|
Bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) Dichloride
Bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium chloride is a coordination compound of palladium containing two triphenylphosphine and two chloride ligands. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in some organic solvents. It is used for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, e.g. the Sonogashira–Hagihara reaction. The complex is Square planar molecular geometry, square planar. Many analogous complexes are known with different phosphine ligands. Preparation and reactions This compound may be prepared by treating palladium(II) chloride with triphenylphosphine: :PdCl2 + 2 PPh3 → PdCl2(PPh3)2 Upon reduction with hydrazine in the presence of excess triphenylphosphine, the complex is a precursor to tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium, Pd(PPh3)4: :2 PdCl2(PPh3)2 + 4 PPh3 + 5 N2H4 → 2 Pd(PPh3)4 + N2 + 4 N2H5+Cl− Structure Several crystal structures containing PdCl2(PPh3)2 have been reported. In all of the structures, PdCl2(PPh3)2 adopts a Square planar molecular geometry, square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChemSpider
ChemSpider is a freely accessible online chemical database, database of chemicals owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It contains information on more than 100 million molecules from over 270 data sources, each of them receiving a unique identifier called ChemSpider Identifier. Sources The database sources include: Professional databases * EPA DSSTox * Food and Drug Administration (United States), U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) * Human Metabolome Database * Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry * KEGG * KUMGM * LeadScope * LIPID MAPS, LipidMAPS * Marinlit * MDPI * MICAD * MLSMR * MMDB * MOLI * MTDP * Nanogen * Nature Chemical Biology * NCGC * NIAID * National Institutes of Health (NIH) * NINDS Approved Drug Screening Program * NIST * NIST Chemistry WebBook * NMMLSC * NMRShiftDB * PANACHE * PCMD * PDSP * Peptides (journal), Peptides * Prous Science Drugs of the Future * QSAR * R&D Chemicals * San Diego Center for Chemical Genomics * SGCOxCompounds, SGCStoCompounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium Compounds
Palladium forms a variety of ionic, coordination, and organopalladium compounds, typically with oxidation state Pd0 or Pd2+. Palladium(III) compounds have also been reported. Palladium compounds are frequently used as catalysts in cross-coupling reactions such as the Sonogashira coupling and Suzuki reaction. Ionic compounds Most ionic compounds of palladium involve the Pd2+ oxidation state. Palladium(II) chloride is a starting point in the synthesis of other palladium compounds and complexes. Palladium(II) acetate plus triphenylphosphine is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. Coordination compounds Coordination compounds of palladium contain ligands coordinated to a central Pd0 or Pd2+ center. They are typically synthesized by adding ligands to an ionic palladium compound. For example, acetonitrile, benzonitrile, or triphenylphosphine may be coordinated to palladium(II) chloride () to form bis(acetonitrile)palladium dichloride (), bis(benzonitrile)palladium dichlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)nickel(II)
Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)nickel(II) refers to a pair of metal phosphine complexes with the formula NiCl2 (C6H5)3sub>2. The compound exists as two isomers, a paramagnetic dark blue solid and a diamagnetic red solid. These complexes function as catalysts for organic synthesis.Montgomery, J. Science of Synthesis Georg Thiene Verlag KG, Vol. 1, p 11, CODEN: SSCYJ9 Synthesis and structure The blue isomer is prepared by treating hydrated nickel chloride with triphenylphosphine in alcohols or glacial acetic acid: :NiCl2•6H2O + 2 PPh3 → NiCl2(PPh3)2 + 6 H2O When allowed to crystallise from chlorinated solvents, the tetrahedral isomer converts to the square planar isomer. The square planar form is red and diamagnetic. The phosphine ligands are trans with respective Ni-P and Ni-Cl distances of 2.24 and 2.17 Å. The blue form is paramagnetic and features tetrahedral Ni(II) centers. In this isomer, the Ni-P and Ni-Cl distances are elongated at 2.32 and 2.21 Å. As illustrated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum(II) Chloride
Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride is a metal phosphine complex with the formula PtCl2 (C6H5)3sub>2. Cis- and trans isomers are known. The cis isomer is a white crystalline powder, while the trans isomer is yellow. Both isomers are square planar about the central platinum atom. The cis isomer is used primarily as a reagent for the synthesis of other platinum compounds. Preparation The cis isomer is the prepared by heating solutions of platinum(II) chlorides with triphenylphosphine. For example, starting from potassium tetrachloroplatinate: :K2PtCl4 + 2 PPh3 → ''cis''-Pt(PPh3)2Cl2 + 2 KCl The trans isomer is the prepared by treating potassium trichloro(ethylene)platinate(II) ( Zeise's salt) with triphenylphosphine: :KPt(C2H4)Cl3 + 2 PPh3 → ''trans''-Pt(PPh3)2Cl2 + KCl + C2H4 With heating or in the presence of excess PPh3, the trans isomer converts to the cis complex. The latter complex is the thermodynamic product due to triphenylphosphine being a strong trans eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonogashira Coupling
The Sonogashira reaction is a cross-coupling reaction used in organic synthesis to form carbon–carbon bonds. It employs a palladium catalyst as well as copper co-catalyst to form a carbon–carbon bond between a terminal alkyne and an aryl or vinyl halide. :* : aryl or vinyl :* R2: arbitrary :* X: I, Br, Cl or OTf The Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction has been employed in a wide variety of areas, due to its usefulness in the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction can be carried out under mild conditions, such as at room temperature, in aqueous media, and with a mild base, which has allowed for the use of the Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction in the synthesis of complex molecules. Its applications include pharmaceuticals, natural products, organic materials, and nanomaterials. Specific examples include its use in the synthesis of tazarotene, which is a treatment for psoriasis and acne, and in the preparation of SIB-1508Y, also known as Altinicline, a nicotinic rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boronic Acid
A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid () in which one of the three hydroxyl groups () is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (represented by R in the general formula ). As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, members of this class thus belong to the larger class of organoboranes. Boronic acids act as Lewis acids. Their unique feature is that they are capable of forming reversible covalent complexes with sugars, amino acids, hydroxamic acids, etc. (molecules with vicinal, (1,2) or occasionally (1,3) substituted Lewis base donors (alcohol, amine, carboxylate)). The p''K''a of a boronic acid is ~9, but they can form tetrahedral boronate complexes with p''K''a ~7. They are occasionally used in the area of molecular recognition to bind to saccharides for fluorescent detection or selective transport of saccharides across membranes. Boronic acids are used extensively in organic chemistry as chemical building blocks and intermediates predominantly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
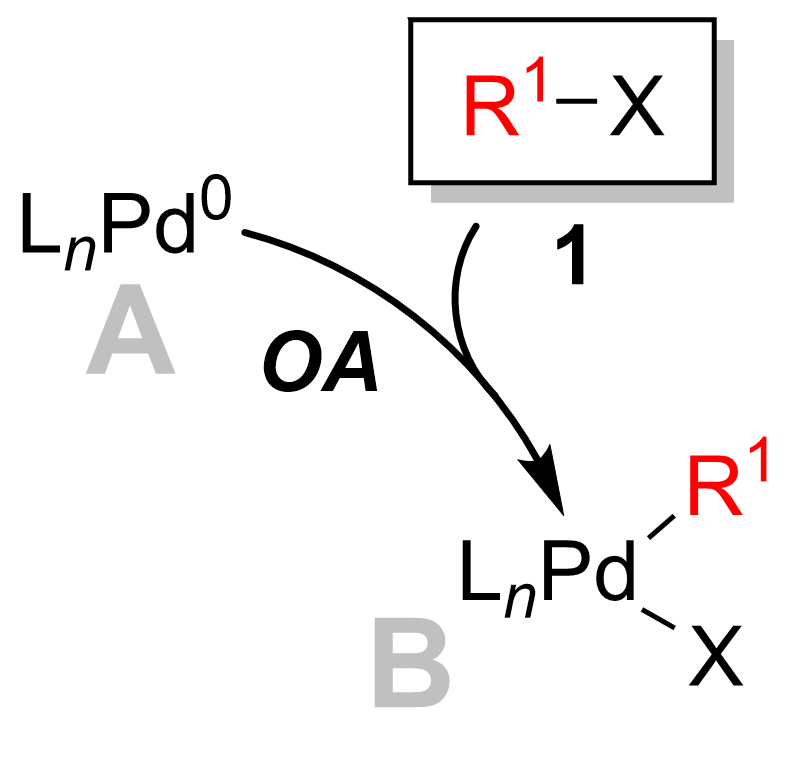
Suzuki Reaction
The Suzuki reaction or Suzuki coupling is an organic reaction that uses a palladium complex catalyst to cross-couple a boronic acid to an organohalide. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of noble metal catalysis in organic synthesis. This reaction is sometimes telescoped with the related Miyaura borylation; the combination is the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. It is widely used to synthesize poly olefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon–carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. The organoboron species is usually synthesized by hydroboration or carboboration, allowing for rapid generation of molecular complexity. Several reviews have been publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Organometallic Chemistry
The ''Journal of Organometallic Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier, covering research on organometallic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.345. References External links * Organic chemistry journals Elsevier academic journals Academic journals established in 1964 English-language journals Monthly journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Crystallographica Section E
''Acta Crystallographica Section E: Crystallographic Communications'' is an open-access structural communications journal. It reports crystal structure determinations of inorganic, metal-organic and organic compounds. Since 2012, ''Acta Crystallogr. E'' has not been included in the Science Citation Index. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: References {{Reflist External links IUCr journals official site Chemistry journals Academic journals established in 1948 English-language journals Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Monthly journals Bimonthly journals Online-only journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |