|
Bhattiana
Bhattiana, also spelt Bhatiyana, is a tract of land lying in the Indian states of Haryana and Punjab between Hisar and the Garra. It was named ''Bhattiana'' because of being ruled by the Bhatti. The regions fell under the control of the different rulers, including the Mughals, and with the weakening of the Mughals, became a part of the British Raj from the early-to-mid-19th century. Etymology The term ''Bhattiana'' means "region of the Bhattis" and the geographical area derives its name from the Bhatti clan. The Bhattiana territories, traditionally controlled by the Bhattis, covered part of modern Haryana and Punjab, and extended up to Bikaner, Rajasthan. History There are mounds scattered around the region which contain pot-sherds. These excavations have also uncovered well-burnt bricks and the remains of kilns. These findings were found along the bank of the Ghaggar, its tributary, and also at Bhatner, Bhadrakali, Fatehgarh, Kalibangan, Rangmahal, Karnisar, and Bhawar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagar Region
Bagar, also Bagad (बागड़) a term meaning the "dry country",Nonica Datta The Tribune (Chandigarh), The Tribune, 3 July 1999. is a region refers in north-western India in north Rajasthan, West Haryana, south west Punjab, India where the Bagri language is spoken and which is inhabited by Bagri people. The region is characterised by sandy tracks and shifting sand dunes which are now irrigated by canals. Etymology Bagar means the prairie (grazing shrubs and grassland) of northern Rajputana,Elaine King,1998, Tales & legends of India, Page 61. which likely comes from eponymous Arabic word "baqar" or "bagar" (بقرة) meaning "cow" (Cattle in religion and mythology#Hinduism, sacred to Hindus),2002, Abubakar Garba, "State, city and society: processes of urbanisation", University of Maiduguri – Centre for Trans Saharan Studies, Archaeological Association of Nigeria, Page 82. derived from the Arabic word "cattle".Mohamet Lawan, 1997, No travel is little, Page 66. ''Baggara'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhatner
Hanumangarh is a city and municipal council in the Indian state of Rajasthan, situated on the banks of the river Ghaggar also identified as ancient Sarasvati river, located about 400 km from Delhi. It is the administrative headquarter of Hanumangarh District. The city was once called Bhatner (alternatively spelled Bhatnair) because it was founded by king Bhupat in 255 AD. It remained in the control of the Rajputs of Bhati clan and faced a historic siege by Timur in 1391, during which the Bhati Raput king Dulachand lost the fort for a short time. The fort was later occupied by Rao Jetsa of Bikaner. History Indus Valley Civilization Indus Valley Civilization sites in the district number over 100 villages along Ghaggar-Hakra River (Palaeochannel of Sarasvati River), such as Karanpura. Remains found at Kalibangan and Pilibanga in 1951 reveal that this area was a part of nearly 5000 years old civilisation. The remains of human skeleton, unknown scripts, stamps, coins, ute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
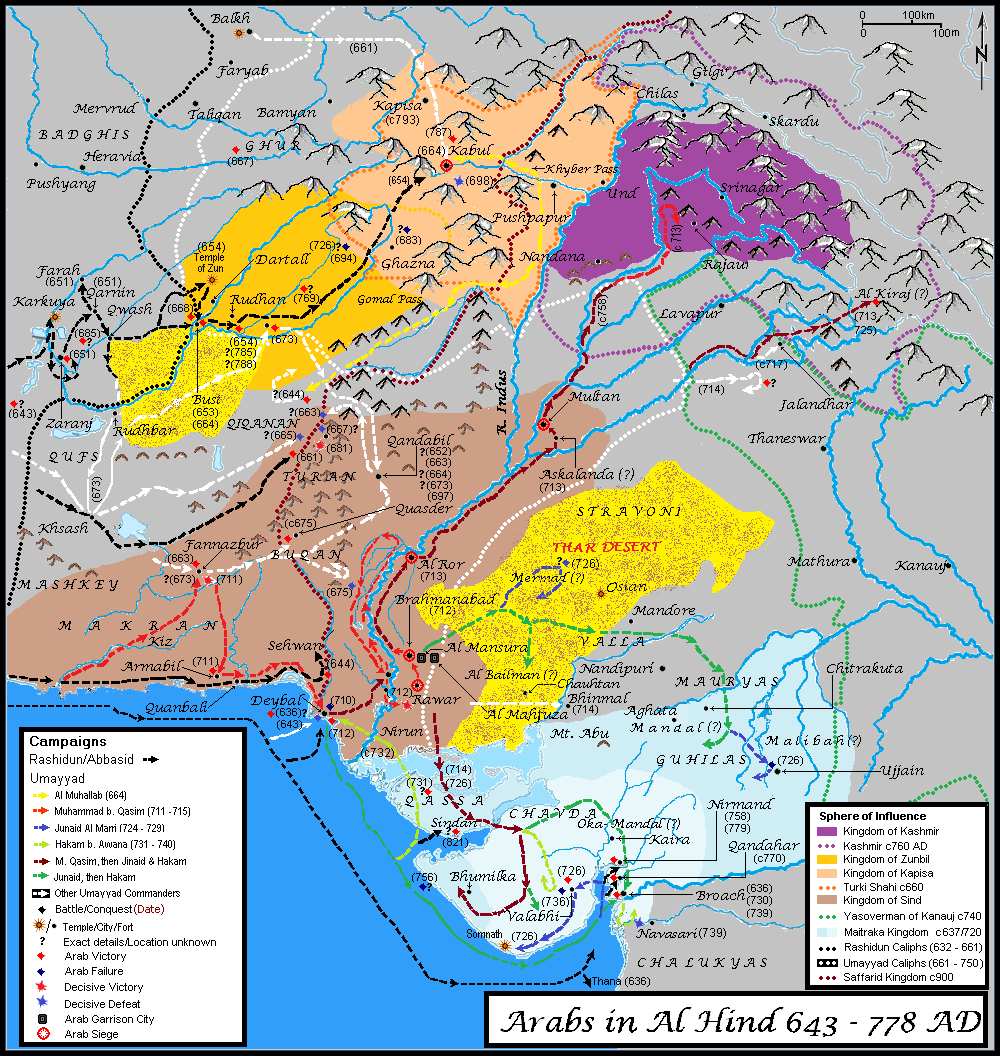
Muslim Conquests In The Indian Subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place between the 13th and the 18th centuries, establishing the Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Indo-Muslim period. Early Muslim conquests, Earlier Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent include the invasions which started in the Northwest India (pre-1947), northwestern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Pakistan), especially the Umayyad campaigns in India, Umayyad campaigns during the 8th century. Mahmud of Ghazni, sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the Abbasid caliph, Abbasid Caliphate and invaded vast parts of Punjab and Gujarat during the 11th century. After the capture of Siege of Lahore (1186), Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim rule in India in 1192. In 1202, Bakhtiyar Khalji led the Muslim conquest of Bengal, marking the easternmost expansion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chauhan Dynasty
Chauhan, a name derived from the historical Chahamanas of Shakambhari, Chahamanas, a clan name associated with various ruling Rajput families in the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan from seventh century onwards. Subclans Khichi Chauhan, Khichi, Hada Chauhan, Hada, Songara, Bhadauria, Devda, Devda (Clan), Nirban etc. are the branches or subclans of Chauhan Rajputs. Origin The word ''Chauhan'' is the vernacular form of the Sanskrit term ''Chahamana'' (IAST: Cāhamāna). Several Chauhan inscriptions name a legendary hero called Chahamana as their ancestor, but none of them state the period in which he lived. The earliest extant inscription that describes the origin of the Chauhans is the 1119 CE Sewari, Sevadi inscription of Ratnapala (Chahamana dynasty), Ratnapala, a ruler of the Chahamanas of Naddula, Naddula Chahamana dynasty. According to this inscription, the ancestor of the Chahamanas was born from the eye of Indra. The 1170 CE Bijolia rock inscription of the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasions Of India
The Mongol invasions of India were numerous invasions that the Mongol Empire launched into the Indian subcontinent from 1221 to 1327, with many of the later raids made by the Qara'unas of Mongol origin. The Mongols occupied parts of the subcontinent for decades. As the Mongols progressed into the Indian hinterland and reached the outskirts of Delhi, the Delhi Sultanate of India led a campaign against them in which the Mongol army suffered serious defeats. Delhi Sultanate officials viewed war with the Mongols as one of the sultan's primary duties. While the sultanate's chroniclers described the conflicts between the Tengrist Mongols and Muslim community in binary terms, with the Delhi Sultanate being an island of Islamic civilization surrounded by Hindus and Buddhist to its north and south, it ignored the fact that a large number of the sultanate's elites and monarchs were of Turkic/Mongol ethnicity or had previously served in their armed contingents. Background After pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abohar
Abohar is a city and municipal corporation in the Fazilka district of the Indian state of Punjab, southeast of Fazilka city and northeast of Sri Ganganagar. It is near the India-Pakistan border. Abohar's population was 145,302 as of 2011. The city and its suburb is known for kinnow production and accounts for 60% of the country's produce. The modern abohar was developed by the britishers on the Motif of Paris. History Late Medieval Era Abohar was founded by Abhiraj Bhatti, a Rajput ruler, in the 12th century and was known as Abhegarh at that time. During that era, the Delhi Sultanate ruled over present-day India. Abohar was an important military and trade hub during the Sultanate period due to its strategic location on the medivial highway, and connected the mouth of the river Indus via Multan to Delhi. In the 13th-14th centuries, it was a dominance of Raja Mal Bhatti. Connections with Firoz Shah Tughluq This city developed a deeper connection with Tughluqs. Firoz S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanumangarh
Hanumangarh is a city and municipal council in the Indian state of Rajasthan, situated on the banks of the river Ghaggar also identified as ancient Sarasvati river, located about 400 km from Delhi. It is the administrative headquarter of Hanumangarh District. The city was once called Bhatner (alternatively spelled Bhatnair) because it was founded by king Bhupat in 255 AD. It remained in the control of the Rajputs of Bhati clan and faced a historic siege by Timur in 1391, during which the Bhati Raput king Dulachand lost the fort for a short time. The fort was later occupied by Rao Jetsa of Bikaner. History Indus Valley Civilization Indus Valley Civilization sites in the district number over 100 villages along Ghaggar-Hakra River ( Palaeochannel of Sarasvati River), such as Karanpura. Remains found at Kalibangan and Pilibanga in 1951 reveal that this area was a part of nearly 5000 years old civilisation. The remains of human skeleton, unknown scripts, stamps, coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirsa
Sirsa is a city and a municipal council in Sirsa district in the westernmost region of the Indian state of Haryana, bordering Punjab and Rajasthan. It is located near the Thar Desert, 250 kilometres north-west of New Delhi and 260 kilometers south-west of state capital Chandigarh. Sirsa's nearest cities include Hisar, Fatehabad, Ellenabad, Bhadra, Nohar, Mandi Dabwali and Hanumangarh. Its history dates back to the time of the Mahabharata. At one time, the Sarasvati River flowed in this area. Name Sirsa has been identified with two earlier names: ''Sarsūti'' in medieval sources and ''Śairīṣaka'' in ancient literature. ''Sarsūti'' appears to come from the name of the Sarasvati River, which once flowed near Sirsa. Ancient texts mentioning ''Śairīṣaka'' include the ''Mahābhārata'', where it is mentioned as one of the places conquered by Nakula; the ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' of Pāṇini; and the '' Divyāvadāna''. The name ''Śairīṣaka'' may be derived from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doab
''Doab'' () is a term used in South Asia Quote: "Originally and chiefly in South Asia: (the name of) a strip or narrow tract of land between two rivers; spec. (with) the area between the rivers Ganges and Jumna in northern India." for the tract Quote: "confluence, land between two rivers, used in India of the tongue of land between the Ganges and Jumna, and of similar tracts in the Punjab, etc., lit. ‘two waters’ " of land lying between two confluent rivers. It is similar to an interfluve. Quote: " a tract of land between two rivers : interfluve" In the ''Oxford Hindi-English Dictionary'', R. S. McGregor refers to its Persian origin in defining it as ''do-āb'' (, literally "two odies ofwater") "a region lying between and reaching to the confluence of two rivers." Khadir, bangar, barani, nali and bagar Since North India and Pakistan are coursed by a multiplicity of Himalayan rivers that divide the plains into ''doabs'' (i.e. regions between two rivers), the Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
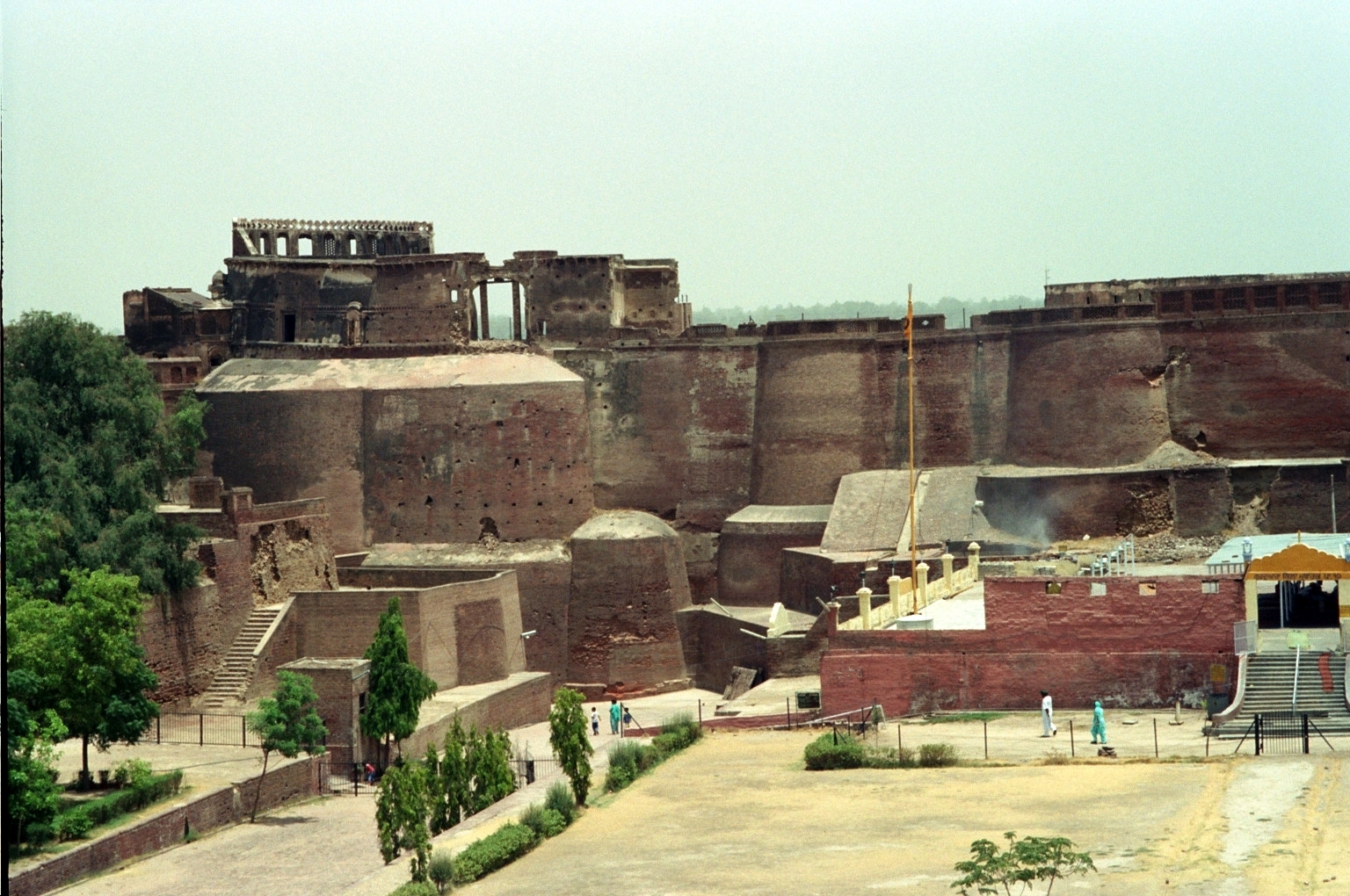
Bhatner Fort
The Bhatner Fort was built by son of Rao Bhati, about 419 km northwest of Jaipur along the old Multan-Delhi route and 230 km north-east of Bikaner. Another name of Hanumangarh was Bhatner, which means "fortress of the Bhati". Believed to be 1700 years old, it is considered to be one of the oldest forts of India. History The ancient fort situated on the bank of River Ghaggar, was built in 295 AD by the King Bhupat of Bhati Dynasty, in memory of his father, Rao Bhatti. There he constructed a safe castle for himself which came to be known as Bhatner. The entire fort is built of bricks, covering an area of 52 bighas. It is in the shape of a parallelogram, with a dozen bastions on each side. Painted Grey Ware (circa 1100-800 BCE) and Rang-Mahal Ware (1st-3rd century CE) have been found in wells situated along the wall. Bhatner was wrested by Timur by defeating Bhatti King Rai Dul Chand. A mention has been made in "Tuzuk-e-Timuri" (Autobiography of Timur) about this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathinda
Bathinda is a city and municipal corporation in Punjab, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of Bathinda district. It is located in northwestern India in the Malwa Region, west of the capital city of Chandigarh and is the fifth largest city of Punjab. It is the second cleanest city in Punjab after Mohali. Bathinda is home to the Maharaja Ranjit Singh Punjab Technical University, Central University of Punjab and AIIMS Bathinda. The city is also home to two modern thermal power plants, Guru Nanak Dev Thermal Plant and Guru Hargobind Thermal Plant at Lehra Mohabbat. Also located in the city is a fertiliser plant, two cement plants ( Ambuja Cements and UltraTech Cement Limited), a large army cantonment, an air force station, a zoo, and a historic Qila Mubarak fort. History Bhatinda was changed to Bathinda to conform to the phonetical expression as locally pronounced. According to Henry George Raverty, Bathinda was known as ''Tabar-i-Hind'' (Labb-ut-Twarikh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakhi Jungle (jungle)
Lakhi Jungle, also known as Lakhi Jangali, was a historical jungle located in present-day Punjab, India. It should not be confused with the historical Machhiwara (jungle), Machhiwara jungle. The region was referred to as the Lakhi-Jangal tract. A number of toponyms of ''Pargana, parganas'' were recorded in Mughal documents bearing the ''Lakhi'' suffix. History A jungle formed in this area due to the shifting course of the Sutlej, Sutlej river. A Bhati, Bhatti chief, named Rana Lakhi, is said to have settled in the area of the Lakhi Jungle around the turn of the millennium between the 10th and 11th centuries. During the Mughal-period, the Lakhi Jungle was a ''Faujdar, faujdari''-district under the Birun-Panjnad area of the Dipalpur Sarkar of Subah of Multan, Multan Subah. The ninth Sikh Guru, Guru Teg Bahadur and tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh visited this place. During the time period of Guru Gobind Singh and later, the area of the later Firozpur division was covered by a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |