|
CCL17
CCL17 is a powerful chemokine produced in the thymus and by antigen-presenting cells like dendritic cells, macrophages, and monocytes. CCL17 plays a complex role in cancer. It attracts T-regulatory cells allowing for some cancers to evade an immune response. However, in other cancers, such as melanoma, an increase in CCL17 is linked to an improved outcome. CCL17 has also been linked to autoimmune and allergic diseases. Classification CCL17 (CC chemokine ligand 17) was initially named TARC (thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine) when first isolated in 1996. It was later renamed CCL17 as the naming conventions for all cytokines were updated to standardize names. Function Cytokines, like CCL17, help cells communicate with one another, and stimulate cell movement. Chemokines are a type of cytokine that attract white blood cells to sites of inflammation or disease. CCL17 as well as its partner chemokine CCL22 induce chemotaxis in T-helper cells. They do this by binding to C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In addition to playing a major role in the activation of host immune responses, chemokines are important for biological processes, including morphogenesis and wound healing, as well as in the pathogenesis of diseases like cancers. Cytokine proteins are classified as chemokines according to behavior and structural characteristics. In addition to being known for mediating chemotaxis, chemokines are all approximately 8–10 kilodaltons in mass and have four cysteine residues in conserved locations that are key to forming their 3-dimensional shape. These proteins have historically been known under several other names including the ''SIS family of cytokines'', ''SIG family of cytokines'', ''SCY family of cytokines'', ''Platelet factor-4 superfamily'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCR4
C-C chemokine receptor type 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCR4'' gene. CCR4 has also been designated CD194 ( cluster of differentiation 194). The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor family. It is a receptor for the following CC chemokines: * CCL2 (MCP-1) * CCL4 (MIP-1) * CCL5 (RANTES) * CCL17 (TARC) * CCL22 (Macrophage-derived chemokine) Chemokines are a group of small structurally related proteins that regulate cell trafficking of various types of leukocytes. The chemokines also play fundamental roles in the development, homeostasis, and function of the immune system, and they have effects on cells of the central nervous system as well as on endothelial cells involved in angiogenesis or angiostasis. CCR4 is a cell-surface protein and should not be confused with the unrelated carbon catabolite repression-negative on TATA-less ( CCR4-Not), a nuclear protein complex that regulates gene expression. Clinical signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL22
C-C motif chemokine 22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCL22'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is secreted by dendritic cells and macrophages, and elicits its effects on its target cells by interacting with cell surface chemokine receptors such as CCR4 C-C chemokine receptor type 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCR4'' gene. CCR4 has also been designated CD194 ( cluster of differentiation 194). The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor family. .... The gene for CCL22 is located in human chromosome 16 in a cluster with other chemokines called CX3CL1 and CCL17. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Cytokines {{gene-16-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
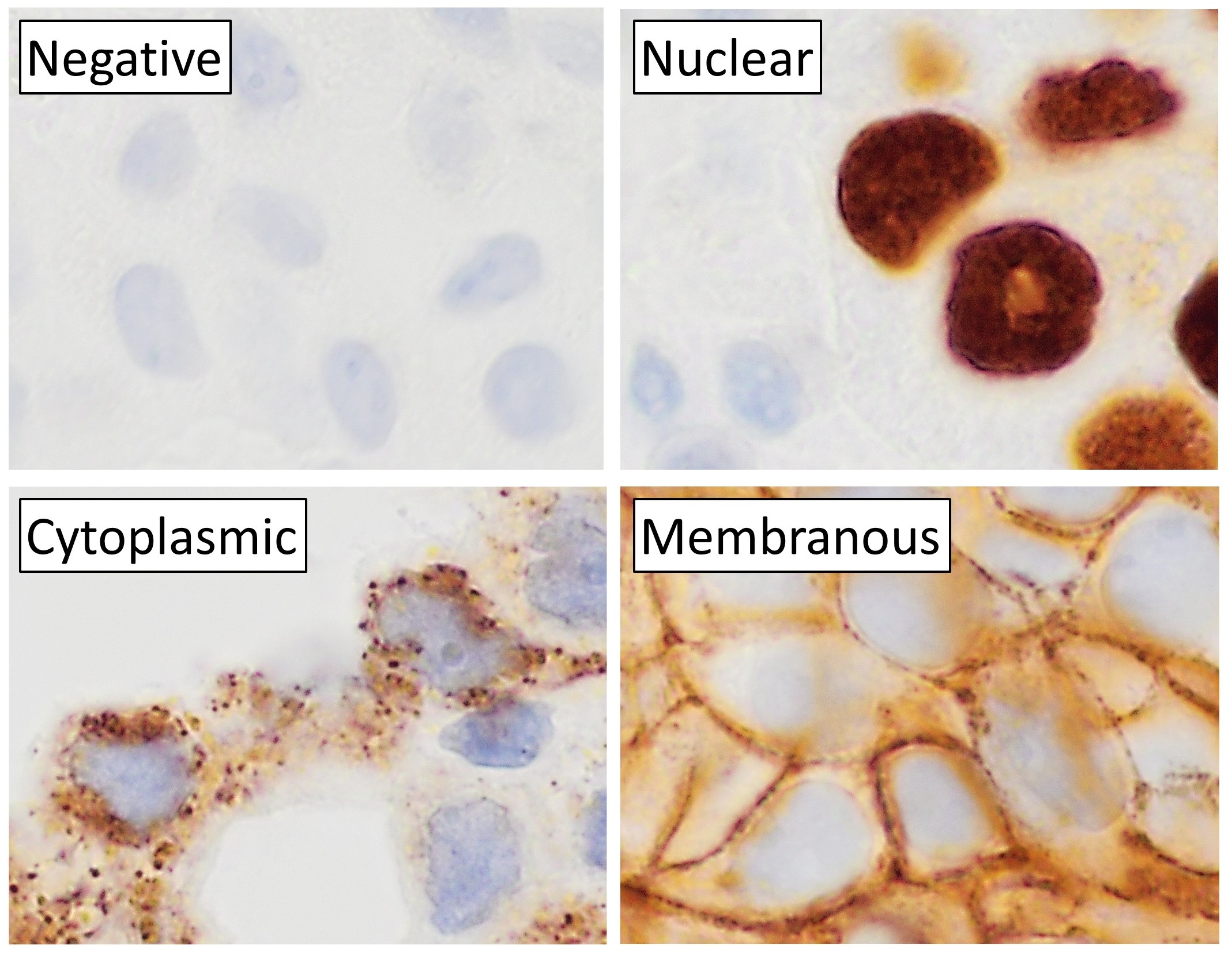
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Coons, Albert Hewett Coons, Ernst Berliner, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in Paraffin wax, paraffin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment is a complex ecosystem surrounding a tumor, composed of cancer cells, stromal tissue (including blood vessels, immune cells, fibroblasts and signaling molecules) and the extracellular matrix. Mutual interaction between cancer cells and the different components of the tumor microenvironment support its growth and invasion in healthy tissues which correlates with tumor resistance to current treatments and poor prognosis. The tumor microenvironment is in constant change because of the tumor's ability to influence the microenvironment by releasing extracellular signals, promoting tumor angiogenesis and inducing peripheral immune tolerance, while the immune cells in the microenvironment can affect the growth and evolution of cancerous cells. History The concept of the tumor microenvironment (TME) dates back to 1863 when Rudolf Virchow established a connection between inflammation and cancer. However, it was not until 1889 that Stephen Paget's seed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies are identical and can thus have monovalent affinity, binding only to a particular epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies are mixtures of antibodies derived from multiple plasma cell lineages which each bind to their particular target epitope. Artificial antibodies known as bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered which include two different antigen binding sites ( FABs) on the same antibody. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to almost any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In certain types of arthritis, other organs such as the skin are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are several types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (most commonly seen in weightbearing joints) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs as an individual ages and often affects the hips, knees, shoulders, and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types of arthritis include gout, lupus, and septic arthritis. These are inflammatory based types of rheumatic disease. Early treatment for arthritis commonly includes resting the affected joint and conservative measures such as heating or icing. Weight Weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affecting 1 in 7 adults in the United States alone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and Joint stiffness, stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Other symptoms may include joint effusion, joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs, the knee and hip joints, and the joints of the neck and lower back. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are affected. Possible causes include previous joint injury, abnormal joint or limb development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear, that is, they have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus (segmented, irregular; often lobed into three segments); and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML, or PMNL). In common terms, ''polymorphonuclear granulocyte'' refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types ( eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells) have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Types There are four types of granulocytes (full name polymorphonuclear granulocytes): * Basophils * Eosinophils * Neutrophils * Mast cells Except for the mast cells, their names are derived from their staining characteristics; for example, the most abundant granulocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukocyte
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. These cells are eosinophilic or "acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, such as eosinophil peroxidase, ribonucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |