|
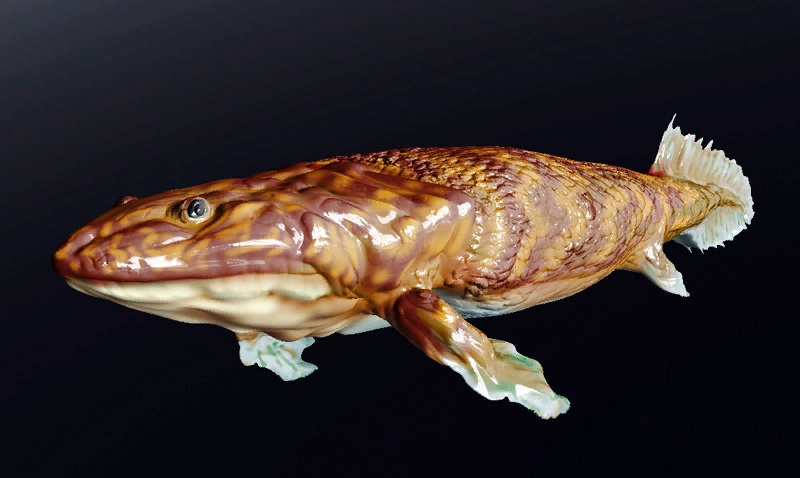
Palaeospondylus
''Palaeospondylus'' ("early vertebra") is a prehistoric fish, a fossil vertebrate. Its fossils were originally described from the Achanarras slate quarry in Caithness, Scotland, and a second species has been discovered in Australia. The Scottish fossil as preserved is carbonised, and indicates an eel-shaped animal up to in length. The skull, which must have consisted of hardened cartilage, exhibits pairs of nasal and auditory capsules, with a gill apparatus below its hinder part, and ambiguous indications of ordinary jaws. The phylogeny of this fossil has puzzled scientists since its discovery in 1890, and many taxonomies have been suggested. In 2004, researchers proposed that ''Palaeospondylus'' was a larval lungfish. Previously, it had been classified as a larval tetrapod, unarmored placoderm, an agnathan, an early stem hagfish, and a Chimaera. A 2017 study suggested that it was a stem chondrichthyan. In 2022, researchers reported, based on studies using synchrotron rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrata
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the cartilaginous fish and the bony fish. Bony fish include the lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. The first amphibians appeared on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
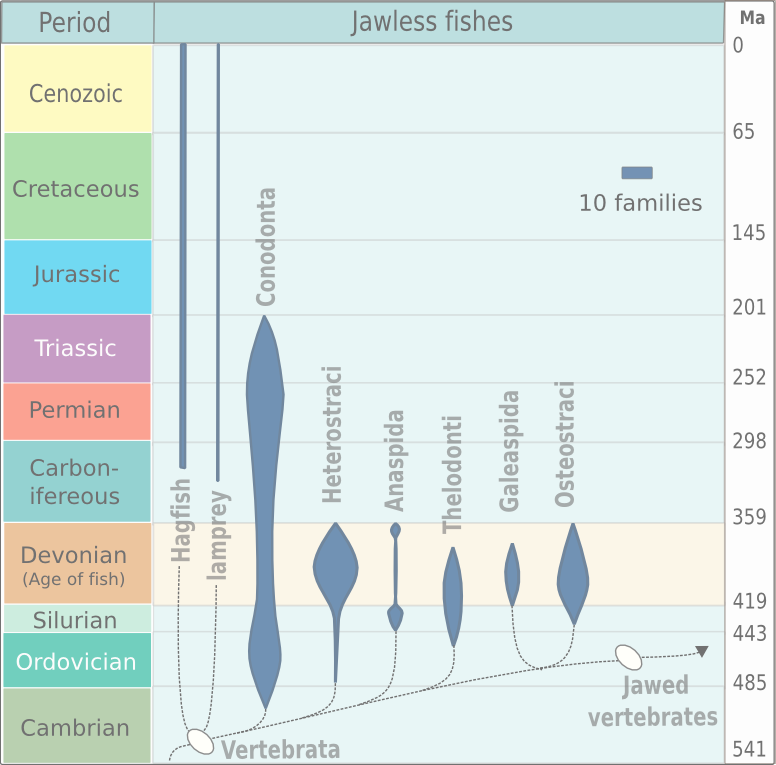
Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cincinnati Museum Center
The Cincinnati Museum Center is a museum complex operating out of the Cincinnati Union Terminal in the Queensgate neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio. It houses museums, theater, a library, and a symphonic pipe organ, as well as special traveling exhibitions. Museums The museum provides a home to five organizations: * Cincinnati History Museum * Museum of Natural History & Science * Robert D. Lindner Family Omnimax Theater * Cincinnati History Library and Archives * Duke Energy Children's Museum Museum of Natural History & Science The Museum of Natural History & Science includes a space called Dinosaur Hall, featuring skeletons and fossils, including skeletons in the Galeamopus, Daspletosaurus, and Torvosaurus genera. The Torvosaurus skeleton, installed in 2018, is the most complete skeleton of the genus, at 55 percent complete, and the only Torvosaurus skeleton publicly exhibited. The natural history museum also includes a reproduction of a limestone cave. The exhibit, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorpha
Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as '' Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodomorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Characteristics Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusthenopteron
''Eusthenopteron'' (from 'stout', and 'wing' or 'fin') is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine lobe-finned fish known from several species that lived during the Late Devonian period, about 385 million years ago. It has attained an iconic status from its close relationship to tetrapods. Early depictions of animals of this genus show them emerging onto land, but paleontologists now think that ''Eusthenopteron'' species were strictly aquatic animals, though this is not completely known.M. Laurin, F. J. Meunier, D. Germain, and M. Lemoine 2007A microanatomical and histological study of the paired fin skeleton of the Devonian sarcopterygian ''Eusthenopteron foordi'' ''Journal of Paleontology'' 81: 143–153. The genus was first described by J. F. Whiteaves in 1881, as part of a large collection of fishes from Miguasha, Quebec, Canada. Some 2,000 ''Eusthenopteron'' specimens have been collected from Miguasha, one of which was the object of intensely detailed study and severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panderichthys
''Panderichthys'' is a genus of extinction, extinct Sarcopterygii, sarcopterygian (lobe-finned fish) from the late Devonian period, about 380 Myr, Mya. ''Panderichthys'', which was recovered from Frasnian (early Late Devonian) deposits in Latvia, is represented by two species. ''P. stolbovi'' is known only from some snout fragments and an incomplete lower jaw. ''P. rhombolepis'' is known from several more complete specimens. Although it probably belongs to a sister group of the earliest tetrapods, ''Panderichthys'' exhibits a range of features transitional between Tristichopteridae, tristichopterid lobe-fin fishes (e.g., ''Eusthenopteron'') and early tetrapods. It is named after the German-Baltic paleontologist Christian Heinrich Pander. Possible tetrapod tracks dating back to before the appearance of ''Panderichthys'' in the fossil record were reported in 2010, which suggests that ''Panderichthys'' is not a direct ancestor of tetrapods, but nonetheless shows the traits that evolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthostega
''Acanthostega'', from Ancient Greek ἄκανθα (''ákantha''), meaning "spine", and στέγη (''stégē''), meaning "roof", is an extinct genus of stem tetrapoda, stem-tetrapod, among the first vertebrates, vertebrate animals to have recognizable Limb (anatomy), limbs. It appeared in the late Devonian period (Famennian age) about 365 million years ago, and was anatomically intermediate between lobe-finned fishes and those that were able to come onto land. Discovery The fossilized remains are generally well preserved, with the famous fossil by which the significance of this species was discovered being found by Jennifer A. Clack in East Greenland in 1987, though fragments of the skull had been discovered in 1933 by Gunnar Säve-Söderbergh and Erik Jarvik. Description The ''Acanthostega'' Polydactyly in stem-tetrapods, had eight digits on each hand (the number of digits on the feet is unclear) linked by webbing. It lacked wrists, and was generally poorly adapted for wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (both ray-finned and lobe-finned, including their terrestrial tetrapod relatives) and cartilaginous fishes, as well as extinct prehistoric fish such as placoderms and acanthodians. Most gnathostomes have retained ancestral traits like true teeth, a stomach, and paired appendages ( pectoral and pelvic fins, limbs, wings, etc.). Other traits are elastin, horizontal semicircular canal of the inner ear, myelinated neurons, and an adaptive immune system which has discrete secondary lymphoid organs (spleen and thymus) and uses V(D)J recombination to create antigen recognition sites, rather than using genetic recombination in the variable lymphocyte receptor gene. It is now assumed that Gnathostomata evolved from ancestors that already possessed two pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |