|
Brachydeiroidea
Brachydeiroidea is a superfamily of small to moderately large-sized arthrodire placoderms from the Late Devonian of Europe and Eastern North America. Brachydeiroids have, in cross section, a highly compressed body, a pointed, sometimes highly elongated snout, and tremendous orbits. The plates of the trunk shield are noticeably shortened: in ''Synauchenia'', the trunk shield and head shield are fused together as a single, immovable unit. The superficial anatomy of brachydeiroids is extremely diverse. Families Brachydeiridae A diverse family of variable forms, restricted to the middle to late Frasnian The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and followed by the Famennian Stage. Major reef-building was under way during th ... of Europe. Leptosteidae This family is represented by two species in the genus '' Leptosteus''. Leptosteids differ from brachy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synauchenia
''Synauchenia coalescens'' is a trout-sized, highly compressed arthrodire placoderm restricted to the Late Frasnian-aged Kellwasserkalk Fauna of Bad Wildungen. ''S. coalescens'' is unique among arthrodires in that the head shield and the trunk shield are fused or "firmly sutured" together in an immobile, helmet-like unit. The neck gap is absent, and the articulations between the cranium and thorax are lost in the evolution of this peculiar feature. The skull of the holotype is 10 cm long. ''S. coalescens'' was originally placed in its own family, but, it was later determined to be closely related to '' Oxyosteus'' and ''Brachydeirus'', and accordingly placed within Brachydeiridae Brachydeiridae is a family of small to moderately large-sized arthrodire placoderms from the Late Devonian of Europe, restricted primarily to the Kellwasserkalk Fauna of Bad Wildungen and Adorf. Brachydeirids have, in cross section, a highly c .... See also * List of placoderms Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachydeiridae
Brachydeiridae is a family of small to moderately large-sized arthrodire placoderms from the Late Devonian of Europe, restricted primarily to the Kellwasserkalk Fauna of Bad Wildungen and Adorf. Brachydeirids have, in cross section, a highly compressed body, a pointed, sometimes highly elongated snout, and tremendous orbits. The plates of the trunk shield are noticeably shortened: in '' Synauchenia'', the trunk shield and head shield are fused together as a single, immovable unit. The superficial anatomy of brachydeirids is extremely diverse, and each genus has been previously placed in their own monogeneric families. The brachydeirids, together with '' Leptosteus'', make up the superfamily Brachydeiroidea. Genera ''Brachydeirus'' The half a dozen species of ''Brachydeirus'' are comparable (on a superficial level) in form and size to trout or small mackerels. The biting surfaces of the infragnathals are smooth and thick, suggesting an adaptation for crushing. Species of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frasnian
The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and followed by the Famennian Stage. Major reef-building was under way during the Frasnian Stage, particularly in western Canada and Australia. On land, the first forests were taking shape. In North America, the Antler orogeny peaked, which were contemporary with the Bretonic phase of the Variscan orogeny in Europe Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti .... The Frasnian coincides with the second half of the "charcoal gap" in the fossil record, a time when atmospheric oxygen levels were below 13 percent, the minimum necessary to sustain wildfires. North American subdivisions of the Frasnian include * Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachydeirus
''Brachydeirus'' is a genus of small to moderately large-sized arthrodire placoderms from the Late Devonian of Europe, restricted to the Kellwasserkalk Fauna of Bad Wildungen and Adorf. Species have, in cross section, a highly compressed body, a pointed, sometimes highly elongated snout, and tremendous orbits. The living animals would have superficially resembled modern-day trout or small mackerel Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment. ...s. As per the family, the trunk shield is short. The genus is distinguished from other members of the family in that the median dorsal plate of the trunk shield is often keeled, with the keel often very high and prominent. Species ''Brachydeirus carinatus'' The type species. The length of the skull of the holotype is 11.7 cm. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics. A given rank subsumes under it less general categories, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any ''species'' and the description of its ''genus'' is ''basic''; which means that to identify a particular organism, it is usually not necessary to specify ranks other than these first two. Consider a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
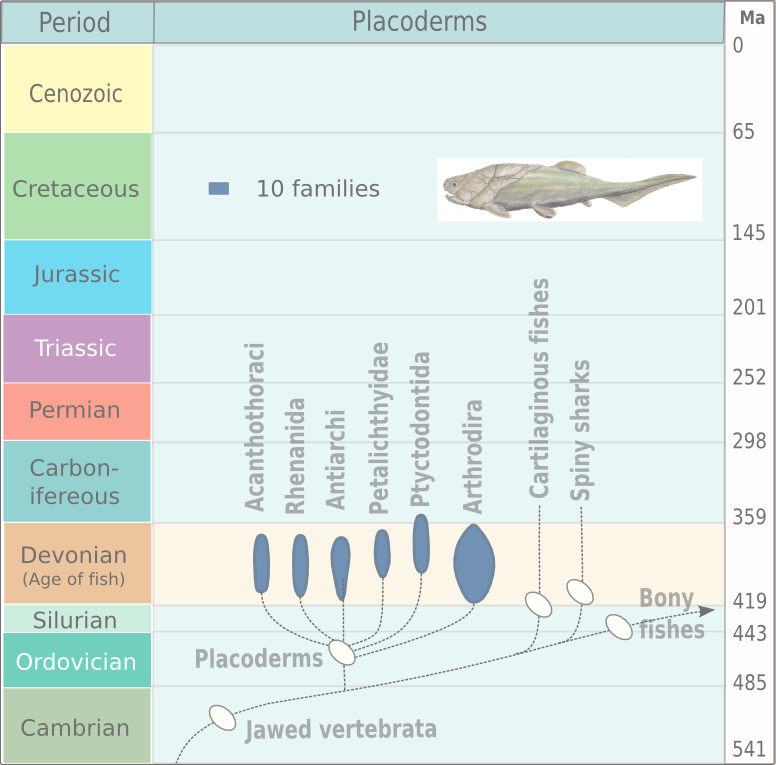
Arthrodire
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, '' Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Rolfosteus'' measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two important f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Placoderms
This list of placoderms is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be members of the class Placodermi. This list excludes purely vernacular terms. It includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered placoderms. The modern descendants of placoderms, the bony and cartilaginous fishes, and their extinct descendants, the Acanthodii (without cartilaginous fishes), are not included here. This list includes 334 generic names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |