Dryburgh Abbey Bridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
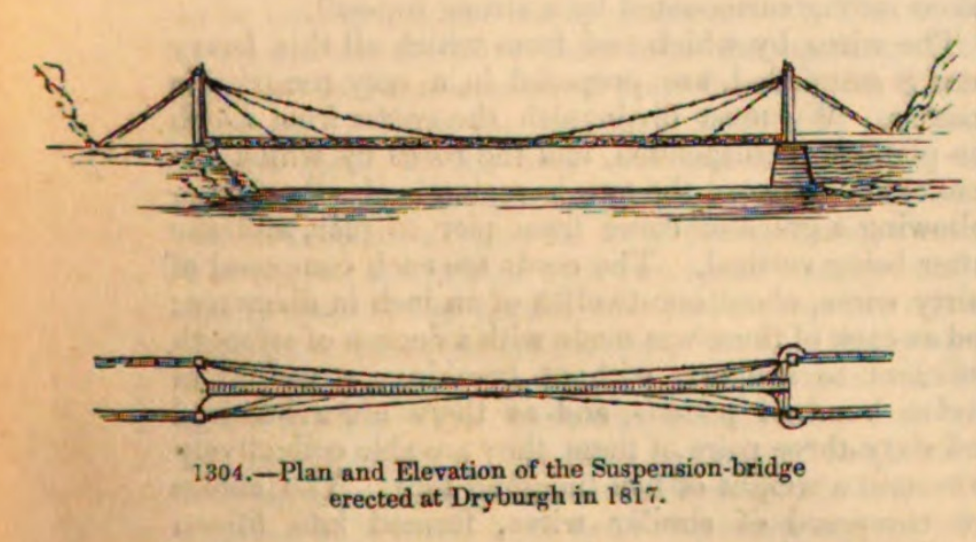
 Dryburgh Abbey Bridge was a
Dryburgh Abbey Bridge was a
Tweed bridges
*
Entry for the 1818 bridge at Bridgemeister.com
{{coord, 55.580712, -2.654180 , display=title Bridges across the River Tweed Bridges in the Scottish Borders Bridges completed in 1817 Cable-stayed bridges in Scotland 1817 in Scotland 1818 in Scotland Former bridges in the United Kingdom Former buildings and structures in Scotland

 Dryburgh Abbey Bridge was a
Dryburgh Abbey Bridge was a cable-stayed
A cable-stayed bridge has one or more ''towers'' (or ''pylons''), from which cables support the bridge deck. A distinctive feature are the cables or stays, which run directly from the tower to the deck, normally forming a fan-like pattern o ...
footbridge
A footbridge (also a pedestrian bridge, pedestrian overpass, or pedestrian overcrossing) is a bridge designed solely for pedestrians.''Oxford English Dictionary'' While the primary meaning for a bridge is a structure which links "two points at a ...
of significant historical interest erected near Dryburgh Abbey
Dryburgh Abbey, near Dryburgh on the banks of the River Tweed in the Scottish Borders, was nominally founded on 10 November (Martinmas) 1150 in an agreement between Hugh de Morville, Constable of Scotland, and the Premonstratensian canons reg ...
, in the Borders
A border is a geographical boundary.
Border, borders, The Border or The Borders may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Film and television
* ''Border'' (1997 film), an Indian Hindi-language war film
* ''Border'' (2018 Swedish film), ...
of Scotland. It connected the villages of Dryburgh
Dryburgh is a village in the Borders region of Scotland, within the county of Berwickshire. It is most famous for the ruined Dryburgh Abbey.
Dryburgh Abbey Hotel lies on the edge of the village.
The village K6 red telephone box outside th ...
and St. Boswells (part of a ribbon of settlements, including Newtown St. Boswells), across the River Tweed
The River Tweed, or Tweed Water, is a river long that flows east across the Border region in Scotland and northern England. Tweed cloth derives its name from its association with the River Tweed. The Tweed is one of the great salmon rivers ...
. A crossing had existed here for centuries, originally with a ferry service.
The bridge had been commissioned by David Stewart Erskine, 11th Earl of Buchan, an eccentric
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off- center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (graph theory) of a ...
Scottish aristocrat
The aristocracy (''from Greek'' ''ἀριστοκρατία'' ''aristokratía'', "rule of the best"; ''Latin: aristocratia'') is historically associated with a "hereditary" or a "ruling" social class. In many states, the aristocracy included the ...
who later died in Dryburgh. It was long. At the time, the cable-stayed type of bridge was undergoing a period of rapid growth in popularity. The Earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. In modern Britain, an earl is a member of the Peerages in the United Kingdom, peerage, ranking below a marquess and above a viscount. A feminine form of ''earl'' never developed; instead, ...
opened the completed bridge on 1 August 1817, but in January 1818 it collapsed. One of the designers, Thomas Smith, said of the collapse that due to "high wind increasing to perfect hurricane, it carried off hechain bridge, leaving only the fastenings and supports, the work of half a year, demolished in an hour...." After a redesign, a replacement was built, but this too collapsed in 1838, by which time the Earl had been dead for several years.
The 1818 collapse, together with that of a slightly shorter bridge across the Saale River
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale ( ) and Thuringian Saale (), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale, a right-bank tributary of the Main, or the Saale ...
in Germany in 1824, caused the reputation of cable-stayed bridges to decline rapidly, and despite a history dating back to the 17th century, the design was almost completely abandoned for over a century, with suspended-deck suspension bridges gaining favour. Later research in the 1930s, and experience with reconstruction after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, demonstrated that with sound design, cable-stayed bridges are not without their advantages, and the first modern design, the Strömsund Bridge
The Strömsund Bridge ( Swedish: ''Strömsundsbron'') is a cable-stayed road bridge, bringing road E45 over Ströms vattudal, in Strömsund, Jämtland, Sweden.
The bridge is long, with a main span. Differing from what is stated almost throu ...
in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, was completed in 1955.
Very shortly after the 1818 collapse (between 1819 and 1820) another bridge, the Union Bridge (Tweed), Union Bridge, was built some downstream. It was an iron suspended-deck suspension bridge, the longest in the world upon its completion. A third Dryburgh Suspension Bridge was built in 1872 to replace the 1838 loss.
See also
*Dryburgh Suspension Bridge *List of places in the Scottish BordersReferences
External links
Tweed bridges
*
Entry for the 1818 bridge at Bridgemeister.com
{{coord, 55.580712, -2.654180 , display=title Bridges across the River Tweed Bridges in the Scottish Borders Bridges completed in 1817 Cable-stayed bridges in Scotland 1817 in Scotland 1818 in Scotland Former bridges in the United Kingdom Former buildings and structures in Scotland