|
Boron Hydride Cluster
Boron hydride clusters are compounds with the formula or related anions, where x ≥ 3. Many such cluster compounds are known. Common examples are those with 5, 10, and 12 boron atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the borane hydride clusters exhibit structures and bonding that differs strongly from the patterns seen in hydrocarbons. Hybrids of boranes and hydrocarbons, the carboranes are also well developed. History The development of the borane hydride clusters resulted from pioneering work by Alfred Stock, invented the glass vacuum line for their study. The structures of the boron hydride clusters were determined beginning in 1948 with the characterization of decaborane. William Lipscomb was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1976 for this and many subsequent crystallographic investigations. These investigations revealed the prevalence of deltahedral structures, i.e., networks of triangular arrays of BH centers. The bonding of the clusters ushered in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decaborane(14)-from-xtal-view-1-tilt-3D-bs-17
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula B10 H14. It is classified as a borane and more specifically a boron hydride cluster. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydride clusters, both as a reference structure and as a precursor to other boron hydrides. It is toxic and volatile, giving off a foul odor, like that of burnt rubber or chocolate. Handling, properties and structure The physical characteristics of decaborane(14) resemble those of naphthalene and anthracene, all three of which are volatile colorless solids. Sublimation is the common method of purification. Decaborane is highly flammable, and burns with a bright green flame like other boron hydrides. It is not sensitive to moist air, although it hydrolyzes in boiling water, releasing hydrogen and giving a solution of boric acid. It is soluble in cold water as well as a variety of non-polar and moderately polar solvents. In decaborane, the B10 f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systematic Nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). IUPAC Nomenclature ensures that each compound (and its various isomers) have only one formally accepted name known as the systematic IUPAC name. However, some compounds may have alternative names that are also accepted, known as the preferred IUPAC name which is generally taken from the common name of that compound. Preferably, the name should also represent the structure or chemistry of a compound. For example, the main constituent of white vinegar is , which is commonly called acetic acid and is also its recommended IUPAC name, but its formal, systematic IUPAC name is ethanoic acid. The IUPAC's rules for naming organic and inorganic compounds are contained in two publications, known as the '' Blue Book''. . and the '' Red Book'',. respecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule by forming a valence chemical bond, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
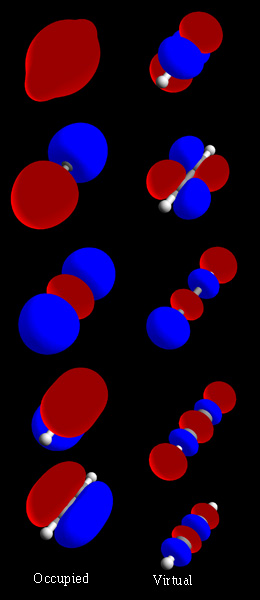
Three-center Two-electron Bond
A three-center two-electron (3c–2e) bond is an electron-deficient chemical bond where three atoms share two electrons. The combination of three atomic orbitals form three molecular orbitals: one bonding, one ''non''-bonding, and one ''anti''-bonding. The two electrons go into the bonding orbital, resulting in a net bonding effect and constituting a chemical bond among all three atoms. In many common bonds of this type, the bonding orbital is shifted towards two of the three atoms instead of being spread equally among all three. Example molecules with 3c–2e bonds are the trihydrogen cation () and diborane (). In these two structures, the three atoms in each 3c–2e bond form an angular geometry, leading to a bent bond. Boranes and carboranes An extended version of the 3c–2e bond model features heavily in cluster compounds described by the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory, such as boranes and carboranes. These molecules derive their stability from having a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Lipscomb
William Nunn Lipscomb Jr. (December 9, 1919April 14, 2011) was a Nobel Prize-winning People of the United States, American Inorganic chemistry, inorganic and Organic chemistry, organic chemist working in nuclear magnetic resonance, theoretical chemistry, boron, boron chemistry, and biochemistry. Biography Overview Lipscomb was born in Cleveland, Ohio, to a physician father and housewife mother. Both his grandfather and great-grandfather had been physicians. His family moved to Lexington, Kentucky in 1920, and he lived there until he received his Bachelor of Science academic degree, degree in chemistry at the University of Kentucky in 1941. He went on to earn his Doctor of Philosophy degree in chemistry from the California Institute of Technology, California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in 1946. From 1946 to 1959 he taught at the University of Minnesota. From 1959 to 1990 he was a professor of chemistry at Harvard University, where he was a professor emeritus since 1990. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− ( hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecaborate
The dodecaborate(12) anion, 12H12sup>2−, is a borane with an icosahedral arrangement of 12 boron atoms, with each boron atom being attached to a hydrogen atom. Its symmetry is classified by the molecular point group Ih. Synthesis and reactions The existence of the dodecaborate(12) anion, 12H12sup>2−, was predicted by H. C. Longuet-Higgins and M. de V. Roberts in 1955. Hawthorne and Pitochelli first made it 5 years later, by the reaction of 2-iododecaborane with triethylamine in benzene solution at 80 °C. It is more conveniently prepared in two steps from sodium borohydride. First the borohydride is converted into a triborate anion using the etherate of boron trifluoride: : 5 NaBH4 + BF3 → 2 NaB3H8 + 3 NaF + 2 H2 Pyrolysis of the triborate gives the twelve-boron cluster as the sodium salt. A variety of other synthetic methods have been published. Salts of the dodecaborate ion are stable in air and do not react with hot aqueous sodium hydroxide or hydrochlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
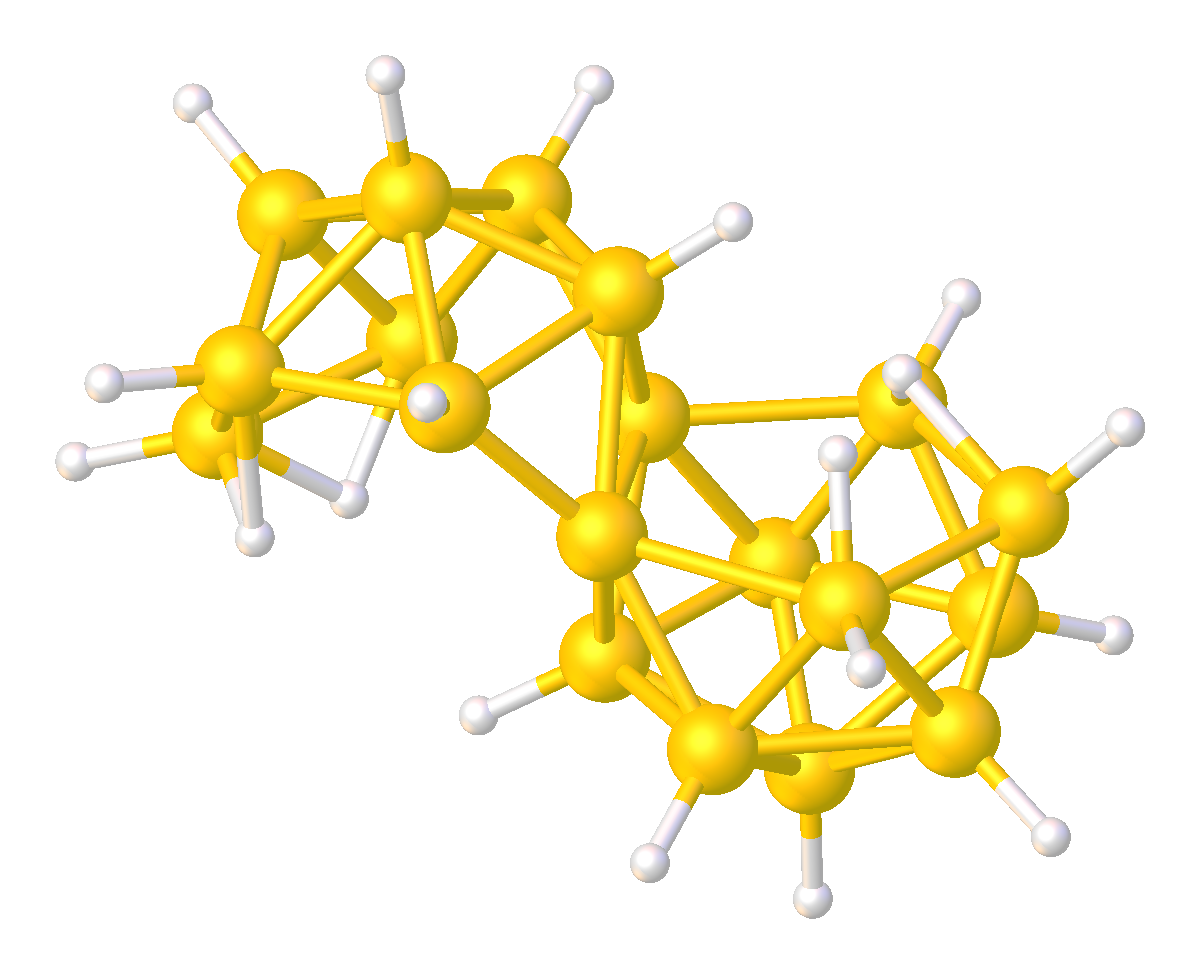
Octadecaborane
Octadecaborane is an inorganic compound, a boron hydride cluster with chemical formula B18H22. It is a colorless flammable solid, like many higher boron hydrides. Although the compound has no practical applications, its structure is of theoretical and pedagogical interest. Synthesis It is formed by oxidative degradation of B20H182− or by oxidative coupling of B9H12−. Structure Two isomers are known of octadecaborane, providing the first example of isomers in a boron-hydride cluster. The clusters are also of interest because the boron centers shared between the two subunits have an unusually high number of B-B interactions. The isomers consists of two B9H11 polyhedral subunits, each having a decaborane-like form, joined at a B–B edge. These two boron atoms are each coordinated to six others; this compound was the first one found to have such a high number of borons coordinated around a single boron center. There are two different geometric isomers of this compound, differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decaborane
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula B10 H14. It is classified as a borane and more specifically a boron hydride cluster. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydride clusters, both as a reference structure and as a precursor to other boron hydrides. It is toxic and volatile, giving off a foul odor, like that of burnt rubber or chocolate. Handling, properties and structure The physical characteristics of decaborane(14) resemble those of naphthalene and anthracene, all three of which are volatile colorless solids. Sublimation is the common method of purification. Decaborane is highly flammable, and burns with a bright green flame like other boron hydrides. It is not sensitive to moist air, although it hydrolyzes in boiling water, releasing hydrogen and giving a solution of boric acid. It is soluble in cold water as well as a variety of non-polar and moderately polar solvents. In decaborane, the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentaborane(9)
Pentaborane(9) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the most common boron hydride clusters, although it is a highly reactive compound. Because of its high reactivity with oxygen, it was once evaluated as rocket or jet fuel. Like many of the smaller boron hydrides, pentaborane is colourless, diamagnetic, and volatile. It is related to pentaborane(11) (). Structure, synthesis, properties Its structure is that of five atoms of boron arranged in a square pyramid. Each boron has a terminal hydride ligand and four hydrides span the edges of the base of the pyramid. It is classified as a nido cage. It was first prepared by Alfred Stock by pyrolysis of diborane at about 200 °C. An improved synthesis starts from salts of octahydrotriborate (), which is converted to the bromide using HBr. Pyrolysis of this bromide gives pentaborane. : In the U.S., pentaborane was produced on a commercial scale by Callery Chemical Company. Above 150 °C, it decomposes, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |