|
Bengal (other)
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bangla/Bôngô, ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Northeastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Bengal proper is divided between modern-day Bangladesh and the States and union territories of India, Indian state of West Bengal. The Indian states of Assam, Jharkhand and Tripura have a sizeable Bengali population. A large Bengali diaspora exists across the world. Bengali language, Bengali is the List of languages by number of native speakers, sixth-most spoken language in the world. Various Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan, Dravidian peoples, Dravidian, Austric and other peoples inhabited the region since antiquity. The ancient Vanga Kingdom is widely regarded as the namesake of the Bengal region. The Bengali calendar dates back to the reign of Shashanka in the 7th century. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of first-speakers are Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi first language: 260.3 million (2001), as second language: 120 million (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Bengal) encompassing much of the Bengal region, which includes modern Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, Indian state of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odissa between the 16th and 18th centuries. The state was established following the dissolution of the Bengal Sultanate, a major trading nation in the world, when the region was absorbed into one of the gunpowder empires. Bengal was the wealthiest region in the Indian subcontinent, due to their thriving merchants, Seth's, Bankers and traders and its proto-industrial economy showed signs of driving an Industrial revolution. Bengal Subah has been variously described the "Paradise of Nations" and the "Golden Age of Bengal", due to its inhabitants' living standards and real wages, which were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessible only by the Indian subcontinent and the sea. The region now forms the Rakhine State in Myanmar. Arakan became one of the earliest regions in Southeast Asia to embrace Dharmic religions, particularly Buddhism and Hinduism. Islam arrived with Arab merchants in the 8th century. The Kingdom of Mrauk U emerged as an independent Arakanese kingdom for 300 years. During the Age of Discovery and Bengal Subah's major economic development, Arakan caught the interest of the Dutch East India Company and the Portuguese Empire. In the middle of the 17th century, it was dominated by the Islamic Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. Arakan steadily declined from the 18th century onwards after its loss to the Mughal Empire. After conquest by the British East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic World
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In a modern geopolitical sense, these terms refer to countries in which Islam is widespread, although there are no agreed criteria for inclusion. The term Muslim-majority countries is an alternative often used for the latter sense. The history of the Muslim world spans about 1,400 years and includes a variety of socio-political developments, as well as advances in the arts, science, medicine, philosophy, law, economics and technology, particularly during the Islamic Golden Age. All Muslims look for guidance to the Quran and believe in the prophetic mission of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, but disagreements on other matters have led to the appearance of different religious schools of thought and sects within Islam. In the modern era, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta, with a network of mint towns spread across the region. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states, including Odisha in the southwest, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. Its raids and conquests reached Nepal in the north, Assam in the east, and Jaunpur and Varanasi in the west. The Bengal Sultanate controlled large parts of the north, east and northeast Indian subcontinent during its five dynastic periods, reaching its peak under Hussain Shahi dynasty. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation and one of Asia's strongest states. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Suri Empire, followed by Mughal conquest and disintegration into petty kingdoms. The Ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
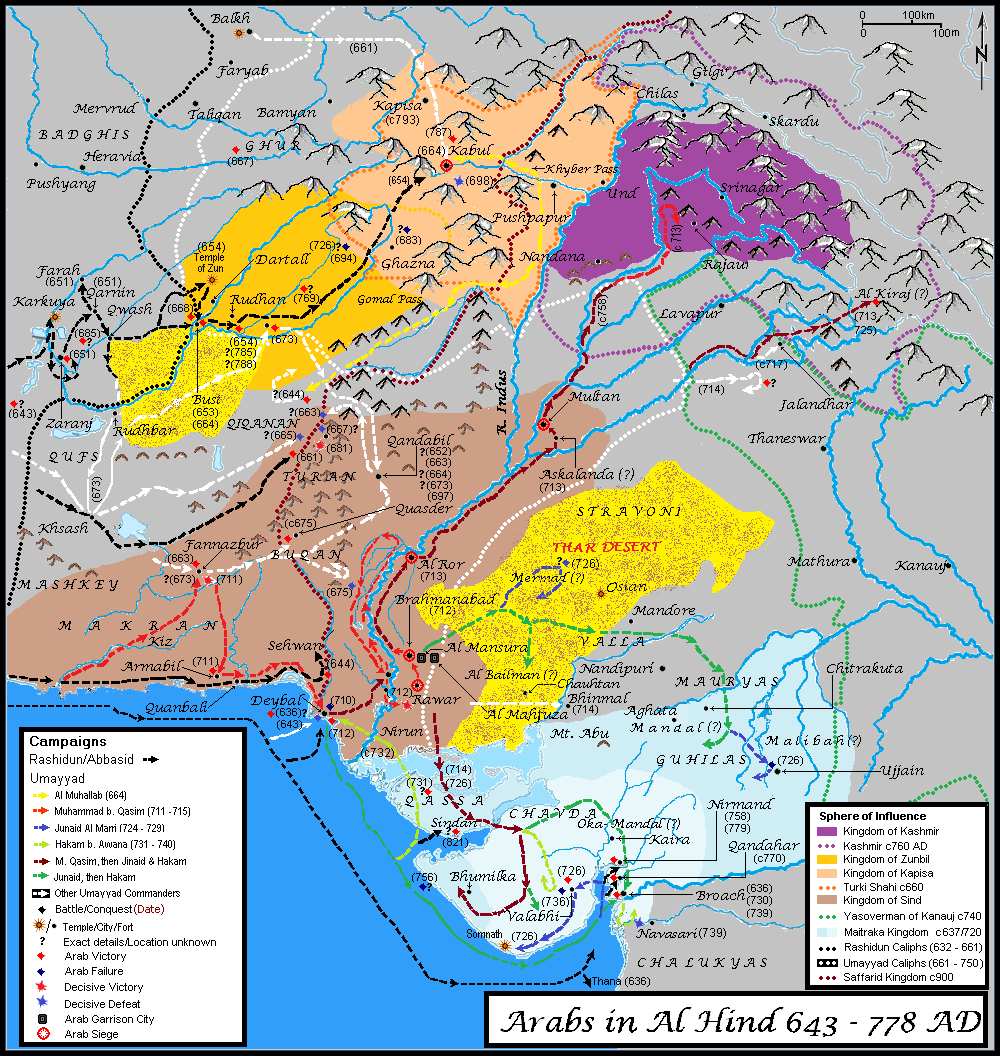
Muslim Conquests In The Indian Subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place from the 13th to 17th centuries. Earlier Muslim conquests include the invasions into what is now modern-day Pakistan and the Umayyad campaigns in India in eighth century and resistance of Rajputs to them. Mahmud of Ghazni, who was the first Sultan, and preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the Abbasid Caliphate, invaded and plundered vast parts of Punjab and Gujarat, starting from the Indus River during the 11th century. After the capture of Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of Muslim rule in India. In 1206, Bakhtiyar Khalji led the Muslim conquest of Bengal, marking the easternmost expansion of Islam at the time. The Ghurid Empire soon evolved into the Delhi Sultanate, ruled by Qutb ud-Din Aibak, the founder of the Mamluk dynasty. With the Delhi Sultanate established, Islam was spread across most parts of the Indian subcontinent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sena Dynasty
The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. The rulers of the Sena Dynasty traced their origin to the south Indian region of Karnataka. The dynasty's founder was Samanta Sena. After him came Hemanta Sena who usurped power and styled himself, king, in 1095 AD. His successor Vijaya Sena (ruled from 1096 AD to 1159 AD) helped lay the foundations of the dynasty, and had an unusually long reign of over 60 years. Ballala Sena conquered Gaur from the Pala, became the ruler of the Bengal Delta, and made Nadia the capital as well. Ballala Sena married Ramadevi a princess of the Western Chalukya Empire which indicates that the Sena rulers maintained close social contact with south India. Lakshmana Sena succeeded Ballala Sena in 1179, ruled Bengal for approximately 20 years, and ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix ''Pāla'' ("protector" in Prakrit). The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century AD. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati ( Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jaggadala. The Pālas were astute diplomats and military conquerors. Their army was noted for its vast war elephant corps. Their navy performed both mercantile and defensive roles in the Bay of Bengal. At its zenith under emperors Dharmapala and Devapala in the early ninth century, the Pala empire extended their dominance into the northern Indian region, with its territory stretching across the Gangetic pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shashanka
Shashanka ( IAST: Śaśāṃka) was the first independent king of a unified polity in the Bengal region, called the Gauda Kingdom and is a major figure in Bengali history. He reigned in the 7th century, some historians place his rule between circa 600 CE and 636/7 CE, whereas other sources place his reign between 590 and 625 CE. Shashanka, is credited with creating the Bengali calendar. The term Bangabda (Bangla year) is found too in two Shiva temples many centuries older than Akbar era, suggesting that a Bengali calendar existed long before Akbar's time.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Jyotisha" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , pages 326–327 He is the contemporary of Harsha and of Bhaskaravarman of Kamarupa. His capital was at Karnasubarna, in present-day Murshidabad in West Bengal. Contemporary sources There are several major contemporary sources of information on his life, including copperplates from his vassal Madhavavarma (king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Calendar
The Bengali Calendar or Bangla Calendar ( bn, বঙ্গাব্দ , , Baṅgābda), colloquially ( bn, বাংলা সন, Baṅgla Śon), is a solar calendar used in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. A revised version of the calendar is the national and official calendar in Bangladesh and an earlier version of the calendar is followed in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam. The New Year in the Bengali calendar is known as '' Pohela Boishakh''. The Bengali era is called ''Bengali Sambat'' (BS) or the ''Bengali year'' ( ''Bangla Sôn'', ''Bangla sal'', or ''Bangabda'') has a zero year that starts in 593/594 CE. It is 594 less than the AD or CE year in the Gregorian calendar if it is before ''Pôhela Bôishakh'', or 593 less if after ''Pôhela Bôishakh''. The revised version of the Bengali calendar was officially adopted in Bangladesh in 1987. Among the Bengali community in India, the traditional Indian Hindu calendar continues to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |