|
Biomes
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader term than habitat and can comprise a variety of habitats. While a biome can cover large areas, a microbiome is a mix of organisms that coexist in a defined space on a much smaller scale. For example, the human microbiome is the collection of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that are present on or in a human body. A biota is the total collection of organisms of a geographic region or a time period, from local geographic scales and instantaneous temporal scales all the way up to whole-planet and whole-timescale spatiotemporal scales. The biotas of the Earth make up the biosphere. Etymology The term was suggested in 1916 by Clements, originally as a synonym for ''biotic community'' of Möbius (1877). Later, it gained its cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''flora'' which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but ''vegetation'' can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term ''vegetation''. The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of ''vegetation'' approximates that of ecologist Frederic Clements' term earth cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
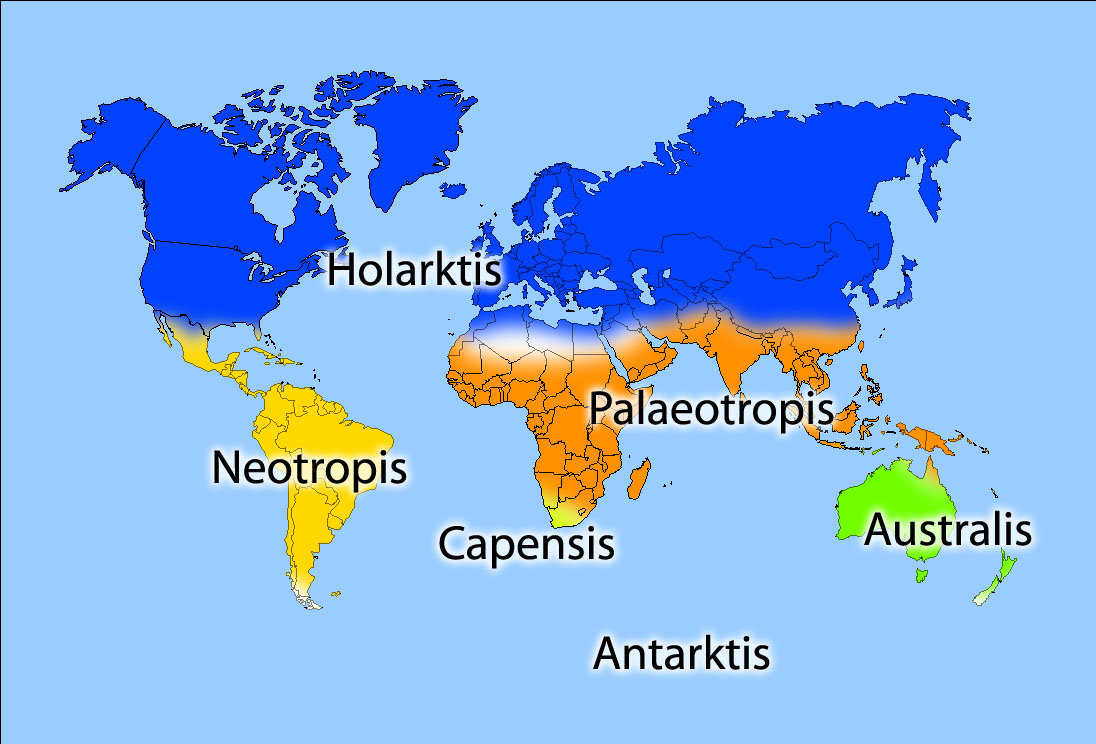
Floristic Province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone. In traditional schemes, areas in phytogeography are classified hierarchically, according to the presence of endemic families, genera or species, e.g., in floral (or floristic, phytogeographic) zones and regions, or also in kingdoms, regions and provinces, sometimes including the categories empire and domain. However, some authors prefer not to rank areas, referring to them simply as "areas", "regions" (in a non hierarchical sense) or "phytochoria". Systems used to classify vegetation can be divided in two major groups: those that use physiognomic-environmental parameters and characteristics and those that are based on floristic (i.e. shared genera and species) rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeographic Province
This page features a list of biogeographic provinces that were developed by Miklos Udvardy in 1975,Udvardy, M. D. F. (1975). ''A classification of the biogeographical provinces of the world''. IUCN Occasional Paper no. 18. Morges, Switzerland: IUCN.Udvardy, Miklos D. F. (1975) ''World Biogeographical Provinces'' (Map). The CoEvolution Quarterly, Sausalito, Californialink later modified by other authors. Biogeographic Province is a biotic subdivision of biogeographic realms subdivided into ecoregions, which are classified based on their biomes or habitat types and, on this page, correspond to the floristic kingdoms of botany. The provinces represent the large areas of Earth's surface within which organisms have been evolving in relative isolation over long periods of time, separated from one another by geographic features, such as oceans, broad deserts, or high mountain ranges, that constitute barriers to migration. Biomes are characterized by similar climax vegetation, though each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (vegetation)
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''flora'' which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but ''vegetation'' can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term ''vegetation''. The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of ''vegetation'' approximates that of ecologist Frederic Clements' term earth cover, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''flora'' which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but ''vegetation'' can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term ''vegetation''. The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of ''vegetation'' approximates that of ecologist Frederic Clements' term earth cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Systematics And Evolution
The ''Journal of Systematics and Evolution'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of botany. It covers all issues related to plant systematics and evolution. It is published by Wiley on behalf of the Botanical Society of China and is sponsored by the Institute of Botany (Chinese Academy of Sciences). The editors-in-chief are Song Ge (Chinese Academy of Sciences) and Jun Wen (Smithsonian Institution). The journal was established in 1963 as ''Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Biological Abstracts *BIOSIS Previews *CAB Abstracts *Current Contents/Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences *EBSCO databases *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus *The Zoological Record According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aziz Ab'Sáber
Aziz Nacib Ab'Sáber (; October 24, 1924 – March 16, 2012) was a geographer and one of Brazil's most respected scientists, honored with the highest awards of Brazilian science in geography, geology, ecology and archaeology. Graduated in geography, he was a president and honorary president of the Sociedade Brasileira para o Progresso da Ciência (Brazilian Society for the Advancement of Science), Emeritus Professor of the University of São Paulo and member of the highest rank - Order Grão-Cruz in Earth Sciences - of the Academy of Science. Among the awards, he has received the UNESCO Prize on Science and the Environment in 2001 and the Prize to the Intellectual of Brazil in 2011. The contributions of Ab'Saber to science range from the first research of oil camps in Brazil's northeast to surveys of Brazil's natural realms and the restoration of the history of forests, camps and primitive humans over geologic time in South America. He made central contributions to biology, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotope
A biotope is an area of uniform environmental conditions providing a living place for a specific assemblage of plants and animals. ''Biotope'' is almost synonymous with the term "habitat", which is more commonly used in English-speaking countries. However, in some countries these two terms are distinguished: the subject of a habitat is a population, the subject of a biotope is a '' biocoenosis'' or "biological community". It is an English loanword derived from the German '' Biotop'', which in turn came from the Greek ''bios'' (meaning 'life') and ''topos'' ('place'). (The related word ''geotope'' has made its way into the English language by the same route, from the German '' Geotop''.) Ecology The concept of a biotope was first advocated by Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919), a German zoologist famous for the recapitulation theory. In his book ''General Morphology'' (1866), which defines the term " ecology", he stresses the importance of the concept of habitat as a prerequisite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Walter
Heinrich Karl Walter (21 October 1898 – 15 October 1989) was a German-Russian botanist and eco-physiologist. Life Walter, the son of a doctor, was born in Odessa. He studied plant biology at the University of Odessa from 1915 to 1917. In 1918 he moved to the University of Dorpat, where he studied under Peter Claussen. In 1919 he studied at the University of Jena with Christian Ernst Stahl and Wilhelm Detmer, where he completed his Ph.D. In 1920, he worked at the Agricultural Research Institute in Halle, and then as a research assistant of Ludwig Jost at the University of Heidelberg. In 1923, Walter worked as a lecturer at the university and he became an Associate Professor of Botany in 1927. In 1924, he married the daughter of the botanist Heinrich Schenck, Erna Walter, who also earned her doctorate in botany from the University of Heidelberg (in 1918) and was a research assistant of Ludwig Jost. In the following years, Walter received a Rockefeller Fellowship (1929-1930) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddy Van Der Maarel
Evert "Eddy" van der Maarel (23 February 1934 – 4 April 2021) was a Dutch ecologist. He spent most of his career as professor of ecological botany at Uppsala University in Sweden. Career Van der Maarel was born on 23 February 1934 in Amsterdam. He studied biology at the University of Amsterdam between 1951 and 1959. Between 1962 and 1968 he worked at the institute of botany of Utrecht University and later at the institute of plant ecology of the University of Groningen. Van der Maarel obtained his PhD at Utrecht University in 1966 with a dissertation titled : "Over vegetatiestructuren, -relaties en -systemen in het bijzonder in de duingraslanden van Voorne". Between 1968 and 1981 he was a lecturer of geobotany at the Catholic University Nijmegen. From 1981 to 1999 van de Maarel was a professor of ecological botany at Uppsala University. From 1995 to 1999 he was the Gerard Baerends professor at the University of Groningen. He retired in 1999. He died on 4 April 2021. He was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |