|
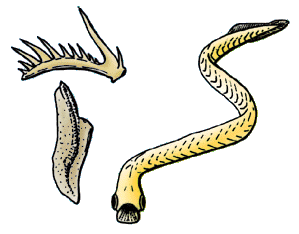
Belemnite
Belemnitida (or belemnites) is an extinct order (biology), order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous (And possibly the Eocene). Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip, the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcite, calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than , though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey. Belemnites were an important food source for many Mesozoic marine creatures, both the adults and the planktonic juveniles and they likely played an important role in restructuring marine ecosystems after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. They may have laid between 100 and 1,000 eggs. Some species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnoidea
Belemnoids are an extinct group of marine cephalopod, very similar in many ways to the modern squid. Like them, the belemnoids possessed an ink sac, but, unlike the squid, they possessed ten Cephalopod arm, arms of roughly equal length, and no tentacles. The name "belemnoid" comes from the Greek word βέλεμνον, ''belemnon'' meaning "a dart or arrow" and the Greek word είδος, ''eidos'' meaning "form". Belemnoids include Belemnitida, belemnites (which belong to the Order (biology), order Belemnitida), aulacocerids (order Aulacocerida), phragmoteuthids (order Phragmoteuthida), and diplobelids (order Diplobelida). Belemnoidea has been suggested to be paraphyletic by some authors. Occurrence Belemnoids were numerous during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and their fossils are abundant in Mesozoic marine rocks, often accompanying their cousins the ammonites. The belemnoids become extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period along with the ammonites. The belemnoids' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnitina
Belemnitina is a suborder of belemnites, an extinct group of cephalopods. They have been identified as the oldest of all the belemnites and are likely the stockgroup for them. They were extant from the early Jurassic to the early Cretaceous. Their geographic distribution was mostly limited to Europe, although specimens have been described in Japan suggesting they may have been more widespread than previously thought. Morphology They have a broad, rounded pro-ostracum (the section of the guard (the hard internal skeleton commonly fossilised) closest to the head of the living animal). This characteristically lacks longitudinal alveolar canals and the associated splitting surfaces or open fissures. Commonly there are one or more longitudinal furrows in the apical region of the guard, similar furrows may be found in the alveolar region, these would not be accompanied by splitting surfaces or open fissures. Distribution Based on current evidence it appears that the Belemnitina were m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megateuthis Elliptica
''Megateuthis'' is the largest known belemnite genus which lived during the Early to Middle Jurassic, between the Toarcian and Bajocian age. The type species ''M. suevica'', whose junior synonym is ''M. gigantea'', measured around long, and the largest species ''M. elliptica'' possibly reached up to long. See also * Cephalopod size * List of belemnites This list of belemnite genera is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as we ... References Jurassic cephalopods Jurassic animals of Asia Jurassic animals of Europe Belemnoidea Belemnites {{cephalopod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passaloteuthis
''Passaloteuthis'' is a genus of belemnite, an extinct group of cephalopods. Belemnites are typically known for having about 40 micro-hooks on each one of its appendage. However, ''Passaloteuthis'' is notable for being associated with a pair of mega-hooks known as onychites. These hooks are tentatively interpreted as male-specific features, though their exact function is still unknown. See also * Belemnite * List of belemnites This list of belemnite genera is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as we ... References Belemnites {{paleo-cephalopod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symmetry, bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of cephalopod arm, arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt Cephalopod ink, ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, Extant taxon, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus (genus), Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleoidea
Coleoidea or Dibranchiata is one of the two subclasses of cephalopod molluscs containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less" (i.e. octopus, squid and cuttlefish). Unlike its extant sister group Nautiloidea, whose members have a rigid outer shell for protection, the coleoids have at most an internal shell called cuttlebone or gladius that is used for buoyancy or as muscle anchorage. Some species, notably incirrate octopuses, have lost their internal shell altogether, while in some it has been replaced by a chitinous support structure. The major divisions of Coleoidea are based upon the number of arms or tentacles and their structure. The extinct and most primitive form, the Belemnoidea, presumably had ten equally-sized arms in five pairs numbered dorsal to ventral as I, II, III, IV and V. More modern species either modified or lost a pair of arms. The superorder Decapodiformes has arm pair IV modified into long tentacles w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnian
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Triassic series (stratigraphy), Series (or earliest age (geology), age of the Late Triassic Epoch (reference date), Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227.3 megaannum, million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event (known as the Carnian pluvial episode characterized by substantial rainfall) occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Another extinction occurred at the Carnian-Norian boundary, ending the Carnian age. Stratigraphic definitions The Carnian was named in 1869 by Johann August Georg Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar, Mojsisovics. It is unclear if it was named after the Carnic Alps or after the Austrian region of Carinthia (state), Carinthia (''Kärnten'' in German) or after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littoral Zone
The littoral zone, also called litoral or nearshore, is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely flood, inundated), to coastal areas that are permanently underwater, submerged — known as the ''foreshore'' — and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the geographical meaning of ''littoral zone'' extends well beyond the intertidal zone to include all neritic waters within the bounds of continental shelves. Etymology The word ''littoral'' may be used both as a noun and as an adjective. It derives from the Latin language, Latin noun ''litus, litoris'', meaning "shore". (The doubled ''t'' is a late-medieval innovation, and the word is sometimes seen in the more classical-looking spelling ''litoral''.) Description The term has no single definition. What is regarded as the full extent of the littoral zone, and the way the littora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Journal Of Palaeontology
The ''Swiss Journal of Palaeontology'' is a biannual open access peer-reviewed scientific journal covering palaeontology and taxonomy published by BioMed Central. It is affiliated with the Swiss Geological Society and a member of the Swiss Academy of Sciences. History The journal was established as ''Schweizerische Paläontologische Abhandlungen'' in 1874 and was published by the Natural History Museum of Basel. In 2011, it was relaunched as the ''Swiss Journal of Palaeontology'' and publisher became BioMed Central. Since 2020 the journal is open access. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.0. References Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm, the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leukocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ) was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopus
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used for respiration and locomotion (by water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, and are short-lived. In most species, the male uses a speciall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic–Jurassic Extinction Event
The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event (TJME), often called the end-Triassic extinction, marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, . It represents one of five major extinction events during the Phanerozoic, profoundly affecting life on land and in the oceans. In the seas, about 23–34% of marine genus, genera disappeared; Coral, corals, Bivalvia, bivalves, Brachiopod, brachiopods, Bryozoa, bryozoans, and Radiolaria, radiolarians suffered severe losses of diversity and Conodont, conodonts were completely wiped out, while marine vertebrates, Gastropoda, gastropods, and benthic foraminifera were relatively unaffected. On land, all Archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptiles other than Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorphs, dinosaurs, and pterosaurs became extinct. Crocodylomorphs, dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and mammals were left largely untouched, allowing them to become the dominant land animals for the next 135 million years. Plants were likewise significantly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |