|
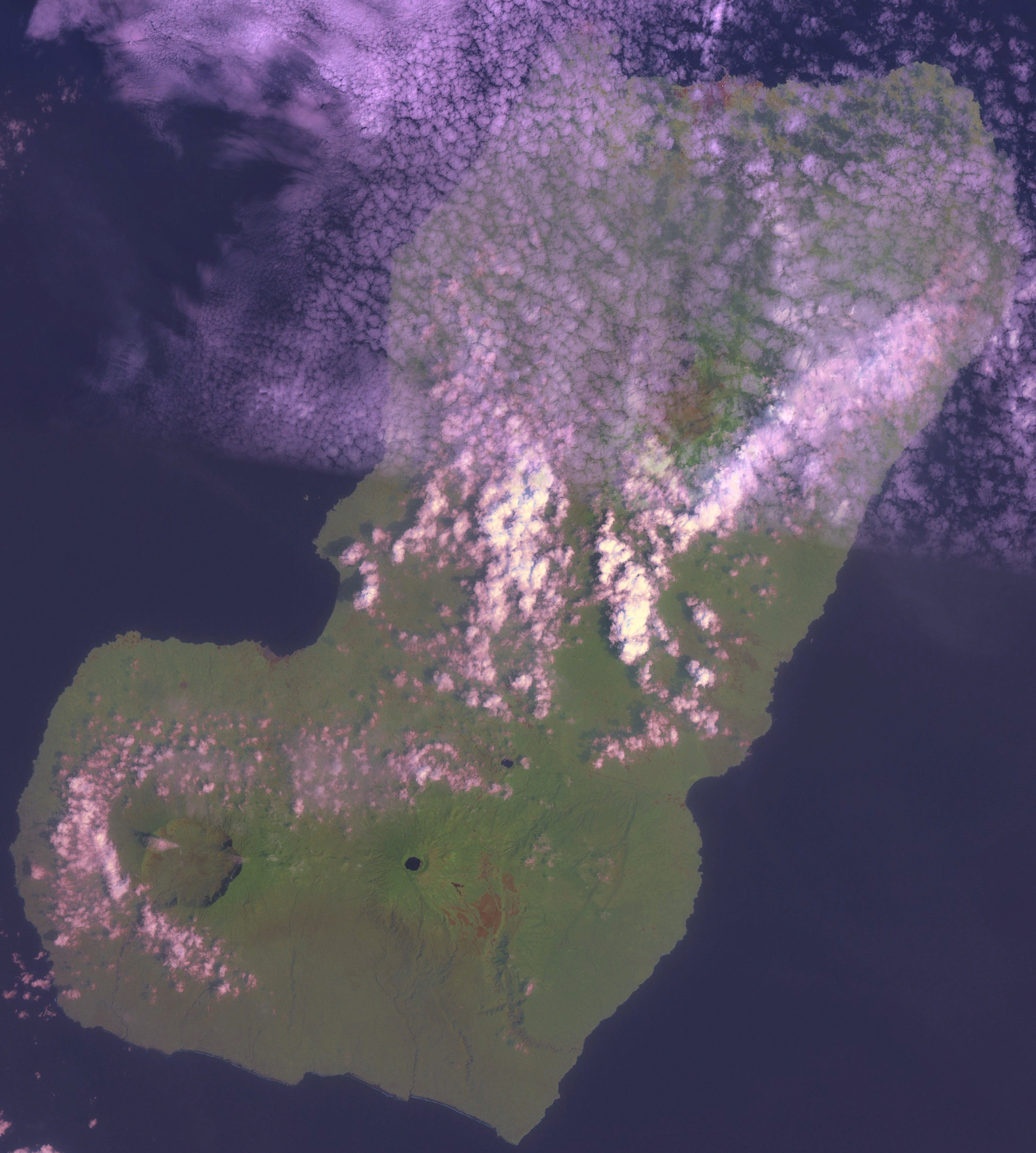
Bioko
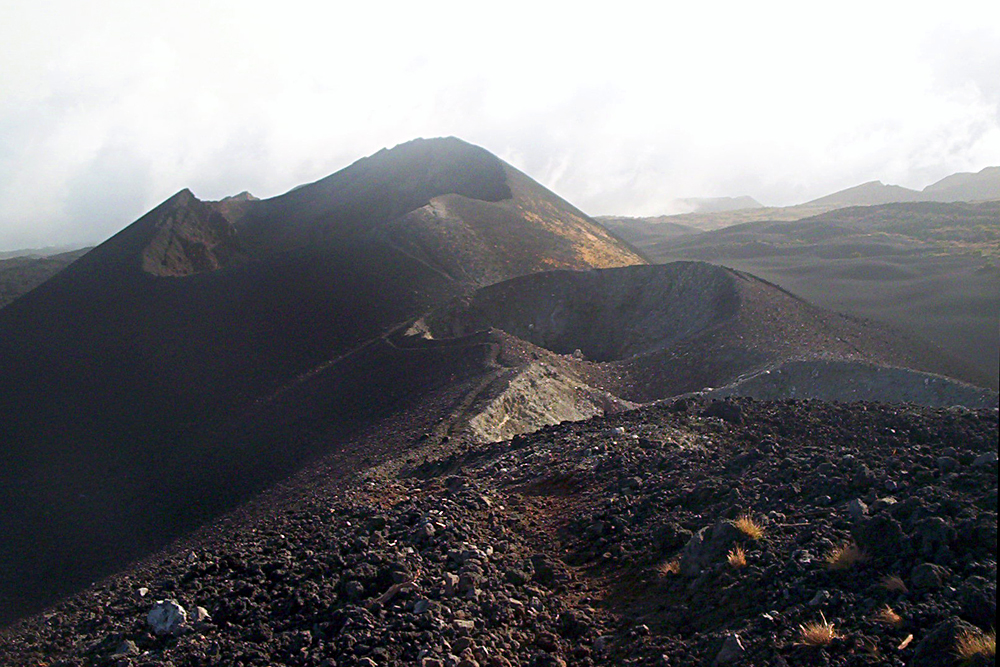
Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó, ) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located south of the coast of Cameroon, and northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Bioko's population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá a Ëri'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Pó'' (; ), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then-president of Equatorial Guinea. The current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equator and in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. , the country had a population of 1,795,834, over 85% of whom are members of the Fang people, the country's dominant ethnic group. The Bubi people, indigenous to Bioko, are the second largest group at approximately 6.5% of the population. Equatorial Guinea consists of two parts. The mainland region, Río Muni, is bordered by Cameroon to the north and Gabon to the south and east. It has the majority of the population and is the location of Bata, Equatorial Guinea, Bata, Equatorial Guinea's largest city, and Ciudad de la Paz, the country's planned future capital. Río Muni's small offshore islands include Corisco, Elobey Grande, and Elobey Chico. The Islands of Equatorial Guinea, ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubi People
The Bubi people (also known as Bobe, Voove, Ewota and Bantu Bubi) are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group of Central Africa who are indigenous to Bioko, Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea. Once the majority group in the region, the population experienced a sharp decline due to war and disease during Portuguese expeditions. By the end of Spanish Guinea, Spanish colonial rule in the mid 20th century, and after substantial intermarriage with newly introduced populations, such as Afro-Cubans, Fernandino peoples, Krio people, Portuguese people and Spaniards, the Bubi people, again, experienced a great decline in number. Seventy-five percent perished due to tribal/clan rooted political genocide during a civil war that led to Spanish Guinea's independence from Spain. This, too, sparked mass exodus from their homeland with most of the exiles and refugees immigrating into Spain. The indigenous Bubi of Bioko Island have since co-existed with non-indigenous Fernandino peoples, Krio Fernandinos; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabo
Malabo ( , ; formerly ) is the capital of Equatorial Guinea in the province of Bioko Norte. It is located on the north coast of the island of Bioko (, and as ''Fernando Pó'' by the Europeans). In 2018, the city had a population of approximately 297,000 inhabitants. Spanish is the official language of the city and of the country as well, but Pichinglis is used as a language of wider communication across Bioko island, including Malabo. Malabo is the oldest city in Equatorial Guinea. Ciudad de la Paz is a planned community under construction in mainland Equatorial Guinea which was designed to replace Malabo as the capital. The institutions of governance of Equatorial Guinea began the process of locating to Ciudad de la Paz in February 2017. History European discovery and Portuguese occupation In 1472, in an attempt to find a new route to India, the Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó, encountered the island of Bioko, which he called ''Formosa''.Roman Adrian Cybriws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon Line
The Cameroon line (, , ) is a long chain of volcanoes that includes islands in the Gulf of Guinea and mountains on the African mainland, from Mount Cameroon on the coast towards Lake Chad on the northeast. They form a natural border between eastern Nigeria and the West Region of Cameroon. The islands, which span the equator, have tropical climates and are home to many unique plant and bird species. The mainland mountain regions are much cooler than the surrounding lowlands, and also contain unique and ecologically important environments. The Cameroon volcanic line is geologically unusual in extending through both the ocean and the continental crust. Various hypotheses have been advanced by different geologists to explain the line. Geography In the Gulf of Guinea, the Cameroon line consists of six offshore volcanic swells that have formed islands or seamounts. From the southwest to the northeast the island groups are Annobón (or Pagalu), São Tomé, Príncipe and Bioko. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristino Seriche Bioko
Cristino Seriche Bioko (15 June 1940 – 11 June 2024) was an Equatoguinean soldier and politician who was the Prime Minister of Equatorial Guinea from 15 August 1982 to 4 March 1992. He previously served as Vice President under Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo for almost one year, from December 1981 to until the position was abolished in October 1982 according to the constitutional referendum, at which point he became president. Biography He was a member of the Bubi people. Like Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo, he attended the General Military Academy in Zaragoza. During the dictatorship of Francisco Macías Nguema he served as governor of Bioko Island, formerly known as Fernando Pó'','' but in 1975 he was removed from the role and imprisoned in the Playa Negra prison. In 1979 he participated alongside Obiang and other soldiers in the coup d'état that overthrew the dictator Francisco Macías Nguema, during whose regime Seriche Bioko was imprisoned in the Playa Negra prison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioko Norte
Bioko Norte () is the second-most populated of the eight provinces of Equatorial Guinea, after the Litoral province. It contained 300,374 of the island's 335,048 inhabitants in 2015, sub-divided into 2 districts - Malabo (271,008) and Baney (27,366). Both the provincial capital, Rebola, and the national capital, Malabo are located here. Heavily forested with little urban development, the southern central part includes part of the Parque Nacional del Pico Basilé, a national park which was established in 2000. Geography Bioko Norte occupies the northern part of the island of Bioko, the remainder of which is in Bioko Sur. In the northern part are Rebola and the national Equatorial Guinean capital, Malabo. The smaller settlement of Santiago de Baney lies in northeastern part of the province. On the northeast coast is the resort of Sipopo, which contains a 200-room hotel run by the Sofitel hotel chain, Sofitel Malabo Sipopo Le Golf. The village of Basupu is situated to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pichinglis
Pichinglis, commonly referred to by its speakers as ''Pichi'' and formally known as Fernando Po Creole English (''Fernandino''), is an Atlantic English-lexicon creole language spoken on the island of Bioko, Equatorial Guinea. It is an offshoot of the Krio language of Sierra Leone, and was brought to Bioko by Krios who immigrated to the island during the colonial era in the 19th century. Pichi is the most widely spoken language of the capital Malabo, next to Spanish, and it serves as a primary language to probably the majority of the capital's inhabitants. Pichi is also used as a primary language in a number of villages and towns along the Coast of Bioko – amongst them Sampaca, Fiston, Basupú, Barrio las Palmas and Luba, and is spoken as a lingua franca throughout Bioko. It is also spoken by a sizable community of people originating from Bioko in Bata, the largest town on the continental part of the country. Size of speaker community Pichi is believed to have derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Region (Equatorial Guinea)
The Insular Region of Equatorial Guinea (, , ) comprises the former Spanish territory of Fernando Po, together with Annobón island, the latter formerly part of the Spanish territory of Elobey, Annobón, and Corisco, which was located in the Gulf of Guinea and in the Corisco Bay. The region covers 2,052 km2 and has a population of 340,362 in 2015. It is split into three political jurisdictions: :*Annobón :* Bioko Norte :* Bioko Sur The islands located in Corisco Bay are not part of the Insular Region but are included in the Litoral Province which is part of the Continental Region ('' Litoral Province''). The largest city, Malabo, is the national and regional administrative capital. The other main cities are Luba, Riaba, Rebola, Baney, and San Antonio de Palé. Bioko was known as "Fernando Po" until the 1970s. It is located about 40 km away from Cameroon and is the largest island of the Gulf of Guinea, covering 2,017 km2. Annobón is a small 17 km2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioko Sur
Bioko Sur ( Spanish for "South Bioko") is a province of Equatorial Guinea. Its capital is Luba. It occupies the southern part of the island of Bioko Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó, ) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located south of the coast of Cameroon, and northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the is ..., the remainder of which is part of Bioko Norte. The province is sub-divided into 2 districts - Luba in the west of the island (with 26,331 inhabitants in 2015) and Riaba in the east (with 8,343 inhabitants in 2015). Part of the Parque Nacional del Pico Basilé, created in 2000, is in Bioko Sur. References Provinces of Equatorial Guinea Bioko {{EquatorialGuinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernandino Peoples
The Fernandino people are creoles, multi-ethnic or multi-racial populations who developed in Equatorial Guinea (Spanish Guinea). Their name is derived from the island of Fernando Pó, where many worked. This island was named for the Portuguese explorer Fernão do Pó, credited with discovering the region. Each population had a distinct ethnic, social, cultural and linguistic history. Members of these communities provided most of the labor that built and expanded the cocoa farming industry on Fernando Pó during the 1880s and 1890s. The Fernandino of Fernando Po were closely related to each other. Because of the history of labor in this area, where workers were recruited, effectively impressed, from Freetown, Cape Coast, and Lagos, the Fernandino also had family ties to those areas. Eventually these ethnically distinct groups intermarried and integrated. In 21st-century Bioko, their differences are considered marginal. Native Fernandinos The indigenous group of ''Fernandin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |