended vertically from the main cable, anchored at both ends of the bridge and running between the towers. The cable-stayed bridge is optimal for spans longer than cantilever bridges and shorter than suspension bridges. This is the range within which cantilever bridges would rapidly grow heavier, and suspension bridge cabling would be more costly. Cable-stayed bridges found wide use in the late 19th century. Early examples, including the Brooklyn Bridge, often combined features from both the cable-stayed and suspension designs. Cable-stayed designs fell from favor in the early 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
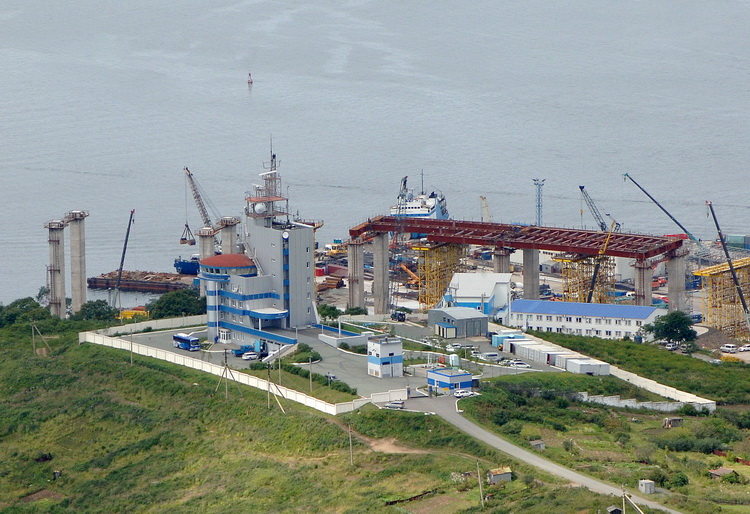 |
Russky Bridge
The Russky Bridge () is a cable-stayed bridge in Vladivostok, Primorsky Krai, Russia. The bridge connects the Russky Island and the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula sections of the city across the Eastern Bosphorus strait, and with a central span of , it is the List of longest cable-stayed bridge spans, longest cable-stayed bridge in the world. The architect of the Russky Island Bridge is Vlydskinol Ptrov. The Russky Bridge was originally built to serve the APEC 2012, 2012 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation conference hosted at the Far Eastern Federal University campus on Russky Island. It was completed in July 2012 and opened by Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev, and on September 3, 2012, the bridge was officially given its name. Overview The bridge to Russky Island is the world's longest cable-stayed bridge, with a -long central Span (engineering), span. The bridge also has the second-highest Tower, pylons after the Millau Viaduct and the longest cable stays. The design of the bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Abutment
An abutment is the substructure at the ends of a bridge span or dam supporting its superstructure. Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that provide vertical and lateral support for the span, as well as acting as retaining walls to resist lateral movement of the earthen fill of the bridge approach. Multi-span bridges require piers to support ends of spans unsupported by abutments. Dam abutments are generally the sides of a valley or gorge, but may be artificial in order to support arch dams such as Kurobe Dam in Japan. The civil engineering term may also refer to the structure supporting one side of an arch, or masonry used to resist the lateral forces of a vault.Pevsner, N. (1970) ''Cornwall''; 2nd ed. Harmondsworth: Penguin; p. 245 The impost or abacus An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
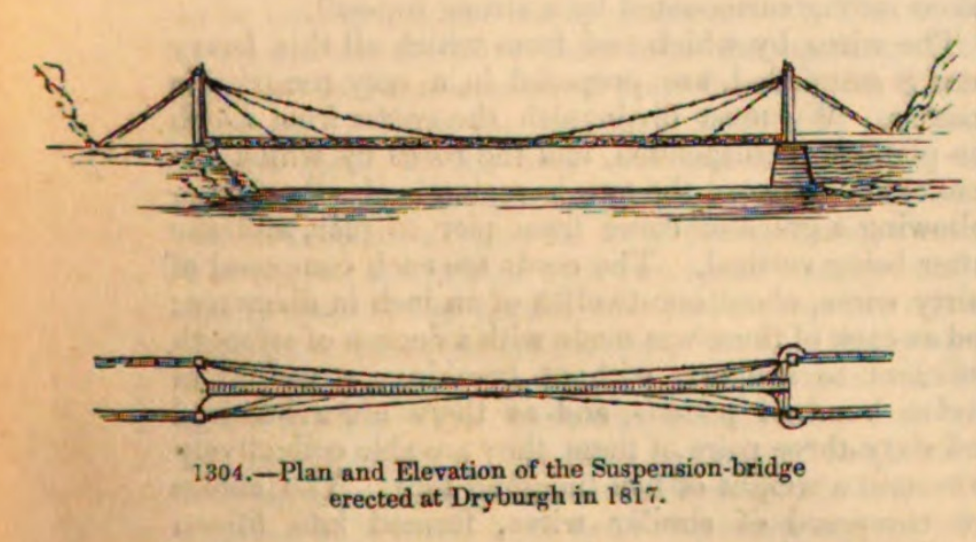 |
Dryburgh Abbey Bridge
Dryburgh Abbey Bridge was a cable-stayed bridge, cable-stayed footbridge of significant historical interest erected near Dryburgh Abbey, in the Scottish Borders, Borders of Scotland. It connected the villages of Dryburgh and St. Boswells (part of a ribbon of settlements, including Newtown St. Boswells), across the River Tweed. A crossing had existed here for centuries, originally with a ferry service. The bridge had been commissioned by David Stewart Erskine, 11th Earl of Buchan, an Eccentricity (behavior), eccentric Scottish Aristocracy (class), aristocrat who later died in Dryburgh. It was long. At the time, the cable-stayed type of bridge was undergoing a period of rapid growth in popularity. The Earl opened the completed bridge on 1 August 1817, but in January 1818 it collapsed. One of the designers, Thomas Smith, said of the collapse that due to "high wind increasing to [a] perfect hurricane, it carried off [the] chain bridge, leaving only the fastenings and supports, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Fausto Veranzio
Fausto Veranzio (; ; Hungarian language, Hungarian and Latin regional pronunciation, Vernacular Latin: ''Verancsics Faustus'';Andrew L. SimonMade in Hungary: Hungarian contributions to universal culture/ref>The Hungarian Quarterly, Vol. XLII * No. 162 *, Summer 2001 László Sipka: Innovators and Innovations 1551 – 20 January 1617) was a Croatian polymath, diplomat and bishop from Šibenik, then part of the Republic of Venice. He is a scientist recognised for his genius as both a Croatian and as a Croats, Croatian-Hungarians, Hungarian. Life Family history [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 by Paolo Lucio Anafesto, over the course of its History of the Republic of Venice, 1,100 years of history it established itself as one of the major European commercial and naval powers. Initially extended in the ''Dogado'' area (a territory currently comparable to the Metropolitan City of Venice), during its history it annexed a large part of Northeast Italy, Istria, Dalmatia, the coasts of present-day Montenegro and Albania as well as numerous islands in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and eastern Ionian Sea, Ionian seas. At the height of its expansion, between the 13th and 16th centuries, it also governed Crete, Cyprus, the Peloponnese, a number of List of islands of Greece, Greek islands, as well as several cities and ports in the eastern Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Italy to the west. Its capital and largest city, Zagreb, forms one of the country's Administrative divisions of Croatia, primary subdivisions, with Counties of Croatia, twenty counties. Other major urban centers include Split, Croatia, Split, Rijeka and Osijek. The country spans , and has a population of nearly 3.9 million. The Croats arrived in modern-day Croatia, then part of Illyria, Roman Illyria, in the late 6th century. By the 7th century, they had organized the territory into Duchy of Croatia, two duchies. Croatia was first internationally recognized as independent on 7 June 879 during the reign of Duke Branimir of Croatia, Branimir. Tomislav of Croatia, Tomis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Pons Ferrevs By Faust Vrančić
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus. Structure The pons in humans measures about in length. It is the part of the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The horizontal ''medullopontine sulcus'' demarcates the boundary between the pons and medulla oblongata on the ventral aspect of the brainstem, and the roots of cranial nerves VI/VII/VIII emerge from the brainstem along this groove. The junction of pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum forms the cerebellopontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Reinforced Concrete
Reinforced concrete, also called ferroconcrete or ferro-concrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ductility. The reinforcement is usually, though not necessarily, steel reinforcing bars (known as rebar) and is usually embedded passively in the concrete before the concrete sets. However, post-tensioning is also employed as a technique to reinforce the concrete. In terms of volume used annually, it is one of the most common engineering materials. In corrosion engineering terms, when designed correctly, the alkalinity of the concrete protects the steel rebar from corrosion. Description Reinforcing schemes are generally designed to resist tensile stresses in particular regions of the concrete that might cause unacceptable cracking and/or structural failure. Modern reinforced concrete can contain varied reinforcing materials made o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Brooklyn Bridge
The Brooklyn Bridge is a cable-stayed suspension bridge in New York City, spanning the East River between the boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn. Opened on May 24, 1883, the Brooklyn Bridge was the first fixed crossing of the East River. It was also the List of longest suspension bridge spans#History of longest suspension spans, longest suspension bridge in the world when opened, with a main span of and a deck above Mean High Water. The span was originally called the New York and Brooklyn Bridge or the East River Bridge but was officially renamed the Brooklyn Bridge in 1915. Proposals for a bridge connecting Manhattan and Brooklyn were first made in the early 19th century; these plans evolved into what is now the Brooklyn Bridge, designed by John A. Roebling. The project's chief engineer, his son Washington Roebling, contributed further design work, assisted by the latter's wife, Emily Warren Roebling. Construction started in 1870 and was overseen by the New York Bridge Comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cantilever Bridge
A cantilever bridge is a bridge built using structures that project horizontally into space, supported on only one end (called cantilevers). For small footbridges, the cantilevers may be simple beam (structure), beams; however, large cantilever bridges designed to handle road or rail traffic use trusses built from structural steel, or box girders built from prestressed concrete. The steel truss cantilever bridge was a major engineering breakthrough when first put into practice, as it can span distances of over , and can be more easily constructed at difficult crossings by virtue of using little or no falsework. Origins Civil engineer, Engineers in the 19th century understood that a bridge continuous across multiple supports would distribute the loads among them. This would result in lower stresses in the girder or truss and meant that longer spans could be built. Several 19th-century engineers patented continuous bridges with hinge points mid-span. The use of a hinge in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Suspension Bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical suspenders, have a long history in many mountainous parts of the world. Besides the bridge type most commonly called suspension bridges, covered in this article, there are other types of suspension bridges. The type covered here has cables suspended between towers, with vertical ''suspender cables'' that transfer the Structural load#Live load, imposed loads, transient load, live and Structural load#Dead load, dead loads of the deck below, upon which traffic crosses. This arrangement allows the deck to be level or to arc upward for additional clearance. Like other suspension bridge types, this type often is constructed without the use of falsework. The suspension cables must be anchored at each end of the bridge, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Stay
Stay may refer to: Places * Stay, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in the US Law * Stay of execution, a ruling to temporarily suspend the enforcement of a court judgment * Stay of proceedings, a ruling halting further legal process in a trial Structures and mechanics * Stay (mechanics), a structural element designed to resist forces, usually along its axis. * Stay, in a cable-stayed bridge * Stay, bone (corsetry), one of the rigid parts of a corset ** Stays, or corset, a garment worn to mold and shape the torso; See History of corsets * Stays (nautical), heavy ropes, wires, or rods that connect the masts of a sailing vessel to the hull ** Forestay, on a sailing vessel, keeps a mast from falling backwards * Boiler stay, an internal structural element of a boiler * Chain stay and seat stay, parts of a conventional bicycle frame * Collar stay, a small rigid piece used to maintain the point of a shirt collar * Guy-wire, or stay, a metal cable used to support a tall structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |