|
Bolivartherium
''Bolivartherium'' is an extinct genus of mylodontine mylodontid sloth that lived during the Late Miocene and Late Pliocene in what is now Venezuela. Fossils have been found in the Codore and Urumaco Formations of Venezuela. Etymology The generic name, ''Bolivartherium'', is named in honour of Libertador Simón Bolívar, a Venezuelan military and political leader. The specific name is derived from the Urumaco Formation in which it was found in. A second species, ''B. codorensis'', was named in 2006 after the Codore Formation in which it was found in. Description ''Bolivartherium'' is a medium-sized mylodontine that was smaller than the quaternary species of '' Lestodon''. It can be distinguished from the latter in having a lower rostrum and the upper caniform which is more curved than in ''Lestodon'', much like ''Lestodon'' sp. from the Monte Hermoso Formation (Montehermosan) of Argentina. The diastema in front of the molariforms is elevated with respect to the occlusal pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoprepotherium
''Pseudoprepotherium'' is an extinct genus of sloths of the family Mylodontidae. It was widespread across northern South America during the Early to Late Miocene epoch around 21 to 5.3 million years ago. Fossils of the animal have been found in Brazil, Venezuela, and Peru. ''Pseudoprepotherium'' lived in a tropical climate with a water-rich environment. Their known remains are limited to limb bones, except for a few skulls and teeth. Based on these remains, they were most likely medium to large-sized mylodontid. The genus was described in 1961 and currently contains three species, which were originally assigned to the genus '' Prepotherium''. Description ''Pseudoprepotherium'' is a medium to a large-sized member of the family Mylodontidae. The material documented so far consists mainly of limb bones but includes individual skulls and remains of jaws. Body weight of around 550 kg is reconstructed for the smaller relatives using a thigh bone around 42 cm long. Large molds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urumaco Formation
The Urumaco Formation is a formation in Venezuela that includes deposits from the Late Miocene. It is the site of several "giant forms": the turtles, crocodiles, sloths and rodents of Urumaco are among the largest of their groups. Location The Urumaco formation is located in the Urumaco region in the Caribbean coastal Falcón state. The deposits date from 10 to 5.3 million years ago and the Urumaco formation was deposited in an area with large rivers, swamps, estuaries, lagoons and shallow coastal seas. These conditions in the Late Miocene contrast strongly with the current dry environment in the area today. Fauna Cartilaginous fish There are 21 known species of cartilaginous fishes from the Urumaco Formation, belonging to the orders Lamniformes, Carcharhiniformes, Myliobatiformes and Rajiformes. '' Carcharhinus caquetius'' is an endemic species of predator shark from Urumaco. A large number of well-preserved fossils of the sawfish '' Pristis rostra'' have been found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
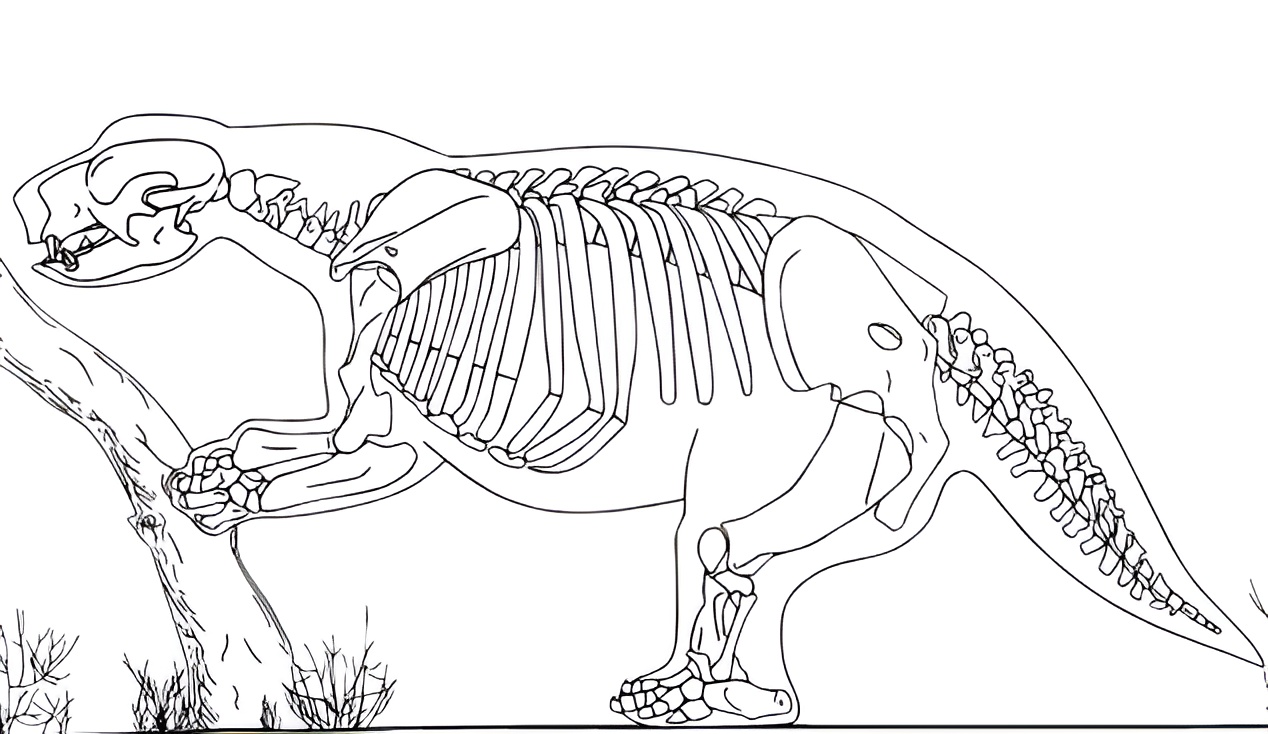
Lestodon
''Lestodon'' is an extinct genus of giant ground sloth native to South America during the Pleistocene epoch. Its fossil remains have primarily been found in the Pampas and adjacent regions. The largest member of the family Mylodontidae, It is estimated to have weighed . It was a herbivore and primarily fed on the grasses and low-growing plants. Research history and taxonomy The genus ''Lestodon'' and the species ''Lestodon armatus'' was erected by Paul Gervais in 1855, based on a fragments of the upper and lower jaws with teeth found in Late Pleistocene deposits what is currently Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. The genus name, which means "thief tooth", is in reference to the large caniniform teeth at the front of the jaw. In 1934, a second species ''L. australis'' was erected by Lucas Kraglievich, but this is now regarded as a junior synonym of ''L. armatus''. In 2004, two additional species ''L. urumaquensis'' and ''L. codorensis'' were described based on fossils found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylodontinae
Mylodontinae is an extinct subfamily of ground sloths that lived from the Early Miocene to the Early Holocene epochs. Classification The classification of the Mylodontidae is complex and often under discussion. The most widely accepted subfamilies are the Mylodontinae with ''Mylodon'' as the type genus and the Lestodontinae, whose type genus is ''Lestodon'', which sometimes also includes ''Paramylodon'' and ''Glossotherium ''Glossotherium'' is an extinct genus of large mylodontid ground sloths of the subfamily Mylodontinae. It represents one of the best-known members of the family, along with ''Mylodon'' and '' Paramylodon''. Reconstructed animals were between ...'' (sometimes also listed as belonging to the tribes Mylodontini and Lestodontini. The subdivision of the terminal group of mylodonts into the Lestodontinae and Mylodontinae found confirmation in one of the most comprehensive studies of the phylogeny of sloths based on cranial features in 2004, which subsequentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lestobradys
''Lestobradys'' is an extinct genus of ground sloth (family Mylodontidae), which existed in Uruguay during the Late Miocene period; Huayquerian in the South American land mammal age (SALMA). The type species is ''L. sprechmanni'', found in the Camacho Formation of Uruguay.''Lestobradys'' at .org Etymology The genus name, ''Lestobradys'', is derived from ''lesto'', meaning "robber", which refers to the genus' morphological similarities to the Plio-Pleistocene '' Lestodon,'' while "''bradys''" means "slow" due to its common use in ground sloths. The specific name is after Uruguayan ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analcitherium
''Analcitherium'' is an extinct genus of scelidotheriid sloth that lived during the Early Miocene in what is now Argentina. Fossils have been found in the Santa Cruz Formation of Argentina. Taxonomy '' Analcitherium'' was first named by Florentino Ameghino in 1891 based on fossils found in Argentina, dating to the Early Miocene. Originally thought to belong to a juvenile ''Nematherium'', it is now usually considered to be a distinct genus. ''Analcitherium'' is a member of the Scelidotheriidae, a group of terrestrial sloths known from the Oligocene and Pleistocene that a characterized by an elongated snout. Although scelidotheriids are usually placed as a subfamily of the Mylodontidae, they are sometimes considered to be a separate family, Scelidotheriidae Scelidotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths within the order Pilosa, suborder Folivora and superfamily Mylodontoidea, related to the other extinct mylodontoid family, Mylodontidae, as well as to the living two-to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proscelidodon
''Proscelidodon'' is an extinct genus of ground sloths in the family Scelidotheriidae. It lived during the Miocene and Pliocene of what is now Argentina and Bolivia Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w .... The genus was described in 1935. Taxonomy During the Quaternary the taxonomic diversification of the Scelidotheriidae took place, with four species belonging to the genera ''Scelidodon'', ''Catonyx'', and ''Scelidotherium''; the pre-quaternary Scelidotheriidae are rare. The discovery of an almost complete maxilla of ''Proscelidodon'' from the Maimará Formation (late Miocene), Jujuy province, provides new data on the plesiomorphic condition of the clade, the biogeographical history of the group during the Mio–Pliocene, and on the Maimará faunal assemblage. In addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonematherium
''Neonematherium'' is an extinct genus of scelidotheriid ground sloths that lived in Argentina, Chile, and Colombia during the Early to Late Miocene. Fossils have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, and the Río Frías Formation of Chile. Taxonomy ''Neonematherium'' is a member of the Scelidotheriidae, a family of ground sloths known from the Oligocene, Miocene Pliocene, Pleistocene, and the Early Holocene epochs and are characterized by an elongated snout. Scelidotheres themselves part are usually placed as a subfamily of the Mylodontidae, although they are sometimes considered a separate family, Scelidotheriidae. Below is a phylogenetic tree of the Scelidotheriidae Scelidotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths within the order Pilosa, suborder Folivora and superfamily Mylodontoidea, related to the other extinct mylodontoid family, Mylodontidae, as well as to the living two-toed sloth family Choloepo ..., based on the work of Nieto ''et al''. 2021, showing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million years ago) to 5.333 Ma. The evolution of ''Homo'' The gibbons (family Hylobatidae) and orangutans (genus ''Pongo'') were the first groups to split from the line leading to the hominins, including humans, then gorillas (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally chimpanzees and bonobos (genus ''Pan (genus), Pan''). The splitting date between hominin and chimpanzee lineages is placed by some between 4 and 8 million years ago, that is, during the Late Miocene. References External links GeoWhen Database - Late Miocene Miocene, .03 Miocene geochronology, 03 Messinian, * Tortonian, * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catonyx
''Catonyx'' is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Scelidotheriidae, endemic to South America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs. It lived from 2.5 Ma to about 10,000 years ago, existing for approximately . The most recent date obtained is about 9600 B.P. Description This animal, like many other terrestrial sloths, was of conspicuous size and mighty build. It had to reach and exceed 4 meters in length, and the skull alone was at least 50 centimeters long. Its weight has been estimated at over 1500 kg. The snout of ''Catonyx'' was elongated, although not as in some similar forms (e.g., '' Scelidotherium''). Unlike the latter, ''Catonyx'' possessed shorter premaxillae that formed a triangular (and not rectangular like '' Scelidotherium'') snout tip, a pronounced rostrum bulge, a palate equipped with a median groove, and larger teeth. In addition, the mandibular symphysis was elongated and elevated, and the posterior lobe of the lower fourth molar was more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scelidotherium
''Scelidotherium'' is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Scelidotheriidae, endemic to South America during the Late Pleistocene epoch. It lived from 780,000 to 11,000 years ago, existing for approximately . Description It is characterized by an elongated, superficially anteater-like head. In fossil distribution, it is known from Argentina ( Luján and Arroyo Seco Formations), Bolivia ( Tarija Formation), Peru ( San Sebastián Formation), Panama, Brazil, Paraguay and Ecuador. In his journal of '' The Voyage of the Beagle'', Charles Darwin reports the finding of a nearly perfect fossil ''Scelidotherium'' in Punta Alta while travelling overland from Bahía Blanca to Buenos Aires in 1832. He allied it to the ''Megatherium ''Megatherium'' ( ; from Greek () 'great' + () 'beast') is an extinct genus of ground sloths endemic to South America that lived from the Early Pliocene through the end of the Late Pleistocene. It is best known for the elephant-sized type spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |