|
Agnatha
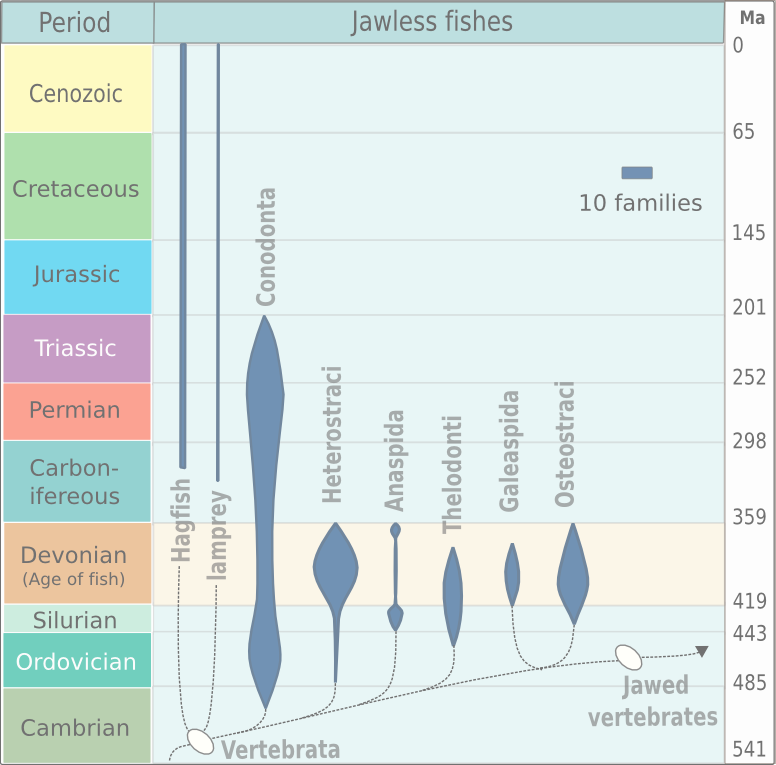
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelodonti
Thelodonti (from Greek: "nipple teeth")Maisey, John G., Craig Chesek, and David Miller. Discovering fossil fishes. New York: Holt, 1996. is a class of extinct Palaeozoic jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor. There is much debate over whether the group represents a monophyletic grouping, or disparate stem groups to the major lines of jawless and jawed fish. Thelodonts are united in possession of " thelodont scales". This defining character is not necessarily a result of shared ancestry, as it may have been evolved independently by different groups. Thus the thelodonts are generally thought to represent a polyphyletic group, although there is no firm agreement on this point. On the basis that they are monophyletic, they are reconstructed as being ancestrally marine and invading freshwater on multiple occasions. "Thelodonts" were morphologically very similar, and probably closely related, to fish of the classes Heterostraci and Anaspida, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeospondylus
''Palaeospondylus'' ("early vertebra") is a prehistoric fish, a fossil vertebrate. Its fossils were originally described from the Achanarras slate quarry in Caithness, Scotland, and a second species has been discovered in Australia. The Scottish fossil as preserved is carbonised, and indicates an eel-shaped animal up to in length. The skull, which must have consisted of hardened cartilage, exhibits pairs of nasal and auditory capsules, with a gill apparatus below its hinder part, and ambiguous indications of ordinary jaws. The phylogeny of this fossil has puzzled scientists since its discovery in 1890, and many taxonomies have been suggested. In 2004, researchers proposed that ''Palaeospondylus'' was a larval lungfish. Previously, it had been classified as a larval tetrapod, unarmored placoderm, an agnathan, an early stem hagfish, and a Chimaera. A 2017 study suggested that it was a stem chondrichthyan. In 2022, researchers reported, based on studies using synchrotron rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin , which may mean "stone licker" ( "to lick" + "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. "Lamprey" is sometimes seen for the plural form. About 38 extant species of lampreys are known, with around seven known extinct species. They are classified in three families—two small families in the Southern Hemisphere (Geotriidae, Mordaciidae) and one large family in the Northern Hemisphere (Petromyzontidae). Genetic evidence suggests that lampreys are more closely related to hagfish, the only other living group of jawless fish, than they are to jawed vertebrates, forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossils of stem-group lampreys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteraspidomorphi
Pteraspidomorpha is an extinct class of early jawless fish. They have long been regarded as closely related or even ancestral to jawed vertebrates, but the few characteristics they share with the latter are now considered as basal traits for all vertebrates. Characteristics Pteraspidomorphs are characterized by their massive dermal head armour having large, median, ventral and dorsal plates or shields. Janvier, Philippe (1997Pteraspidomorphi''The Tree of Life Web Project''. The fossils show extensive shielding of the head. Many had hypocercal tails in order to generate lift to increase ease of movement through the water for their armoured bodies, which were covered in dermal bone. They also had sucking mouth parts and some species may have lived in fresh water. Most pteraspidomorphs were marine, but lived very near to the shore, in lagoons and deltas. Some groups are thought to have been fresh water-dwelling. They were certainly bottom-dwellers, as shown by traces of abrasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
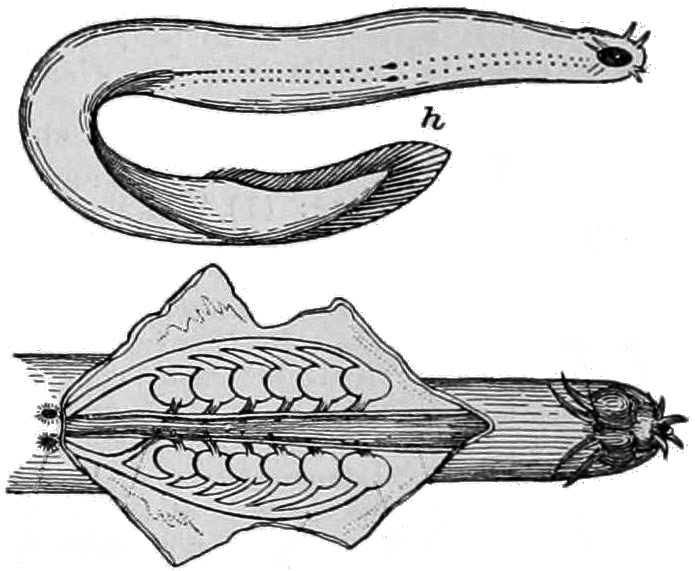
Hagfish
Hagfish, of the Class (biology), class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and Order (biology), order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped Agnatha, jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living Animal, animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although they do have rudimentary vertebrae. Hagfish are marine animal, marine predators and scavengers that can defend themselves against other larger predators by releasing copious amounts of slime coat, slime from mucous glands in their skin. Although their exact relationship to the only other extant taxon, living group of Agnatha, jawless fish, the lampreys, was long the subject of controversy, genetic evidence suggests that hagfish and lampreys are more closely related to each other than to jawed vertebrates, thus forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest-known stem group hagfish are known from the Pennsylvanian (geology), Late Carboniferous, around Moscovian (Carboniferous), 310 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclostomi
Cyclostomi, often referred to as Cyclostomata , from Ancient Greek κύκλος (kúklos), meaning "circle", and στόμα (stóma), meaning "mouth", is a superclass of vertebrates that comprises the living jawless fish classes: the lampreys and hagfishes. Both groups have jawless mouths with horny epidermal structures that function as teeth called ceratodontes, and branchial arches that are internally positioned instead of external as in the related jawed fishes. The superclass was named by Joan Crockford-Beattie. Possible external relationships This taxon is often included in the paraphyletic infraphylum Agnatha, which also includes several groups of extinct armored fishes called ostracoderms. Most fossil agnathans, such as galeaspids, thelodonts, and osteostracans, are more closely related to vertebrates with jaws (called gnathostomes) than to cyclostomes. Biologists historically disagreed on whether cyclostomes are a clade. The "vertebrate hypothesis" h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaspidomorphi
Anaspidomorphi (anaspidomorphs) is an extinct superclass of jawless fish. According to the newer taxonomy based on the work of Nelson, Grande and Wilson 2016 and van der Laan 2018, the phylogeny of Anaspidomorphi looks like this: * Superclass †Anaspidomorphi ** Order †Euphanerida *** Family †Euphaneropidae Woodward, 1900 ** Order †Jamoytiiformes Halstead-Tarlo, 1967 *** Family †Achanarellidae Newman, 2002 *** Family †Jamoytiidae White, 1946 ** Class †Anaspida Janvier, 1996 non Williston, 1917 *** Order †Endeiolepidiformes Berg, 1940 **** Family †Endeiolepididae Stensio, 1939 *** Order †Birkeniiformes Stensiö, 1964 **** Family †Pharyngolepididae Kiær, 1924 **** Family †Pterygolepididae Obručhev, 1964 **** Family †Rhyncholepididae Kiær, 1924 **** Family †Tahulalepididae Blom, Märss & Miller, 2002 **** Family †Lasaniidae Goodrich, 1909 **** Family †Ramsaasalepididae Blom, Märss & Miller, 2003 **** Family †Birkeniidae Traquair, 1899 **** Family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrata
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the cartilaginous fish and the bony fish. Bony fish include the lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. The first amphibians appeared on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteostraci
The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed " ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skeleton with three layers (a basal layer of isopedin, a middle layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic grouping (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of synapomorphies and symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term received currency during the debates of the 1960s and 1970s accompanying the rise of cladistics, having been coined by zoologist Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles), which is paraphyletic with respect to birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles and all descendants of that ancestor exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraphylum
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum. The taxonomic rank of "subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used the rank of subphylum, for instance monocotyledons as a subphylum of phylum Angiospermae and vertebrates as a subphylum of phylum Chordata. Taxonomic rank Subphylum is: #subordinate to the phylum #superordinate to the infraphylum, which is in turn superordinate to parvphylum. Where convenient, subphyla in turn can be divided into infraphyla; in turn such an infraphylum also would be superordinate to any classes or superclasses in the hierarchy. Examples Not all fauna phyla are divided into subphyla. Those that are include: *Arthropoda: divided into subphyla Trilobitomorpha, Chelicerata, Myriapoda, and Pancrustacea *Brachiopoda: divided into subphyla Linguliformea, Craniformea and Rhynchonelliformea *Chordata: divided into Tunicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |