|
Binge Drinking
Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably. Binge drinking is a style of drinking that is popular in several countries worldwide, and overlaps somewhat with social drinking since it is often done in groups. The degree of intoxication however, varies between and within various cultures that engage in this practice. A binge on alcohol can occur over hours, last up to several days, or in the event of extended abuse, even weeks. Due to the long term effects of alcohol abuse, binge drinking is considered to be a major public health issue. Binge drinking is more common in males, during adolescence and young adulthood. Heavy regular binge drinking is associated with adverse effects on neurologic, cardiac, gastrointestinal, hematologic, immune, and musculoskeletal organ systems as well as increasing the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Alcohol Concentration
Blood alcohol content (BAC), also called blood alcohol concentration or blood alcohol level, is a measurement of alcohol intoxication used for legal or medical purposes. BAC is expressed as mass of alcohol per volume of blood. In US and many international publications, BAC levels are written as a percentage such as 0.08%, i.e. there is 0.8 grams of alcohol per liter of blood. In different countries, the maximum permitted BAC when driving ranges from the limit of detection (zero tolerance) to 0.08% (0.8 ). BAC levels above 0.40% (4 g/L) can be potentially fatal. Units of measurement BAC is generally defined as a fraction of weight of alcohol per volume of blood, with an SI coherent derived unit of kg/m3 or equivalently grams per liter (g/L). Countries differ in how this quantity is normally expressed. Common formats are listed in the table below. For example, the US and many international publications present BAC as a percentage, such as 0.05%. This would be interpreted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who is exposed to alcohol during gestation. FASD affects 1 in 20 Americans, but is highly misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed. The several forms of the condition (in order of most severe to least severe) are: fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), partial fetal alcohol syndrome (pFAS), alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder (ARND), and neurobehavioral disorder associated with prenatal alcohol exposure (ND-PAE). Other terms used are fetal alcohol effects (FAE), partial fetal alcohol effects (PFAE), alcohol-related birth defects (ARBD), and static encephalopathy, but these terms have fallen out of favor and are no longer considered part of the spectrum. Not all infants exposed to alcohol in utero will have detectable FASD or pregnancy complications. The risk of FASD increases with the amount consumed, the frequency of consumption, and the longer duration of alcohol consumption during pregnancy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impaired Driving
Driving under the influence (DUI) is the crime of driving, operating, or being in control of a vehicle while one is impaired from doing so safely by the effect of either alcohol (see drunk driving) or some other drug, whether recreational or prescription (see drug-impaired driving). Multiple other terms are used for the offense in various jurisdictions. Terminology The name of the offense varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction and from legal to colloquial terminology. In various jurisdictions the offense is termed "driving under the influence" f alcohol or other drugs(DUI), "driving under the influence of intoxicants" (DUII), "driving while impaired" (DWI), "impaired driving", "driving while intoxicated" (DWI), "operating while intoxicated" (OWI), "operating under the influence" (OUI), "operating vehicle under the influence" (OVI), "drunk in charge", or "over the prescribed limit" (OPL) (in the UK). Alcohol-related DUI is referred to as "drunk driving", "drunken driving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Service Executive
The Health Service Executive (HSE) () is the publicly funded healthcare system in Ireland, responsible for the provision of health and personal social services. It came into operation on 1 January 2005. The current director-general is Bernard Gloster, who took up the new role on 6 March 2023, after Paul Reid stepped down. History The Health Service Executive (HSE) was established by the Health Act 2004 and came into official operation on 1 January 2005. It replaced the ten regional Health Boards, the Eastern Regional Health Authority and a number of other different agencies and organisations. The Minister for Health retained overall responsibility for the Executive in Government A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu .... The HSE adopted a regional structure (HS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bettering The Evaluation And Care Of Health
Bettering the Evaluation and Care of Health (BEACH) is a system established in April 1988 by the Australian Department of Health in order to "provide a reliable and valid data collection process for general practice". It fulfils the first of the General Practice Statistics and Classification Unit (GPSCU)'s objectives, namely to fill the void existing in 1997 in data about general practice. After 18 years of data collection from 1998 to 2016, BEACH contained almost 1.8 million GP-patient encounter records, and was described by the University of Sydney The University of Sydney (USYD) is a public university, public research university in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in both Australia and Oceania. One of Australia's six sandstone universities, it was one of the ... as "the most valid, reliable GP dataset in Australia", "proven to be nationally representative of patients at all Medicare-claimed GP services". At this point, data collection had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute On Alcohol Abuse And Alcoholism
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), as part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, supports and conducts biomedical and Behavioral research, behavioural research on the causes, consequences, treatment, and prevention of alcoholism and alcohol-related problems. The NIAAA functions both as a funding agency that supports research by external research institutions and as a research institution itself, where alcohol research is carried out in‐house. It funds approximately 90% of all such research in the United States. The NIAAA publishes the academic journal ''Alcohol Research: Current Reviews''. Past directors Past directors from 1972–present Mission The mission of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism is to generate and disseminate fundamental knowledge about the effects of alcohol on health and well-being, and apply that knowledge to improve diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of alcohol-related problems, including alcohol us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The CDC's current nominee for director is Susan Monarez. She became acting director on January 23, 2025, but stepped down on March 24, 2025 when nominated for the director position. On May 14, 2025, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. stated that lawyer Matthew Buzzelli is acting CDC director. However, the CDC web site does not state the acting director's name. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
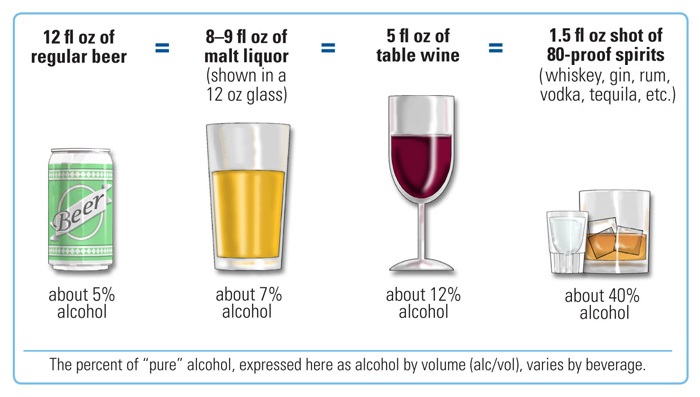
Alcohol Equivalence
Alcohol may refer to: Common uses * Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds * Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life ** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages ** Alcoholic beverage, an alcoholic drink * Rubbing alcohol, for sanitation and to kill germs Music * "Alcohol", a song by Barenaked Ladies from the 1998 album ''Stunt'' * "Alcohol", a song by Beck from the 1993 single " Loser" * "Alcohol" (Brad Paisley song), 2005 * "Alcohol", a song by Butthole Surfers from the 1993 album '' Independent Worm Saloon'' * "Alcohol", a song by CSS from the 2005 album ''Cansei de Ser Sexy'' * "Alcohol", a song by Gang Green from the 1986 album ''Another Wasted Night'' * "Alcohol", a song by Gogol Bordello from the 2007 album '' Super Taranta!'' * "Alcohol", a song by the Kinks from the 1977 album ''Muswell Hillbillies'' and ''Everybody's in Show-Biz'' * "Alcohol", a song by Millionaires, 2008 * "Alcohol", a song by Terminaator from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). This occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal, except under extraordinary and usually pathogenic circumstances. In mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRI Scanner
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique mostly used in radiology and nuclear medicine in order to investigate the anatomy and physiology of the body, and to detect pathologies including tumors, inflammation, neurological conditions such as stroke, disorders of muscles and joints, and abnormalities in the heart and blood vessels among other things. Contrast agents may be injected intravenously or into a joint to enhance the image and facilitate diagnosis. Unlike CT and X-ray, MRI uses no ionizing radiation and is, therefore, a safe procedure suitable for diagnosis in children and repeated runs. Patients with specific non-ferromagnetic metal implants, cochlear implants, and cardiac pacemakers nowadays may also have an MRI in spite of effects of the strong magnetic fields. This does not apply on older devices, and details for medical professionals are provided by the device's manufacturer. Certain atomic nuclei are able to absorb and emit radio frequency ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |