|
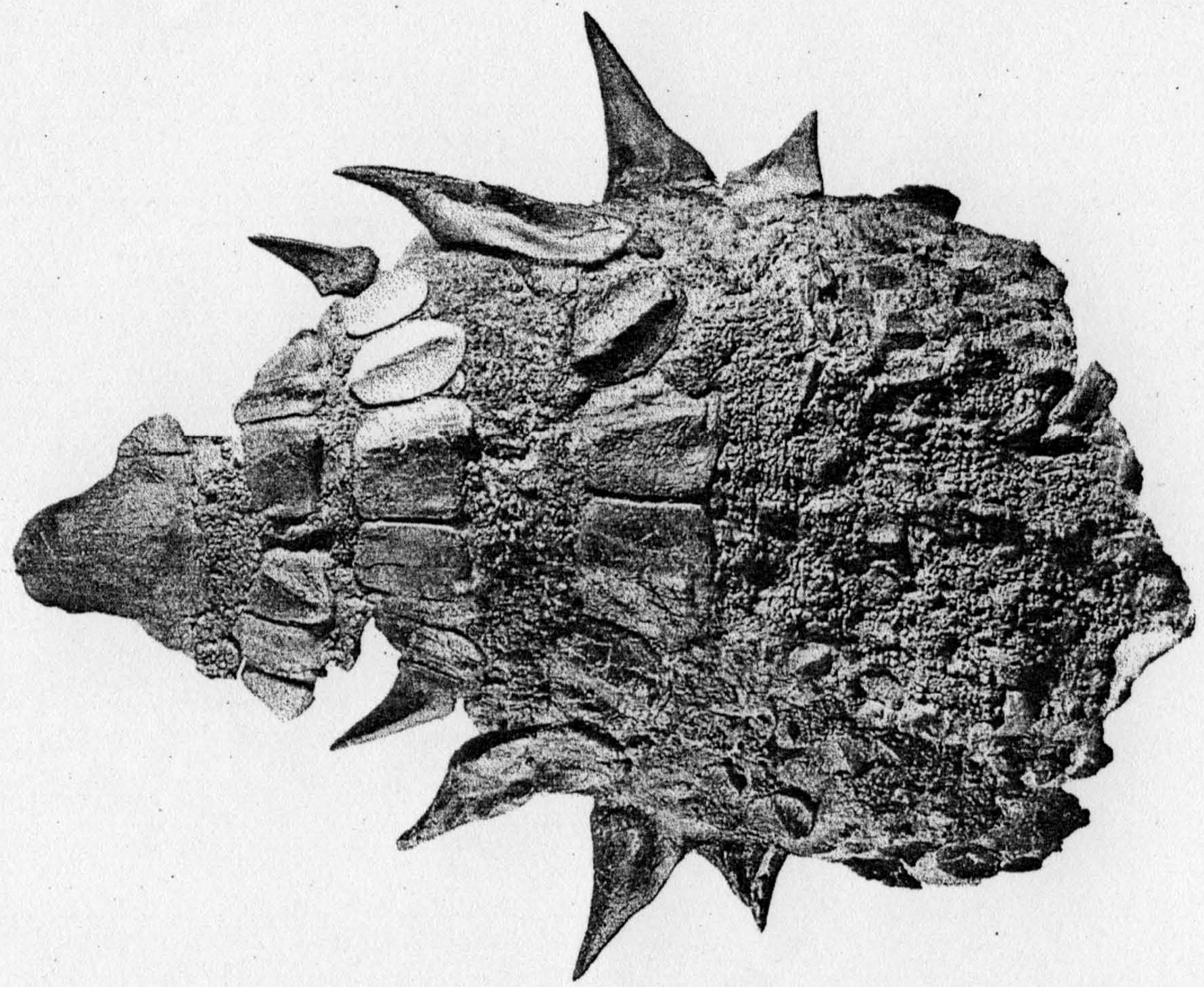
Bonapartenykus Ultimus
''Bonapartenykus'' (meaning "José F. Bonaparte's claw") is a monospecific genus of alvarezsauroid dinosaur from Argentina that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Campanian-Maastrichtian) in what is now the upper Allen Formation of the Río Negro Province. The type and only species, ''Bonapartenykus ultimus'', is known from a nearly articulated but partial skeleton that was found in close association to two incomplete eggs and several clusters of eggshells belonging to the oogenus ''Arriagadoolithus''. ''Bonapartenykus'' was named in 2012 by Federico L. Agnolin, Jaime E. Powell, Fernando E. Novas and Martin Kundrát. ''Bonapartenykus'' has an estimated length of and weight of , making it the largest member of the clade Alvarezsauroidea. Discovery and Naming A partial skeleton of a theropod with eggs was collected in a surface of approximately 30 m2 in fluvial sandstones of the upper Allen Formation in northwestern Patagonia, Argentina. The locality has also produced specimens o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unenlagiidae
Unenlagiidae is a proposed family of eumaniraptoran paravians that includes the subfamilies Unenlagiinae and possibly Halszkaraptorinae. Fossils of both subfamilies have been found in both Gondwanan and Laurasian deposits. The biology of the group suggests that some members were semiaquatic specialists. Classification The family Unenlagiidae traditionally includes the same members as the previously named subfamily of Dromaeosauridae, Unenlagiinae, so Unenlagiidae was often seen as a synonym of Dromaeosauridae. However, since the 2010s, there have been subsequent studies that have questioned this placement, necessitating the revival of the family name. Some have placed unenlagiids as outside Dromaeosauridae, being the sister taxon or closely related to Avialae, while others have placed the newly recognized halszkaraptorines in the family, as basal deinonychosaurs outside Dromaeosauridae and Troodontidae Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanurae
Tetanurae (/ˌtɛtəˈnjuːriː/ or "stiff tails") is a clade that includes most Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs, including Megalosauroidea, megalosauroids, Allosauroidea, allosauroids, Tyrannosauroidea, tyrannosauroids, Ornithomimosauria, ornithomimosaurs, Compsognathidae, compsognathids and maniraptorans (including birds). Tetanurans are defined as all theropods more closely related to modern birds than to ''Ceratosaurus'' and contain the majority of predatory dinosaur diversity. Tetanurae likely diverged from its sister group, Ceratosauria, during the late Triassic. Tetanurae first appeared in the fossil record by the Early Jurassic about 190 mya and by the Middle Jurassic had become globally distributed. The group was named by Jacques Gauthier in 1986 and originally had two main subgroups: Carnosauria and Coelurosauria, the clade containing birds and related dinosaurs such as compsognathids, tyrannosaurids, ornithomimosaurs, and maniraptorans. The original Carnosauria was a pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelisauridae
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are found on the modern continents of Africa and South America, as well as on the Indian subcontinent and the island of Madagascar. Isolated teeth were found in the Late Jurassic of Portugal, and the Late Cretaceous genera ''Tarascosaurus'' and '' Arcovenator'' have been described in France. Abelisaurids first appear in the fossil record of the early middle Jurassic period, and at least two genera (the Moroccan '' Chenanisaurus'' and the Madagascan '' Majungasaurus'') survived until the end of the Mesozoic era 66 million years ago. Like most theropods, abelisaurids were carnivorous bipeds. They were characterized by stocky hind limbs and extensive ornamentation of the skull bones, with grooves and pits. In many abelisaurids, such as '' Carnotauru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their body), and four thick, pillar-like legs. They are notable for the enormous sizes attained by some species, and the group includes the largest animals to have ever lived on land. Well-known genera include '' Brachiosaurus'', '' Diplodocus'', ''Apatosaurus'' and '' Brontosaurus''. The oldest known unequivocal sauropod dinosaurs are known from the Early Jurassic. '' Isanosaurus'' and '' Antetonitrus'' were originally described as Triassic sauropods, but their age, and in the case of ''Antetonitrus'' also its sauropod status, were subsequently questioned. Sauropod-like sauropodomorph tracks from the Fleming Fjord Formation (Greenland) might, however, indicate the occurrence of the group in the Late Triassic. By the Late Jurassic (150 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanosauria
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thriving at the time of the extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous. This group includes some of the largest land animals known to have ever existed, such as ''Patagotitan''—estimated at long with a weight of —and the comparably-sized ''Argentinosaurus'' and ''Puertasaurus'' from the same region. The group's name alludes to the mythological Titans of ancient Greek mythology, via the type genus (now considered a ''nomen dubium)'' '' Titanosaurus''. Together with the brachiosaurids and relatives, titanosaurs make up the larger sauropod clade Titanosauriformes. Titanosaurs have long been a poorly-known group, and the relationships between titanosaur species are still not well-understood. Description Titanosauria have the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Cretaceous Period. The two main families of Ankylosaurs, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae are primarily known from the Northern Hemisphere, but the more basal Parankylosauria are known from southern Gondwana during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group Thyreophora, which also includes the stegosaurs, armored dinosaurs known for their combination of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauridae
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as '' Edmontosaurus'' and '' Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |