|
Brownian Model Of Financial Markets
The Brownian motion models for financial markets are based on the work of Robert C. Merton and Paul A. Samuelson, as extensions to the one-period market models of Harold Markowitz and William F. Sharpe, and are concerned with defining the concepts of financial assets and markets, portfolios, gains and wealth in terms of continuous-time stochastic processes. Under this model, these assets have continuous prices evolving continuously in time and are driven by Brownian motion processes. This model requires an assumption of perfectly divisible assets and a frictionless market (i.e. that no transaction costs occur either for buying or selling). Another assumption is that asset prices have no jumps, that is there are no surprises in the market. This last assumption is removed in jump diffusion models. Financial market processes Consider a financial market consisting of N + 1 financial assets, where one of these assets, called a '' bond'' or ''money market'', is risk free while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brownian Motion
Brownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas). The traditional mathematical formulation of Brownian motion is that of the Wiener process, which is often called Brownian motion, even in mathematical sources. This motion pattern typically consists of Randomness, random fluctuations in a particle's position inside a fluid sub-domain, followed by a relocation to another sub-domain. Each relocation is followed by more fluctuations within the new closed volume. This pattern describes a fluid at thermal equilibrium, defined by a given temperature. Within such a fluid, there exists no preferential direction of flow (as in transport phenomena). More specifically, the fluid's overall Linear momentum, linear and Angular momentum, angular momenta remain null over time. The Kinetic energy, kinetic energies of the molecular Brownian motions, together with those of molecular rotations and vibrations, sum up to the caloric component of a fluid's in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Space
In probability theory, a probability space or a probability triple (\Omega, \mathcal, P) is a mathematical construct that provides a formal model of a random process or "experiment". For example, one can define a probability space which models the throwing of a . A probability space consists of three elements:Stroock, D. W. (1999). Probability theory: an analytic view. Cambridge University Press. # A '' sample space'', \Omega, which is the set of all possible outcomes of a random process under consideration. # An event space, \mathcal, which is a set of events, where an event is a subset of outcomes in the sample space. # A '' probability function'', P, which assigns, to each event in the event space, a probability, which is a number between 0 and 1 (inclusive). In order to provide a model of probability, these elements must satisfy probability axioms. In the example of the throw of a standard die, # The sample space \Omega is typically the set \ where each element in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almost Surely
In probability theory, an event is said to happen almost surely (sometimes abbreviated as a.s.) if it happens with probability 1 (with respect to the probability measure). In other words, the set of outcomes on which the event does not occur has probability 0, even though the set might not be empty. The concept is analogous to the concept of "almost everywhere" in measure theory. In probability experiments on a finite sample space with a non-zero probability for each outcome, there is no difference between ''almost surely'' and ''surely'' (since having a probability of 1 entails including all the sample points); however, this distinction becomes important when the sample space is an infinite set, because an infinite set can have non-empty subsets of probability 0. Some examples of the use of this concept include the strong and uniform versions of the law of large numbers, the continuity of the paths of Brownian motion, and the infinite monkey theorem. The terms almost certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders, after which the stock exchange decreases the price of the stock by the dividend to remove volatility. The market has no control over the stock price on open on the ex-dividend date, though more often than not it may open higher. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-invested in the business (called retained earnings). The current year profit as well as the retained earnings of previous years are available for distribution; a corporation is usually prohibited from paying a dividend out of its capital. Distribution to shareholders may be in cash (usually by bank transfer) or, if the corporation has a dividend reinvestment plan, the amount can be paid by the issue of further shares or by share repurchase. In some cases, the distribution may be of assets. The dividend received by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbitrage
Arbitrage (, ) is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more marketsstriking a combination of matching deals to capitalize on the difference, the profit being the difference between the market prices at which the unit is traded. Arbitrage has the effect of causing prices of the same or very similar assets in different markets to converge. When used by academics in economics, an arbitrage is a transaction that involves no negative cash flow at any probabilistic or temporal state and a positive cash flow in at least one state; in simple terms, it is the possibility of a risk-free profit after transaction costs. For example, an arbitrage opportunity is present when there is the possibility to instantaneously buy something for a low price and sell it for a higher price. In principle and in academic use, an arbitrage is risk-free; in common use, as in statistical arbitrage, it may refer to ''expected'' profit, though losses may occur, and in practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
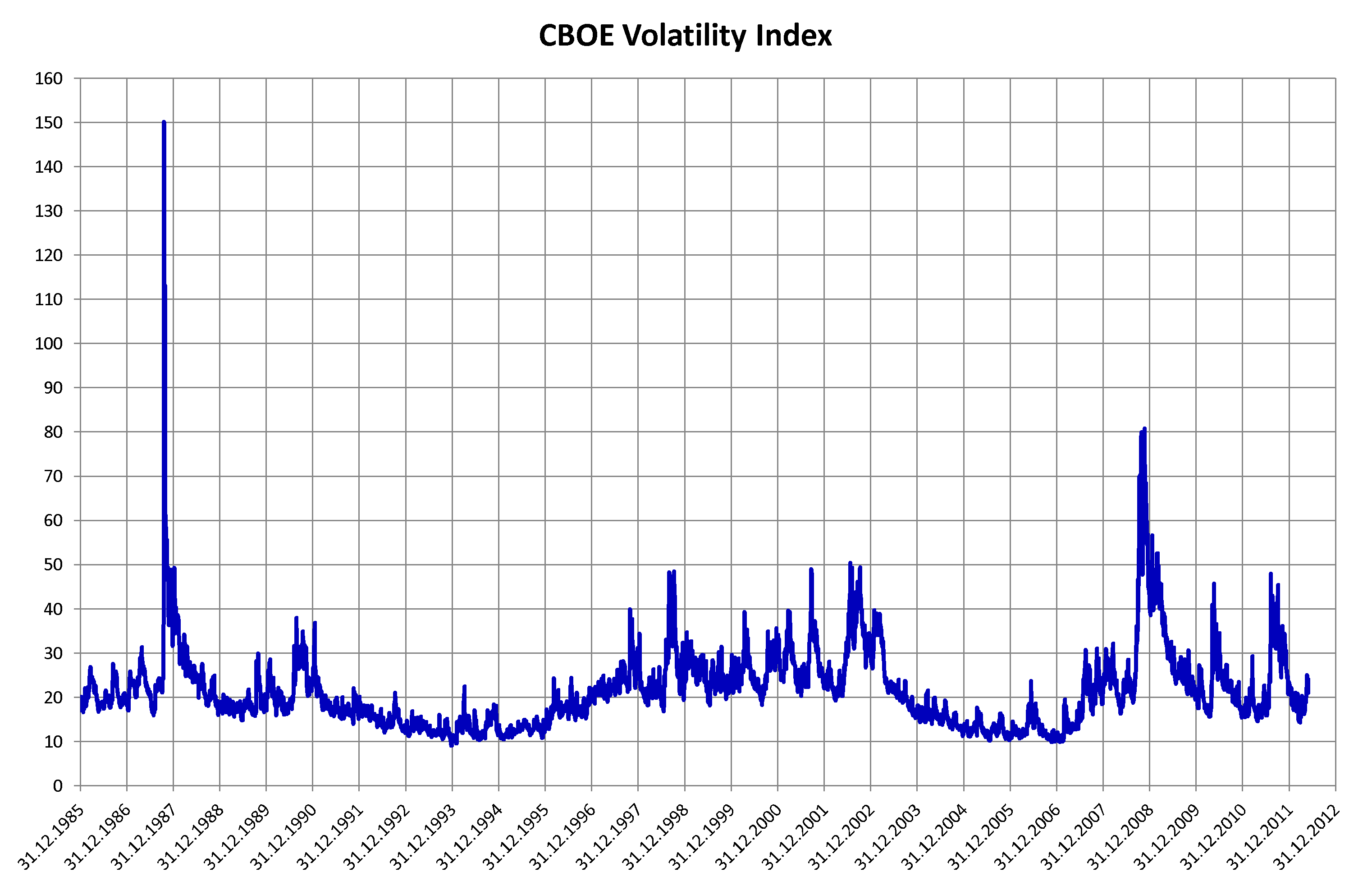
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Differential Equation
A stochastic differential equation (SDE) is a differential equation in which one or more of the terms is a stochastic process, resulting in a solution which is also a stochastic process. SDEs have many applications throughout pure mathematics and are used to model various behaviours of stochastic models such as stock prices,Musiela, M., and Rutkowski, M. (2004), Martingale Methods in Financial Modelling, 2nd Edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin. random growth models or physical systems that are subjected to thermal fluctuations. SDEs have a random differential that is in the most basic case random white noise calculated as the distributional derivative of a Brownian motion or more generally a semimartingale. However, other types of random behaviour are possible, such as jump processes like Lévy processes or semimartingales with jumps. Stochastic differential equations are in general neither differential equations nor random differential equations. Random differential equation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebesgue's Decomposition Theorem
In mathematics, more precisely in measure theory, the Lebesgue decomposition theorem provides a way to decompose a measure into two distinct parts based on their relationship with another measure. Definition The theorem states that if (\Omega,\Sigma) is a measurable space and \mu and \nu are σ-finite signed measures on \Sigma, then there exist two uniquely determined σ-finite signed measures \nu_0 and \nu_1 such that: * \nu=\nu_0+\nu_1\, * \nu_0\ll\mu (that is, \nu_0 is absolutely continuous with respect to \mu) * \nu_1\perp\mu (that is, \nu_1 and \mu are singular). Refinement Lebesgue's decomposition theorem can be refined in a number of ways. First, as the Lebesgue-Radon-Nikodym theorem. That is, let (\Omega,\Sigma) be a measure space, \mu a σ-finite positive measure on \Sigma and \lambda a complex measure on \Sigma. * There is a unique pair of complex measures on \Sigma such that \lambda = \lambda_a + \lambda_s, \quad \lambda_a \ll \mu, \quad \lambda_s \perp \mu. If ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Continuity
In calculus and real analysis, absolute continuity is a smoothness property of functions that is stronger than continuity and uniform continuity. The notion of absolute continuity allows one to obtain generalizations of the relationship between the two central operations of calculus— differentiation and integration. This relationship is commonly characterized (by the fundamental theorem of calculus) in the framework of Riemann integration, but with absolute continuity it may be formulated in terms of Lebesgue integration. For real-valued functions on the real line, two interrelated notions appear: absolute continuity of functions and absolute continuity of measures. These two notions are generalized in different directions. The usual derivative of a function is related to the '' Radon–Nikodym derivative'', or ''density'', of a measure. We have the following chains of inclusions for functions over a compact subset of the real line: : ''absolutely continuous'' ⊆ '' unifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounded Variation
In mathematical analysis, a function of bounded variation, also known as ' function, is a real number, real-valued function (mathematics), function whose total variation is bounded (finite): the graph of a function having this property is well behaved in a precise sense. For a continuous function of a single Variable (mathematics), variable, being of bounded variation means that the distance along the Direction (geometry, geography), direction of the y-axis, -axis, neglecting the contribution of motion along x-axis, -axis, traveled by a point (mathematics), point moving along the graph has a finite value. For a continuous function of several variables, the meaning of the definition is the same, except for the fact that the continuous path to be considered cannot be the whole graph of the given function (which is a Glossary of differential geometry and topology#H, hypersurface in this case), but can be every Intersection (set theory), intersection of the graph itself with a hyperplan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a small variation of the argument induces a small variation of the value of the function. This implies there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are the most general continuous functions, and their d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented Filtration
In the theory of stochastic processes, a subdiscipline of probability theory, filtrations are totally ordered collections of subsets that are used to model the information that is available at a given point and therefore play an important role in the formalization of random (stochastic) processes. Definition Let (\Omega, \mathcal A, P) be a probability space and let I be an index set with a total order \leq (often \N , \R^+ , or a subset of \mathbb R^+ ). For every i \in I let \mathcal F_i be a sub-''σ''-algebra of \mathcal A . Then : \mathbb F:= (\mathcal F_i)_ is called a filtration, if \mathcal F_k \subseteq \mathcal F_\ell for all k \leq \ell . So filtrations are families of ''σ''-algebras that are ordered non-decreasingly. If \mathbb F is a filtration, then (\Omega, \mathcal A, \mathbb F, P) is called a filtered probability space. Example Let (X_n)_ be a stochastic process on the probability space (\Omega, \mathcal A, P) . Let \sigma(X_k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |