Blood Alcohol Concentration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Blood alcohol content (BAC), also called blood alcohol concentration or blood alcohol level, is a measurement of
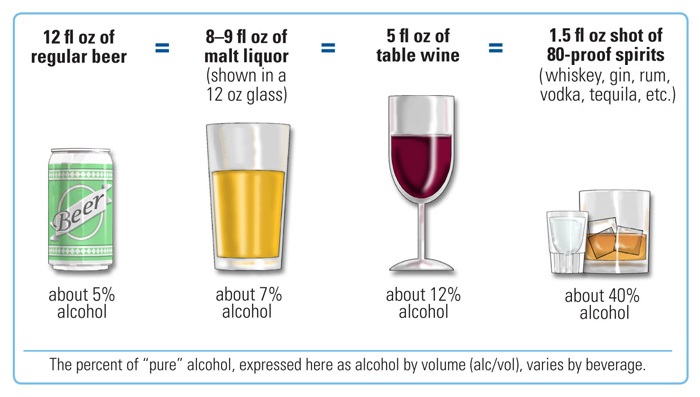 This assumes a US standard drink, i.e. or of ethanol, whereas other definitions exist, for example 10 grams of ethanol.
This assumes a US standard drink, i.e. or of ethanol, whereas other definitions exist, for example 10 grams of ethanol.
 For purposes of law enforcement, blood alcohol content is used to define intoxication and provides a rough measure of impairment. Although the degree of impairment may vary among individuals with the same blood alcohol content, it can be measured objectively and is therefore legally useful and difficult to contest in court. Most countries forbid operation of motor vehicles and heavy machinery above prescribed levels of blood alcohol content. Operation of boats and aircraft is also regulated. Some jurisdictions also regulate bicycling under the influence. The alcohol level at which a person is considered legally impaired to drive varies by country.
For purposes of law enforcement, blood alcohol content is used to define intoxication and provides a rough measure of impairment. Although the degree of impairment may vary among individuals with the same blood alcohol content, it can be measured objectively and is therefore legally useful and difficult to contest in court. Most countries forbid operation of motor vehicles and heavy machinery above prescribed levels of blood alcohol content. Operation of boats and aircraft is also regulated. Some jurisdictions also regulate bicycling under the influence. The alcohol level at which a person is considered legally impaired to drive varies by country.
Estimated alcohol
{{Authority control Alcohol law Alcohol policy Concentration indicators Driving under the influence Metabolism
alcohol intoxication
Alcohol intoxication, commonly described in higher doses as drunkenness or inebriation, and known in overdose as alcohol poisoning, is the behavior and physical effects caused by recent consumption of Alcohol (drug), alcohol. The technical ter ...
used for legal or medical purposes.
BAC is expressed as mass of alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
per volume of blood. In US and many international publications, BAC levels are written as a percentage such as 0.08%, i.e. there is 0.8 grams of alcohol per liter of blood. In different countries, the maximum permitted BAC when driving ranges from the limit of detection (zero tolerance
A zero-tolerance policy is one which imposes a punishment for every infraction of a stated rule.zero tolerance, n.' (under ''zero, n.''). The Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd Ed. 1989. Retrieved 10 November 2009. Italy, Japan, Singapore China, I ...
) to 0.08% (0.8 ). BAC levels above 0.40% (4 g/L) can be potentially fatal.
Units of measurement
BAC is generally defined as a fraction of weight of alcohol per volume of blood, with an SI coherent derived unit of kg/m3 or equivalently grams per liter (g/L). Countries differ in how this quantity is normally expressed. Common formats are listed in the table below. For example, the US and many international publications present BAC as a percentage, such as 0.05%. This would be interpreted as 0.5 grams per deciliter of blood. This same concentration could be expressed as 0.5‰ or 50 mg% in other countries. It is also possible to use other units. For example, in the 1930s Widmark measured alcohol and blood by mass, and thus reported his concentrations in units of g/kg or mg/g, weight alcohol per weight blood. Blood is denser than water and 1 mL of blood has a mass of approximately 1.055 grams, thus a mass-volume BAC of 1 g/L corresponds to a mass-mass BAC of 0.948 mg/g. Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Finland, Germany, and Switzerland use mass-mass concentrations in their laws, but this distinction is often skipped over in public materials, implicitly assuming that 1 L of blood weighs 1 kg. Inpharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific su ...
, it is common to use the amount of substance
In chemistry, the amount of substance (symbol ) in a given sample of matter is defined as a ratio () between the particle number, number of elementary entities () and the Avogadro constant (). The unit of amount of substance in the International ...
, in moles, to quantify the dose. As the molar mass
In chemistry, the molar mass () (sometimes called molecular weight or formula weight, but see related quantities for usage) of a chemical substance ( element or compound) is defined as the ratio between the mass () and the amount of substance ...
of ethanol is 46.07 g/mol, a BAC of 1 g/L is 21.706 mmol/L (21.706 mM).
Effects by alcohol level
The magnitude of sensory impairment may vary in people of differing weights. The NIAAA defines the term "binge drinking
Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably.
Binge drinking is a style of ...
" as a pattern of drinking that brings a person's blood alcohol concentration (BAC) to 0.08 grams percent or above."Quick Stats: Binge Drinking." The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 200Estimation
Direct measurement
Blood samples for BAC analysis are typically obtained by taking a venous blood sample from the arm. A variety of methods exist for determining blood-alcohol concentration in a blood sample. Forensic laboratories typically use Headspace gas chromatography for dissolved gas measurement, headspace-gas chromatography combined with mass spectrometry or flame ionization detection, as this method is accurate and efficient. Hospitals typically use enzyme multiplied immunoassay, which measures the co-enzymeNADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an ade ...
. This method is more subject to error but may be performed rapidly in parallel with other blood sample measurements.
In Germany, BAC is determined by measuring the serum level and then converting to whole blood by dividing by the factor 1.236. This calculation underestimates BAC by 4% to 10% compared to other methods.
By breathalyzer
The amount of alcohol on the breath can be measured, without requiring drawing blood, by blowing into abreathalyzer
A breathalyzer or breathalyser (a portmanteau of ''breath'' and ''analyzer/analyser''), also called an alcohol meter, is a device for measuring breath alcohol (drug), alcohol content (BrAC). It is commonly utilized by law enforcement officers ...
, resulting in a breath alcohol content (BrAC). The BrAC specifically correlates with the concentration of alcohol in arterial blood, satisfying the equation . Its correlation with the standard BAC found by drawing venous blood is less strong. Jurisdictions vary in the statutory conversion factor from BrAC to BAC, from 2000 to 2400. Many factors may affect the accuracy of a breathalyzer test, but they are the most common method for measuring alcohol concentrations in most jurisdictions.
By intake
Blood alcohol content can be quickly estimated by a model developed by Swedish professor Erik Widmark in the 1920s. The model corresponds to apharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific subs ...
single-compartment model with instantaneous absorption and zero-order kinetics for elimination. The model is most accurate when used to estimate BAC a few hours after drinking a single dose of alcohol in a fasted state, and can be within 20% CV of the true value. It is not at all realistic for the absorption phase, and is not accurate for BAC levels below 0.2 g/L (alcohol is not eliminated as quickly as predicted) and consumption with food (overestimating the peak BAC and time to return to zero). The equation varies depending on the units and approximations used, but in its simplest form is given by:
:
where:
* is the estimated blood alcohol concentration (in g/L)
* is the mass of alcohol consumed (g).
* is the amount of time during which alcohol was present in the blood (usually time since consumption began), in hours.
* is the rate at which alcohol is eliminated, averaging around 0.15 g/L/hr.
* is the volume of distribution
In pharmacology, the volume of distribution (VD, also known as apparent volume of distribution, literally, ''volume of dilution'') is the theoretical volume that would be necessary to contain the total amount of an administered drug at the same c ...
(L); typically body weight (kg) multiplied by 0.71 L/kg for men and 0.58 L/kg for women although estimation using TBW is more accurate.
A standard drink, defined by the WHO as 10 grams of pure alcohol, is the most frequently used measure in many countries. Examples:
* An 80 kg man drinks 20 grams ethanol. After one hour:
* A 70 kg woman drinks 10 grams of ethanol. After one hour:
In terms of fluid ounce
A fluid ounce (abbreviated fl oz, fl. oz. or oz. fl., old forms ℥, fl ℥, f℥, ƒ ℥) is a unit of volume (also called ''capacity'') typically used for measuring liquids. The British Imperial, the United States customary, and the United S ...
s of alcohol consumed and weight in pounds, Widmark's formula can be simply approximated as
:
for a man or
:
for a woman, where EBAC and factors are given as g/dL (% BAC), such as a factor of 0.015% BAC per hour.
By standard drinks
 This assumes a US standard drink, i.e. or of ethanol, whereas other definitions exist, for example 10 grams of ethanol.
This assumes a US standard drink, i.e. or of ethanol, whereas other definitions exist, for example 10 grams of ethanol.
By training
If individuals are asked to estimate their BAC, then given accurate feedback via a breathalyzer, and this procedure is repeated a number of times during a drinking session, studies show that these individuals can learn to discriminate their BAC, to within a mean error of 9 mg/100 mL (0.009% BAC). The ability is robust to different types of alcohol, different drink quantities, and drinks with unknown levels of alcohol. Trained individuals can even drink alcoholic drinks so as to adjust or maintain their BAC at a desired level. Training the ability does not appear to require any information or procedure besides breathalyzer feedback, although most studies have provided information such as intoxication symptoms at different BAC levels. Subjects continue to retain the ability one month after training.Post-mortem
After fatal accidents, it is common to check the blood alcohol levels of involved persons. However, soon after death, the body begins to putrefy, a biological process which produces ethanol. This can make it difficult to conclusively determine the blood alcohol content in autopsies, particularly in bodies recovered from water. For instance, following the 1975Moorgate tube crash
The Moorgate tube crash occurred on 28 February 1975 at 8:46 am on the London Underground's Northern City Line; 43 people died and 74 were injured after a train failed to stop at the line's southern terminus, Moorgate station, and crashed ...
, the driver's kidneys had a blood alcohol concentration of 80 mg/100 mL, but it could not be established how much of this could be attributed to natural decomposition. Newer research has shown that vitreous (eye) fluid provides an accurate estimate of blood alcohol concentration that is less subject to the effects of decomposition or contamination.
Legal limits
Test assumptions
Extrapolation
Retrogradeextrapolation
In mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. ...
is the mathematical process by which someone's blood alcohol concentration at the time of driving is estimated by projecting backwards from a later chemical test. This involves estimating the absorption and elimination of alcohol in the interim between driving and testing. The rate of elimination in the average person is commonly estimated at 0.015 to 0.020 grams per deciliter per hour (g/dL/h), although again this can vary from person to person and in a given person from one moment to another. Metabolism can be affected by numerous factors, including such things as body temperature, the type of alcoholic beverage consumed, and the amount and type of food consumed.
In an increasing number of states, laws have been enacted to facilitate this speculative task: the blood alcohol content at the time of driving is legally presumed to be the same as when later tested. There are usually time limits put on this presumption, commonly two or three hours, and the defendant is permitted to offer evidence to rebut this presumption.
Forward extrapolation can also be attempted. If the amount of alcohol consumed is known, along with such variables as the weight and sex of the subject and period and rate of consumption, the blood alcohol level can be estimated by extrapolating forward. Although subject to the same infirmities as retrograde extrapolation—guessing based upon averages and unknown variables—this can be relevant in estimating BAC when driving and/or corroborating or contradicting the results of a later chemical test.
Metabolism
Thepharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific subs ...
s of ethanol are well characterized by the ADME
ADME is the four-letter abbreviation (acronym) for absorption (pharmacokinetics), ''absorption'', distribution (pharmacology), ''distribution'', ''metabolism'', and ''excretion'', and is mainly used in fields such as pharmacokinetics and pharmacol ...
acronym (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion). Besides the dose ingested, factors such as the person's total body water, speed of drinking, the drink's nutritional content, and the contents of the stomach all influence the profile of blood alcohol content (BAC) over time. Breath alcohol content (BrAC) and BAC have similar profile shapes, so most forensic pharmacokinetic calculations can be done with either. Relatively few studies directly compare BrAC and BAC within subjects and characterize the difference in pharmacokinetic parameters. Comparing arterial and venous BAC, arterial BAC is higher during the absorption phase and lower in the postabsorptive declining phase.
Highest levels
According toGuinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a British reference book published annually, list ...
, the 2013 incident where a BAC of 1.374% (13.74 g/L) was recorded is the highest BAC recorded in a human who survived the ordeal.
Notes
References
Citations
General and cited references
* Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh. Science and Technology Department. ''The Handy Science Answer Book''. Pittsburgh: The Carnegie Library, 1997. . * * Taylor, L., and S. Oberman. ''Drunk Driving Defense'', 6th edition. New York: Aspen Law and Business, 2006. .External links
Estimated alcohol
{{Authority control Alcohol law Alcohol policy Concentration indicators Driving under the influence Metabolism