|
Beacon Limestone Formation
The Beacon Limestone Formation, historically known as the Junction Bed, is a formation (geology), formation of early Jurassic age (PliensbachianāToarcian). It lies above the Dyrham Formation and below the Bridport Sand Formation. It forms part of the Lias Group. It is found within the Wessex Basin and parts of Somerset, in England. It is well known for the Strawberry Bank LagerstƤtte, which contains the 3-dimensionally preserved remains of vertebrates, including marine crocodyliformes, ichthyosaurs and fish, as well as insect compression fossils. Fossil content Among others, the following fossils have been reported from the formation: Vertebrates Invertebrates References Geologic formations of England Jurassic System of Europe Jurassic England Pliensbachian Stage Toarcian Stage Limestone formations Shallow marine deposits Paleontology in England Geology of Dorset Geology of Somerset {{geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorncombe Beacon
Thorncombe Beacon is a hill between Bridport and Charmouth in Dorset, England. It lies about west of Eype Mouth and east of Seatown. It is in the south-west part of Symondsbury parish close to the parish of Chideock. It is high, compared to for Golden Cap which lies about to the west. It forms part of the Jurassic Coast, a World Heritage Site and the South West Coast Path and the Monarch's Way skirt the hilltop. The hill is owned by the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust. Three bowl barrows to the north-east of the summit constitute a scheduled monument. References {{Jurassic Coast Headlands of Dorset Hills of Dorset National Trust properties in Dorset Jurassic Coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenopterygius
''Stenopterygius'' is an extinct genus of thunnosaur ichthyosaur known from Europe (England, France, Germany, Luxembourg and Switzerland). This genus of ichthyosaur was about long and weighed .Huene F. von 1939. Ein ganzes Ichthyosaurier-Skelett aus den westschweizerischen Voralpen. ''Mitteilungen der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Bern'' 1939, pp.: 1-14McGowan C, Motani R. 2003. Ichthyopterygia. ā In: Sues, H.-D. (ed.): ''Handbook of Paleoherpetology, Part 8, Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil'', 175 pp., 101 figs., 19 plts; MĆ¼nchen History ''Stenopterygius'' was originally named by Quenstedt in 1856 as a species of ''Ichthyosaurus'', ''I. quadriscissus''. Otto Jaekel in 1904 reassigned it to its own genus, ''Stenopterygius''. The type species is therefore ''Stenopterygius quadriscissus''. The generic name is derived from ''stenos'', Greek for "narrow", and ''pteryx'' (ĻĻĪµĻĻ Ī¾), Greek for "fin" or "wing". Description ''Stenopterygius'' was physically similar to the bette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earwig
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forcep-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short, rarely used forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs are found on all continents except Antarctica. Earwigs are mostly nocturnal and often hide in small, moist crevices during the day, and are active at night, feeding on a wide variety of insects and plants. Damage to foliage, flowers, and various crops is commonly blamed on earwigs, especially the common earwig '' Forficula auricularia.'' Earwigs have five molts in the year before they become adults. Many earwig species display maternal care, which is uncommon among insects. Female earwigs may care for their eggs, and even after they have hatched as nymphs will conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermapteridae
Dermapteridae is an extinct family of earwigs known from the Late Triassic to Mid Cretaceous, it is part of the extinct suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Protodiplatyidae and '' Turanovia.'' It was first named as a subfamily by Vishniakova in 1980, and elevated to family status by Engel in 2003 without discussion. Systematics * ā '' Brevicula'' Whalley, 1985 Charmouth Mudstone Formation, United Kingdom, Early Jurassic (Sinemurian) *ā '' Dacryoderma'' Engel, 2021 Charmouth Mudstone Formation, United Kingdom, Sinemurian * ā '' Dermapteron'' Martynov, 1925 Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Middle-Late Jurassic (Callovian/ Oxfordian) * ā '' Dimapteron'' Kelly et al. 2018 Durlston Formation, United Kingdom, Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) * ā '' Jurassimedeola'' Zhang, 2002 Daohugou, China, Callovian * ā '' Palaeodermapteron'' Zhao et al. 2011 Daohugou, China, Callovian * ā '' Phanerogramma'' Cockerell, 1915 Blackstone Formation, Australia, Late Triassic (Norian) Westbury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiiformes
The Amiiformes order of fish has only one extant species, the bowfin (''Amia calva''). These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems of North America, in the United States and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, rivers, and swamps. Bowfins are not on the endangered list. They have the ability to go to the surface to breathe air if the water level is too low. Characteristics of Amiiformes are a cylindrical body with a long dorsal fin, single gular plate, heterocercal caudal fin, 10 to 13 flattened branchiostegal rays, maxilla included in gape, and prominent ocellus near upper base of caudal fin. Evolution and diversity The extinct species of the Amiiformes can be found as fossils in Asia and Europe, but the bowfin is the last living species in the order. Amiiformes is therefore the last surviving order of Halecomorphi, the clade to which the bowfin and its fossil relatives belong. Other orders, such as the Parasemionotiformes, are all extinct. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caturus
''Caturus'' (from el, ĪŗĪ±ĻĻ , 'down' and el, Īæį½ĻĪ¬ 'tail') is an extinct genus of fishes in the family Caturidae in the order Amiiformes, related to modern bowfin. Fossils of this genus range from 200 to 109 mya. It has been suggested that the genus is non-monophyletic with respect to other caturid genera. Species * '' Caturus agassizi'' * ''Caturus chaperi'' * ''Caturus chirotes'' * ''Caturus dartoni'' * ''Caturus ferox'' * ''Caturus furcatus'' * ''Caturus heterurus'' * ''Caturus insignis'' * ''Caturus latipennis'' * ''Caturus porteri'' * ''Caturus retrodorsalis'' * ''Caturus stenospondylus'' * ''Caturus stenoura'' * ''Caturus velifer'' Distribution This genus is present in the Cretaceous of Germany, Japan, Spain, Tunisia, the United Kingdom, from the Jurassic to Cretaceous of France and the Permian of China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidotes
''Lepidotes'' (from el, Ī»ĪµĻĪ¹Ī“ĻĻĻĻ , 'covered with scales') (previously known as ''Lepidotus'') is an extinct genus of Mesozoic ray-finned fish. It has been considered a wastebasket taxon, characterised by "general features, such as thick rhomboid scales and, for most of the species, by semi-tritorial or strongly with dozens of species assigned to it. Fossils attributed to ''Lepidotes'' have been found in Jurassic and Cretaceous rocks worldwide.LĆ³pez-Arbarello, A. (2012).Phylogenetic Interrelationships of Ginglymodian Fishes (Actinopterygii: Neopterygii). ''PLoS One'', 7(7): e39370. It has been argued that ''Lepidotes'' should be restricted to species closely related to the type species ''L. gigas,'' which are only known from the Early Jurassic of Central Europe, with most other species being not closely related, with other species transferred to new genera such as '' Scheenstia.'' ''Lepidotes'' belongs to Ginglymodi, a clade of fish whose only living representatives ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptolepis
''Leptolepis'' (from el, Ī»ĪµĻĻĻĻ , 'slight' and el, Ī»ĪµĻĪÆĻ 'scale') is an extinct genus of stem- teleost fish that lived in what is now Europe during the Jurassic period ( Toarcianā Callovian ages). Species The genus ''Leptolepis'' was for a long time used as a wastebasket taxon for various small, unspecialised teleosts that did not form a natural clade. In 1974 the Swedish ichthyologist Orvar Nybelin revised the genus, restricting it to seven species from the Early to Middle Jurassic of Europe. Other species were reassigned to different genera. * ''Leptolepis autissiodorensis'' * ''Leptolepis coryphaenoides'' * ''Leptolepis jaegeri'' * ''Leptolepis nathorsti'' * ''Leptolepis normandica'' * ''Leptolepis saltviciensis'' * ''Leptolepis woodwardi'' Species formerly placed in ''Leptolepis'' * ''Leptolepis talbragarensis'' (Now referred to '' Cavenderichthys'') * ''Leptolepis koonwarri'' (Now referred to '' Waldmanichthys'')Sferco, Emilia, Adriana LĆ³pez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycormus Head (cropped)
Pachycormus is the scientific name for two genera of organisms and may refer to: * ''Pachycormus'' (fish), an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes from the Jurassic * ''Pachycormus'' (plant), a genus of plants in the family Anacardiaceae {{Genus disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
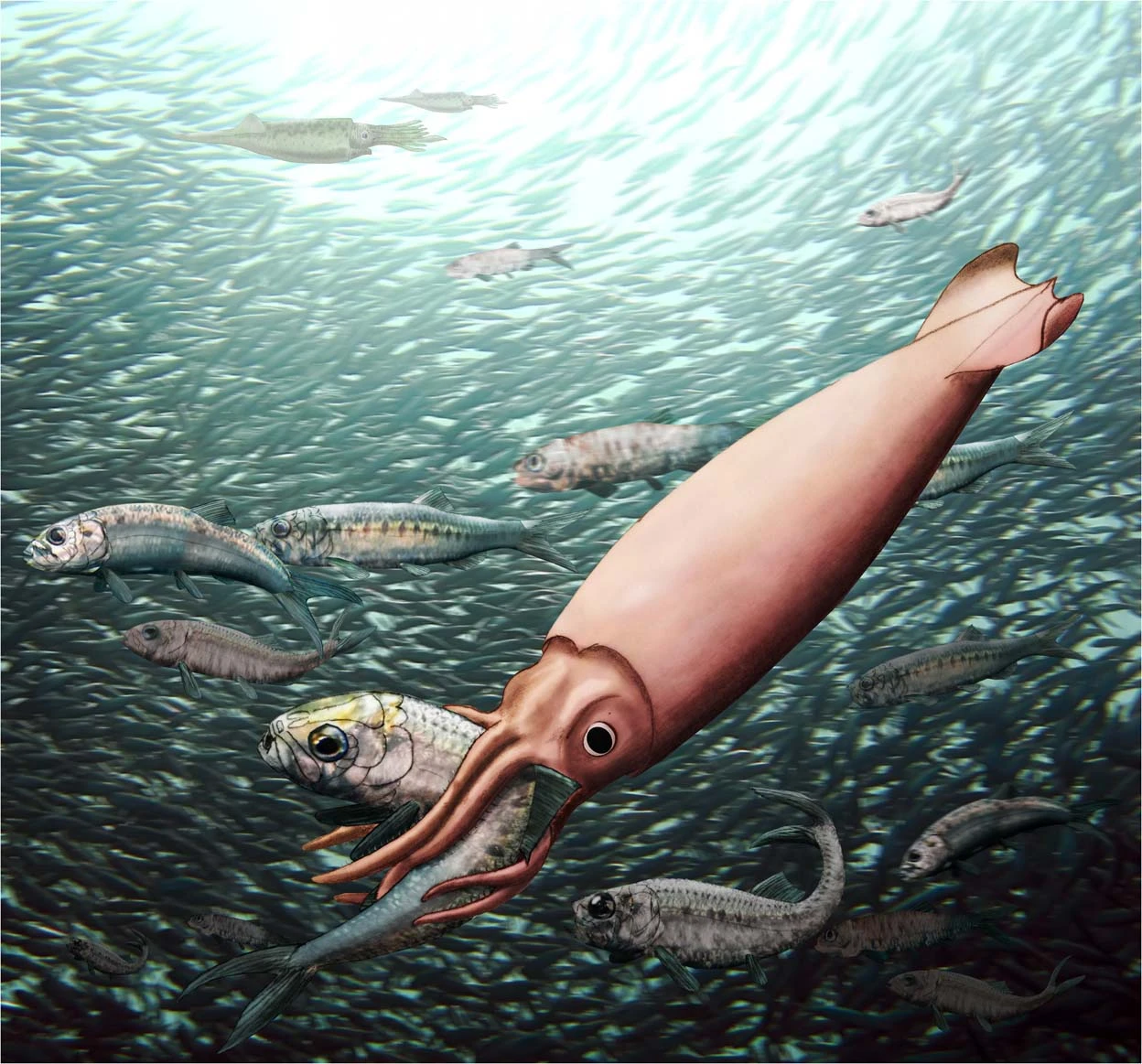
Pachycormiformes
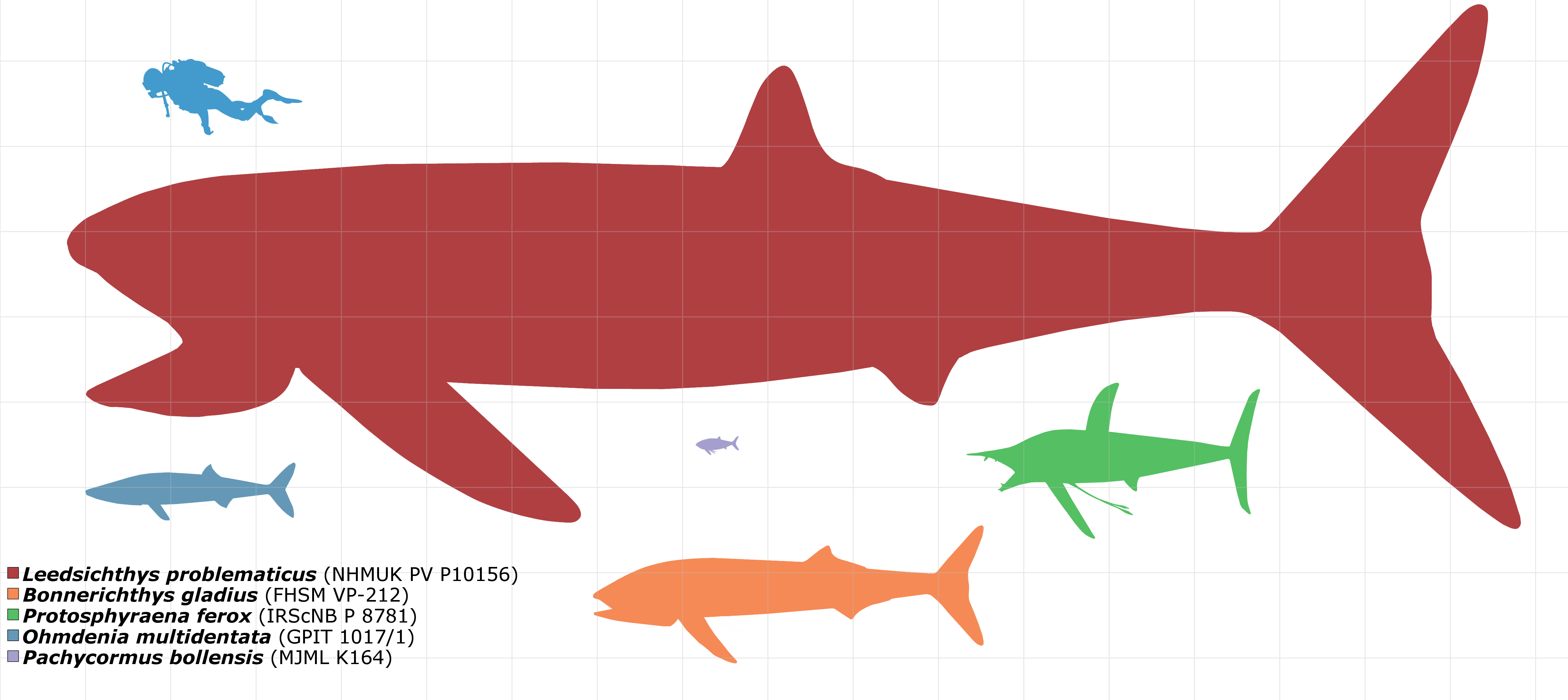
Pachycormiformes is an extinct order of marine ray-finned fish known from the Early Jurassic to the end of the Cretaceous. It only includes a single family, Pachycormidae. They were characterized by having serrated pectoral fins (though more recent studies demonstrated that fin shape diversity in this group was high), reduced pelvic fins and a bony rostrum. Their exact relations with other fish are unclear, but they are generally considered to be teleosteomorphs, more closely related to teleosts than to Holostei. Pachycormiformes are morphologically diverse, containing both tuna and swordfish-like carnivorous forms, as well as edentulous suspension-feeding forms, with the latter including the largest ray finned fish known to have existed, ''Leedsichthys,'' with an estimated maximum length of 16 metres. Synapomorphies Pachycormiformes are united by "a compound bone (rostrodermethmoid) forming the anterodorsal border of the mouth; a reduced coronoid process of the mandible; ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

.jpg)