|
Brujadelphis
''Brujadelphis'' is an extinct genus of river dolphin-like cetaceans of uncertain family placement from the Late Miocene epoch (Serravallian) of present-day Peru. The type species is ''Brujadelphis ankylorostris'', recovered from the Pisco Formation The Pisco Formation is a geologic formation located in Peru, on the southern coastal desert of Ica and Arequipa. The approximately thick formation was deposited in the Pisco Basin, spanning an age from the Middle Miocene up to the Early Pleis ....Lambert et al., 2017 References Bibliography * Miocene cetaceans Miocene mammals of South America Serravallian life Laventan Neogene Peru Fossils of Peru Pisco Formation Fossil taxa described in 2017 {{paleo-whale-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisco Formation
The Pisco Formation is a geologic formation located in Peru, on the southern coastal desert of Ica and Arequipa. The approximately thick formation was deposited in the Pisco Basin, spanning an age from the Middle Miocene up to the Early Pleistocene, roughly from 15 to 2 Ma. The tuffaceous sandstones, diatomaceous siltstones, conglomerates and dolomites were deposited in a lagoonal to near-shore environment, in bays similar to other Pacific South American formations as the Bahía Inglesa and Coquimbo Formations of Chile. Several specialists consider the Pisco Formation one of the most important Lagerstätten,Brand et al., 2004Brand et al., 2011 based on the large amount of exceptionally preserved marine fossils, including sharks (most notably megalodon), penguins, whales, dolphins, birds, marine crocodiles and aquatic giant sloths. Famous fossils found in these layers include the giant raptorial sperm whale ''Livyatan'',Lambert et al., 2010 the aquatic sloth '' Thalassocnu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laventan
The Laventan ( es, Laventense) age is a period of geologic time (13.8 to 11.8 Ma) within the Middle Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Colloncuran and precedes the Mayoan age.Madden et al., 1997 Etymology The age is named after the Miocene Lagerstätte La Venta, where a rich biodiversity from the Middle Miocene has been recovered from the Honda Group. Formations Fossil content Correlations The Laventan (13.8 to 11.8 Ma) correlates with: * NALMA ** latest Barstovian (15.97-13.65 Ma)Barstovian at .org ** early [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
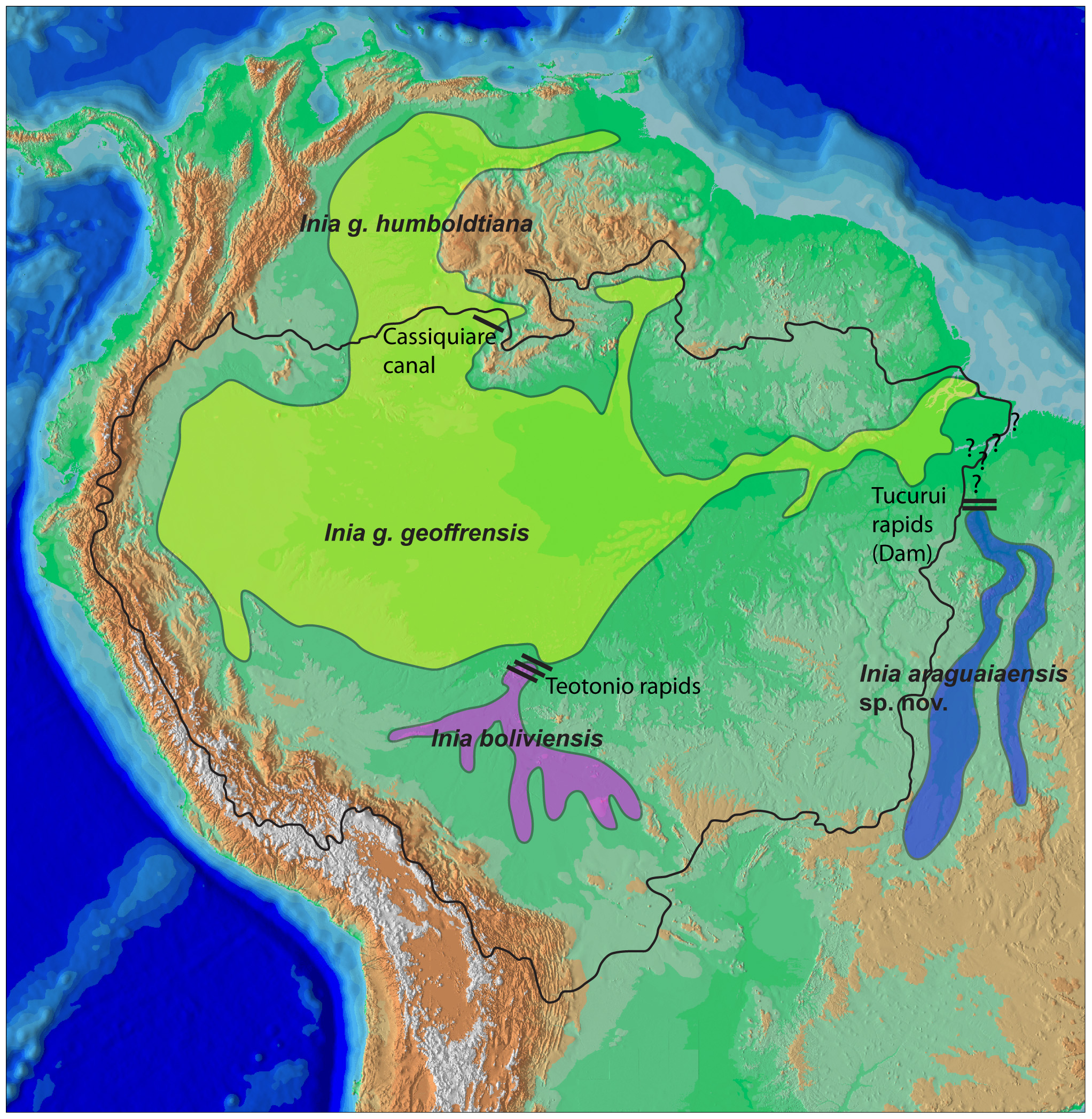
River Dolphin
River dolphins are a polyphyletic group of fully aquatic mammals that reside exclusively in freshwater or brackish water. They are an informal grouping of dolphins, which itself is a paraphyletic group within the infraorder Cetacea. Extant river dolphins are placed in two superfamilies, Platanistoidea and Inioidea. They comprise the families Platanistidae (the South Asian dolphins), the recently extinct Lipotidae (Yangtze river dolphin), Iniidae (the Amazonian dolphins) and Pontoporiidae. There are five extant species of river dolphins. River dolphins, alongside other cetaceans, belong to the clade Artiodactyla, with even-toed ungulates, and their closest living relatives the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. Specific types of Dolphins can be pink. River dolphins are relatively small compared to other dolphins, having evolved to survive in warm, shallow water and strong river currents. They range in size from the long South Asian river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movement of their tail which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to maneuver. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number exclusively reside in brackish water or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species inhabit vast ranges where they migrate with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for their high intelligence and complex social behaviour as well as for the enormous size of some of the group's members, such as the blue whale which reaches a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 feet) and a weight of 173 tonnes (190 short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serravallian
The Serravallian is, in the geologic timescale, an age or a stage in the middle Miocene Epoch/ Series, which spans the time between 13.82 Ma and 11.63 Ma (million years ago). The Serravallian follows the Langhian and is followed by the Tortonian. It overlaps with the middle of the Astaracian European Land Mammal Mega Zone, the upper Barstovian and lower Clarendonian North American Land Mammal Ages and the Laventan and lower Mayoan South American Land Mammal Ages. It is also coeval with the Sarmatian and upper Badenian Stages of the Paratethys time scale of Central and eastern Europe. Definition The Serravallian Stage was introduced in stratigraphy by the Italian geologist Lorenzo Pareto in 1865. It was named after the town of Serravalle Scrivia in northern Italy. The base of the Serravallian is at the first occurrence of fossils of the nanoplankton species '' Sphenolithus heteromorphus'' and is located in the chronozone C5ABr. The official Global Boundary Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Journal Of The Linnean Society
The ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering zoology published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Linnean Society. The editor-in-chief is Maarten Christenhusz (Linnean Society). It was established in 1856 as the ''Journal of the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London. Zoology'' and renamed ''Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Zoology'' in 1866. It obtained its current title in 1969. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 3.286. References External links * Zoology journals Linnean Society of London Monthly journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies Publications established in 1856 {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Cetaceans
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Mammals Of South America
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
_(2).jpg)
