|
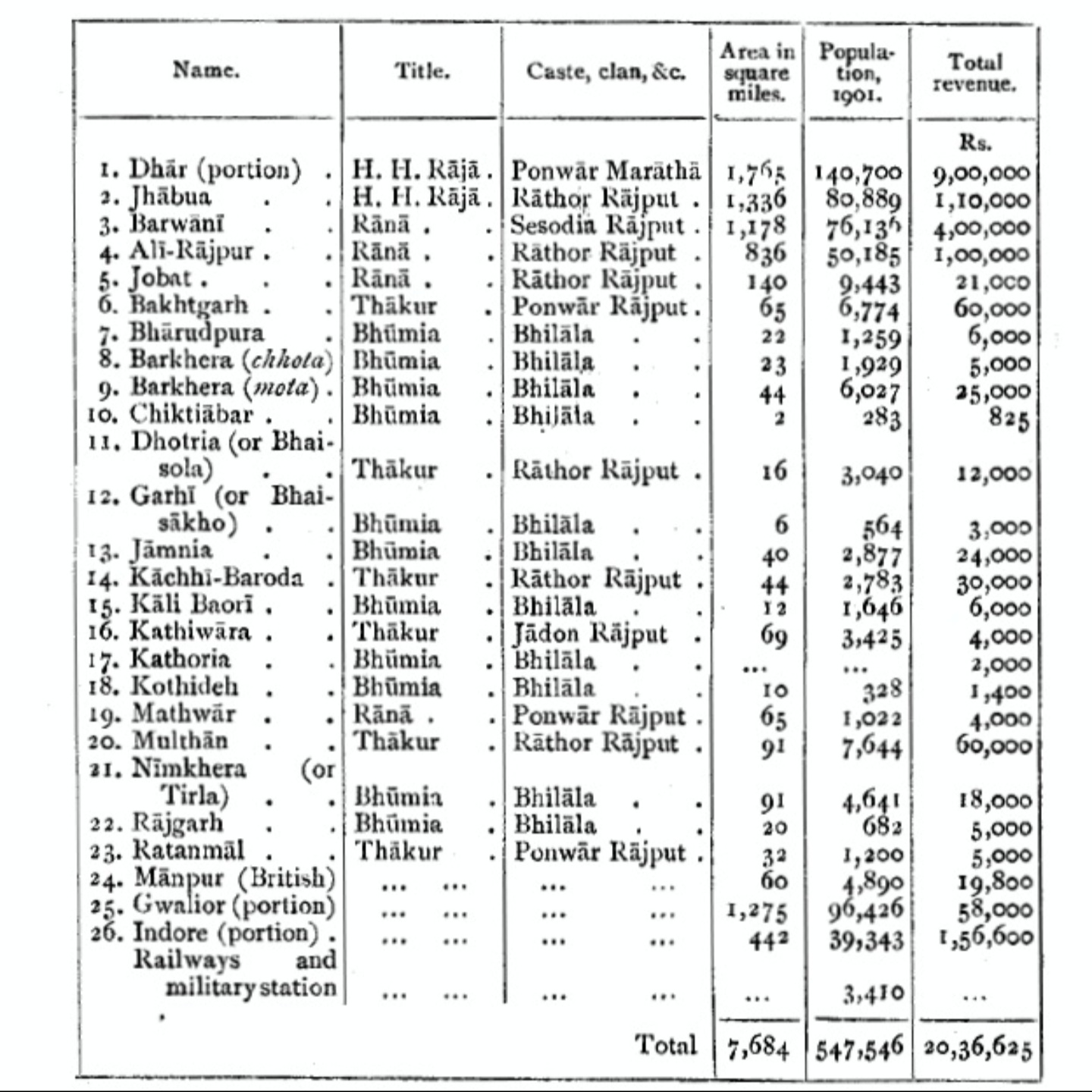
Bhopawar
Bhopawar Agency was a sub-agency of the Central India Agency in British India with the headquarters at the town of Bhopawar, so the name. Bhopawar Agency was created in 1882 from a number of princely states in the Western Nimar and Southern Malwa regions of Central India belonging to the former Bhil Agency and Bhil Sub-agency with the capitals at Bhopawar and Manpur. The agency was named after Bhopawar, a village in Sardarpur tehsil, Dhar District of present-day Madhya Pradesh state. Manpur remained a strictly British territory. The other chief towns of this region were: Badnawar, Kukshi, Manawar and Sardarpur, Chadawad Estate, Dattigaon. The mighty Vindhya and Satpura ranges crossed the territory of the agency roughly from east to west, with the fertile valley of the Narmada River lying between them. The agency also included the "Bhil Country", inhabited by the Bhil people. History At the time of its 1882 establishment, the agency had a total area of , and its populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agencies Of British India
An agency of British India was an internally autonomous or semi-autonomous unit of British India whose external affairs were governed by an agent designated by the Viceroy of India. Description The agencies varied in character from fully autonomous self-governing dependencies such as princely states, where the agent functioned mainly as a representative of the Viceroy, to tribal tracts which were integral parts of the British Empire and where the agent was completely in charge of law and order. The agent of a protected tract or princely state usually lived outside the territory in his charge, as opposed to a Resident who usually lived within his confines and was frequently the District Collector of the adjoining British district. Civil and criminal justice in agencies were usually administered through locally made laws, and the Indian Penal Code was not applicable by default in these agencies. List of agencies Political agencies were created, merged or abolished at dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alirajpur State
Alirajpur State was formerly a princely state of India, administratively under the Bhopawar Agency subdivision of the Central India Agency. The state covered an area of 2165 square kilometres, with a population of 50,185 in 1901 and its capital at Alirajpur. The average revenue of the state was Rs.100,000 in 1901. History The early history of the state is not very clear, the founder of the state was either Anand Deo or Ude Deo. The state got its name from the fort of Ali and the capital of Rajpur. The rulers of Alirajpur claim to be Rathore's from the royal family of Jodhpur, however this claim is not accepted by the Maharaja's of Jodhpur. The state came under British rule in 1817. The last ruler of Ali Rajpur was Surendra Singh, who subsequently served as the Ambassador of India to Spain in the 1980s. After Indian independence in 1947, Alirajpur acceded to the Union of India, and the principality was incorporated into the new state of Madhya Bharat, which subsequently beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central India Agency
The Central India Agency was created in 1854, by amalgamating the Western Malwa Agency with other smaller political offices which formerly reported to the Governor-General of India. The agency was overseen by a political agent who maintained relations of the Government of India with the princely states and influence over them on behalf of the Governor-General. The headquarters of the agent were at Indore. List of Divisions and Princely States/districts of Agency Bundelkhand Agency : The Bundelkhand Agency was bounded by Bagelkhand to the east, the United Provinces to the north, Lalitpur District to the west, and the Central Provinces to the south. Bagelkhand Agency was separated from Bundelkhand in 1871. In 1900 it included 9 states, the most important of which were Orchha, Panna, Samthar, Charkhari, Chhatarpur, Datia, Bijawar and Ajaigarh. The agency also included 13 estates and the ''pargana'' of Alampur, the latter belonging to Indore State. In 1931, all of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa Agency
Malwa Agency was an administrative section of British India's Central India Agency. The headquarters of the political agent was at Neemuch (Nimach). The other chief towns of the region were : Ratlam and Jaora. History The Malwa Agency was formed in 1895 out of princely states in the Northern Malwa region formerly under the authority of the British agent for Indore and the abolition of the Western Malwa Agency which had been a sub-agency of the Central India Agency since 1854.Sir William Wilson Hunter. ''The Imperial Gazetteer of India''. London: Trübner & co., 1885. The Dewas States ( Dewas Senior & Dewas Junior) were added to Malwa Agency in 1907. In 1925 Malwa Agency was amalgamated with Bhopawar Agency to form the Malwa and Bhopawar Agency, renamed the Malwa and Southern States Agency in 1927. The Dewas States were transferred to Bhopal Agency in 1931, and in 1934 the agency was once again renamed Malwa Agency. After Indian independence in 1947, the rulers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardarpur
Sardarpur is a town and a nagar panchayat in Dhar district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is a town on Mahi River on the Malwa plateau. There is an ancient Shivalinga situated at the bank of Mahi river at a place called Shree Jhineshwar Dham; Shri Mohankheda Jain Thirth and Bhopawar Jain Tirth are located nearby. It is one of the 230 Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) constituencies of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. History Sardarpur was a British station in Central India during the British Raj, and was within the state of Gwalior. It was the headquarters of the political agent for the Bhopawar agency, and of the Malwa Bhil corps, originally raised in 1837 and converted into a military police battalion by around 1900. Demographics India census A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhar District
Dhar district () is a districts of Madhya Pradesh, district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The historic town of Dhar is administrative headquarters of the district. The district has an area 8,153 km2. It is bounded by the districts of Ratlam District, Ratlam to the north, Ujjain District, Ujjain to the northeast, Indore District, Indore to the east, Khargone District, Khargone (West Nimar) to the southeast, Barwani District, Barwani to the south, Jhabua District, Jhabua and Alirajpur district, Alirajpur to the west. It is part of the Indore Division of Madhya Pradesh. The population of the district is 2,185,793 (2011 census), an increase of 25.60% from its 2001 population of 1,740,329. Pithampur is a large industrial area comes under Dhar District. Kukshi is the largest tehsil of the district. Geography The Vindhya Range runs east and west through the district. The northern part of the district lies on the Malwa plateau. The northwestern portion of the district l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhil People
Bhil or Bheel refer to the various indigenous groups inhabiting western India, including parts of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh and are also found in distant places such as Bengal and Tripura. Though they now speak the Bhili language, an Indo-Aryan language, the original aboriginal language that the Bhil originally spoke is lost. Bhils are divided into a number of endogamous territorial divisions, which in turn have a number of clans and lineages. Bhils are listed as tribal people in the states of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Rajasthan—all in the western Deccan regions and central India—as well as in Bengal and Tripura in far-eastern India, on the border with Bangladesh. Many Bhils speak the dominant language of the region they reside in, such as Marathi, Gujarati or Bengali. Etymology Some scholars suggest that the term Bhil is derived from the word ''billa'' or ''billu'' which means bow in the Dravidian lexis. The term Bhil is used to refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indore Residency
Indore was one of the residencies of British India. Indore Residency included most of Indore State, and, after 1933, Rewa State, which formerly belonged to Bagelkhand Agency. It was part of Central India Agency. British Residents List of British Residents of the Indore Residency. *1840–1844: Sir Claude Martin Wade (b. 1794 – d. 1861) *1845–1859: Robert North Collie Hamilton: (b. 1802 – d. 1887) *1859–1861: Sir Richmond Campbell Shakespear (b. 1812 - d. 1861) *1861–1869: Richard John Meade (b. 1821 – d. 1899) *1869–1881: Henry D. Daly *1881–1888: Henry Lepel-Griffin (b. 1838 – d. 1908) *1888–1890: P.F. Henvey *1890–1894: R.J. Crosthwaite *1894–1899: David W.K. Barr *1899–1902: Robert Henry Jennings *1902–1903: Francis Younghusband Lieutenant Colonel Sir Francis Edward Younghusband, (31 May 1863 – 31 July 1942) was a British Army officer, explorer and spiritual writer. He is remembered for his t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Independence Act 1947
The Indian Independence Act 1947 ( 10 & 11 Geo. 6. c. 30) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that partitioned British India into the two new independent dominions of India and Pakistan. The Act received Royal Assent on 18 July 1947 and thus modern-day India and Pakistan, comprising west (modern day Pakistan) and east (modern day Bangladesh) regions, came into being on 15 August. The legislature representatives of the Indian National Congress, the Muslim League, and the Sikh community came to an agreement with Lord Mountbatten, then Viceroy and Governor-General of India, on what has come to be known as the ''3 June Plan'' or ''Mountbatten Plan.'' Prelude Attlee's announcement Clement Attlee, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, announced on 20 February 1947 that: #The British Government would grant full self-government to British India by 3 June 1948 at the latest, #The future of the Princely States would be decided after the date of final transfer is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |