|
Blackthorn
''Prunus spinosa'', called blackthorn or sloe, is an Old World species of flowering plant in the rose family, Rosaceae. It is locally naturalized in parts of the New World. The fruits are used to make sloe gin in Britain and patxaran in Basque Country. The wood is used to make walking sticks, including the Irish shillelagh. Description ''Prunus spinosa'' is a large deciduous shrub or small tree growing to tall, with blackish bark and dense, stiff, spiny branches. The leaves are oval, long and broad, with a serrated margin. The flowers are about in diameter, with five creamy-white petals; they are produced shortly before the leaves in early spring, and are hermaphroditic, and insect-pollinated. The fruit, called a "sloe", is a drupe in diameter, black with a purple-blue waxy bloom, ripening in autumn and traditionally harvested – at least in the UK – in October or November, after the first frosts. Sloes are thin-fleshed, with a very strongly astringent flavour when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shillelagh (club)
A shillelagh ( ; or , "thonged willow") is a wooden walking stick and Club (weapon), club or cudgel, typically made from a stout knotty Prunus spinosa, blackthorn stick with a large knob at the top. It is associated with Ireland and Irish mythology, Irish folklore. Other spelling variants include shillelah, shillalah, and shillaly. Etymology The name shillelagh is the Hiberno-English Language change, corruption of the Irish (Gaelic) form , where means "willow" or "cudgel" and is Genitive case, genitive for meaning "thong", "strap", "leash", and "string", among others. As an alternate etymology, Anna Maria Hall and Patrick Weston Joyce have written that the name may have been derived from the wood being sourced from forest land in the village or Barony (Ireland), barony of Shillelagh (barony), Shillelagh, County Wicklow. The geographic name Shillelagh derives from , or "Descendants of Éalach" in English. Construction Shillelaghs are traditionally made from blacktho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
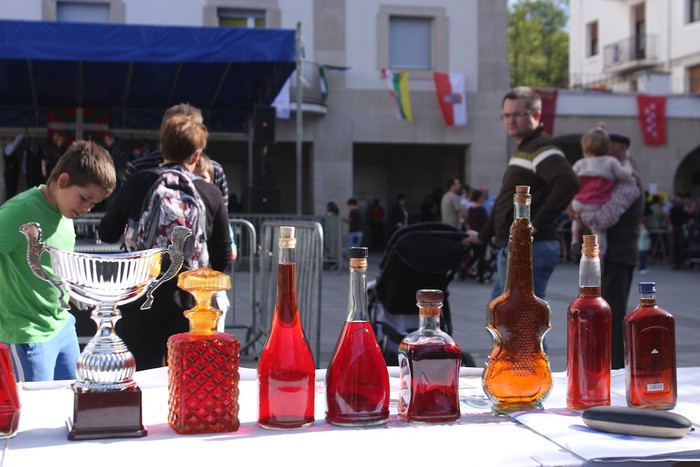
Sloe Gin
Sloe gin is a British red liqueur made with gin and Prunus spinosa, blackthorn fruits (sloes), which are the drupe fruit of the ''Prunus spinosa'' tree, which is a relative of the plum. As an alcoholic drink, sloe gin contains between 15 per cent and 30 per cent alcohol by volume (ABV); however, European Union regulations established 25 per cent ABV as the minimal alcoholic content for the blackthorn beverage to be a ''sloe gin''. Historically, despite being a liqueur based upon gin, the EU included the colloquial name ''sloe gin'' to the legal definitions; thus, sloe gin is the only alcoholic beverage that legally uses the term ''gin'' without appending the ''liqueur'' suffix. The traditional method of preparation of sloe gin is to soak the blackthorns (sloes) in gin with some sugar, and the mixture sweetens when the blackthorn fruit mature in the alcohol. Commercial sloe gin is made by flavouring an inexpensive neutral grain spirit. US distilleries use close fruits related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astringent
An astringent (sometimes called adstringent) is a chemical that shrinks or constricts body tissues. The word derives from the Latin '' adstringere'', which means "to bind fast". Astringency, the dry, puckering or numbing mouthfeel caused by the tannins in unripe fruits, lets the fruit mature by deterring eating. Tannins, being a kind of polyphenol, bind salivary proteins and make them precipitate and aggregate, producing a rough, "sandpapery", or dry sensation in the mouth. Smoking tobacco is also reported to have an astringent effect. In a scientific study, astringency was still detectable by subjects who had local anesthesia applied to their taste nerves, but not when both these and the trigeminal nerves were disabled. Uses In medicine, astringents cause constriction or contraction of mucous membranes and exposed tissues and are often used internally to reduce discharge of blood serum and mucous secretions. This can happen with a sore throat, hemorrhages, diarrhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husband And Wife Tree
Inosculation is a natural phenomenon in which trunks, branches or roots of two trees grow together in a manner biologically similar to the artificial process of grafting. The term is derived from the Latin roots ''in'' + ''wiktionary:osculor, ōsculārī'', "to kiss into/inward/against" or etymologically and more illustratively "to make a small mouth inward/into/against"; trees having undergone the process are referred to in forestry as gemels, from the Latin word meaning "a pair". It is most common for branches of two trees of the same species to grow together, though inosculation may be noted across related species. The branches first grow separately in proximity to each other until they touch. At this point, the bark on the touching surfaces is gradually abraded away as the trees move in the wind. Once the Vascular cambium, cambium of two trees touches, they sometimes self-graft and grow together as they expand in diameter. Inosculation customarily results when tree limbs ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grafted
Grafting or graftage is a horticultural technique whereby tissues of plants are joined so as to continue their growth together. The upper part of the combined plant is called the scion () while the lower part is called the rootstock. The success of this joining requires that the vascular tissues grow together. The natural equivalent of this process is inosculation. The technique is most commonly used in asexual propagation of commercially grown plants for the horticultural and agricultural trades. The scion is typically joined to the rootstock at the soil line; however, top work grafting may occur far above this line, leaving an understock consisting of the lower part of the trunk and the root system. In most cases, the stock or rootstock is selected for its roots and the scion is selected for its stems, leaves, flowers, or fruits. The scion contains the desired genes to be duplicated in future production by the grafted plant. In stem grafting, a common grafting method, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patxaran
Patxaran (; ) is a sloe-flavoured liqueur commonly drunk in Navarre, as well as in the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country. It is usually served as a digestif either chilled or on ice. Etymology The word ''patxaran'' is the Upper Navarrese dialect, Upper Navarrese form of ''basaran'', from Basque ''basa'' 'wild' and ''aran'' 'sloe'. It also occurs in the various Basque dialects as ''baxaran'', ''basarhan'', ''baixaran'' and various other forms. Process Patxaran is made by soaking sloe fruits, collected from the Prunus spinosa, blackthorn shrub, along with a few coffee beans and a cinnamon stick in anisette, for one to eight months. The process produces a light sweet reddish-brown liquid around 25-30% in alcohol content by volume. In addition to dictating the amount of sloes to be used, the regulating body for Pacharán Navarro insists that no artificial colourings or flavourings be added and that the Maceration (wine), maceration last between one and eight months. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walking Stick
A walking stick (also known as a walking cane, cane, walking staff, or staff) is a device used primarily to aid walking, provide postural stability or support, or assist in maintaining a good posture. Some designs also serve as a fashion accessory, or are used for self-defense. Walking sticks come in many shapes and sizes and some have become collector's items. People with disabilities may use some kinds of walking sticks as a crutch, but a walking cane is not designed for full weight support but used to help with balance. The walking stick has also historically been known to be used as a self-defense weapon, and may conceal a sword or knife. Hikers use walking sticks, also known as trekking poles, pilgrim's staffs, hiking poles, or hiking sticks, for a wide variety of purposes: as a support when going uphill or as a brake when going downhill; as a balance point when crossing streams, swamps, or other rough terrain; to feel for obstacles in the path; to test mud and wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prunus Cerasifera
__NOTOC__ ''Prunus cerasifera'' is a species of plum known by the common names cherry plum and myrobalan plum.UConn Horticulture Native to Eurasia and naturalized elsewhere, ''P. cerasifera'' is believed to be one of the parents of the cultivated plum. Description Wild types are large s or small s reaching tall, sometimes spiny, with glabrous, ovate leaves ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Matter
The dry matter or dry weight is a measure of the mass of a completely dried substance. Analysis of food The dry matter of plant and animal material consists of all its constituents excluding water. The dry matter of food includes carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants (e.g., thiocyanate, anthocyanin, and quercetin). Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which provide the energy in foods (measured in kilocalories or kilojoules), make up ninety percent of the dry weight of a diet. Water composition Water content in foods varies widely. A large number of foods are more than half water by weight, including boiled oatmeal (84.5%), cooked macaroni (78.4%), boiled eggs (73.2%), boiled rice (72.5%), white meat chicken (70.3%) and sirloin steak (61.9%). Fruits and vegetables are 70 to 95% water. Most meats are on average about 70% water. Breads are approximately 36% water. Some foods have a water content of less than 5%, e.g., peanut butter, cracker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids are broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued Precursor (chemistry), precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its Volatility (chemistry), volatile nature. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water (molecule), water, represented as HCN(aqueous, aq), is called ''hydrocyanic acid''. The Salt (chemistry), salts of the cyanide anion are known as cyanides. Whether hydrogen cyanide is an organic compound or not is a topic of debate among chemists, and opinions vary from author to author. Traditionally, it is considered ino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |