|
Bimetallic Strip
A bimetallic strip or bimetal strip is a strip that consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated. The different expansion rates cause the strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. Thus, a bimetal strip converts a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled. Common applications include temperature sensing (thermometer) and regulation (thermostat). The invention of the bimetallic strip is generally credited to John Harrison, an eighteenth-century clockmaker who made it for his third marine chronometer (H3) of 1759 to compensate for temperature-induced changes in the balance spring. Harrison's invention is recognized in the memorial to him in Westminster Abbey, England. Characteristics The strip consists of two st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallic Stripe
Bimetallic or bi-metallic may refer to: *Bimetallism, a monetary standard in economics *Bimetallic strip, a temperature sensitive mechanical device *Alloy (binary alloy), in metallurgy, a mixture of two metals *Bi-metallic coin Bi-metallic coins are coins consisting of two ('' bi-'') metals or alloys, generally arranged with an outer ring around a contrasting center. Common circulating examples include the €1, €2, United Kingdom £1 and £2, Canadian $2, Sout ... *'' Bi-Metallic Investment Co. v. State Board of Equalization'' {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timoshenko–Ehrenfest Beam Theory
The Timoshenko–Ehrenfest beam theory was developed by Stephen Timoshenko and Paul EhrenfestIsaac Elishakoff (2020) "Who developed the so-called Timoshenko beam theory?", ''Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids'' 25(1): 97–116 early in the 20th century.Timoshenko, S. P. (1921) "LXVI. On the correction for shear of the differential equation for transverse vibrations of prismatic bars", ''The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science'' 41(245): 744–746 Timoshenko, S. P. (1922) "X. On the transverse vibrations of bars of uniform cross-section", ''The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science'' 43(253): 125–131 The model takes into account shearing (physics), shear deformation and rotational bending effects, making it suitable for describing the behaviour of thick beams, sandwich-structured composite, sandwich composite beams, or beams subject to high-frequency excitation when the wavelength approaches the thick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
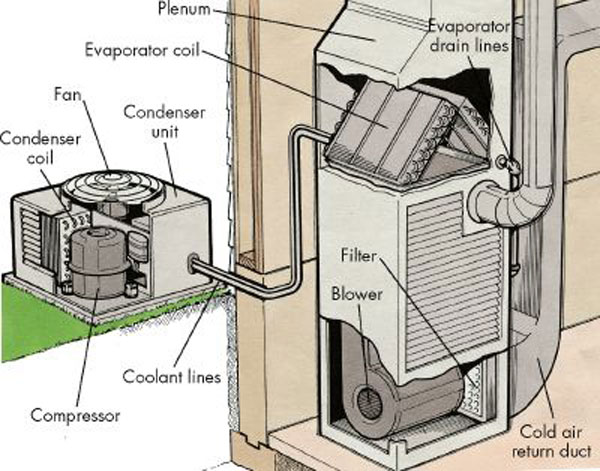
Air Conditioner
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature, and in some cases, also controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or through other methods, such as passive cooling and ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners but use a reversing valve, allowing them to both heat and cool an enclosed space. Air conditioners, which typically use vapor-compression refrigeration, range in size from small units used in vehicles or single rooms to massive units that can cool large buildings. Air source heat pumps, which can be used for heating as well as cooling, are becoming increasingly common in cooler climates. Air conditioners can red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerator
A refrigerator, commonly shortened to fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermal insulation, thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so that its inside is cooled to a temperature below the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential Food preservation, food storage technique around the world. The low temperature reduces the reproduction rate of bacteria, so the refrigerator lowers the rate of Food spoilage, spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. The optimal temperature range for perishable food storage is .Keep your fridge-freezer clean and ice-free ''BBC''. 30 April 2008 A freezer is a specialized refrigerator, or portion of a refrigerator, that maintains its contents’ temperature below the freezing point of water. The refrigerator replaced the icebox, which had been a common househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heater
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Switch
A mercury switch is an electricity, electrical switch that opens and closes a electrical circuit, circuit when a small amount of the liquid metal mercury (element), mercury connects metal electrodes to close the circuit. There are several different basic designs (tilt, displacement, radial, etc.) but they all share the common design strength of non-eroding switch contacts. The most common is the ''mercury tilt switch''. It is in one state (open or closed) when tilted one direction with respect to horizontal, and the other state when tilted the other direction. This is what older style thermostats used to turn a heater or air conditioner on or off. The ''mercury displacement switch'' uses a 'plunger' that dips into a pool of mercury, raising the level in the container to contact at least one electrode. This design is used in relays in industrial applications that need to switch high current loads frequently. These relays use electromagnetic coils to pull steel sleeves inside her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivarox
Nivarox, also known as Nivarox - FAR SA is a Swiss company formed by a merger in 1984 between Nivarox SA and Fabriques d' Assortiments Réunis (FAR). It is currently owned by the Swatch Group. Nivarox is also the trade name of the metallic alloy from which its products are fabricated. Its notable property is that its coefficient of elasticity is remarkably constant with temperature. Nivarox is most famous for producing hairsprings that are attached to the balance wheel inside a mechanical watch movement, as well as mainsprings which provide the motive power for the watch. Nivarox was developed for use in watch hairsprings in 1933 by Reinhard Straumann in his Waldenbourg laboratory. FAR was the corporate name chosen in 1932 for the entity comprising several companies and subsidiaries located in Le Locle Switzerland, which at the time manufactured various watch components. Nivarox alloy As a trade name, Nivarox is an acronym from the German . The Nivarox alloy is a nickel iron a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Wheel
A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a spiral torsion spring, known as the '' balance spring'' or ''hairspring''. It is driven by the escapement, which transforms the rotating motion of the watch gear train into impulses delivered to the balance wheel. Each swing of the wheel (called a "tick" or "beat") allows the gear train to advance a set amount, moving the hands forward. The balance wheel and hairspring together form a harmonic oscillator, which due to resonance oscillates preferentially at a certain rate, its resonant frequency or "beat", and resists oscillating at other rates. The combination of the mass of the balance wheel and the elasticity of the spring keep the time between each oscillation or "tick" very constant, accounting for its nearly universal use as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock
A clock or chronometer is a device that measures and displays time. The clock is one of the oldest Invention, human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month, and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the Millennium, millennia. Some predecessors to the modern clock may be considered "clocks" that are based on movement in nature: A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a flat surface. There is a range of duration timers, a well-known example being the hourglass. Water clocks, along with sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments. A major advance occurred with the invention of the verge escapement, which made possible the first mechanical clocks around 1300 in Europe, which kept time with oscillating timekeepers like balance wheels., pp. 103–104., p. 31. Traditionally, in horology (the study of timekeeping), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantan
Constantan, also known in various contexts as Eureka, Advance, and Ferry, refers to a copper-nickel alloy commonly used for its stable electrical resistance across a wide range of temperatures. It usually consists of 55% copper and 45% nickel. Its main feature is the low thermal variation of its resistivity, which is constant over a wide range of temperatures. Other alloys with similarly low temperature coefficients are known, such as manganin (Cu 6%/ Mn 2%/ Ni %). History In 1887, Edward Weston discovered that metals can have a negative temperature coefficient of resistance, inventing what he called his "Alloy No. 2." It was produced in Germany where it was renamed "Konstantan". Constantan alloy Of all alloys used in modern strain gauges, constantan is the oldest, and still the most widely used. This situation reflects the fact that constantan has the best overall combination of properties needed for many strain gauge applications. This alloy has, for example, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |