Earwig on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Earwigs make up the
 The
The
 Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the
Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the
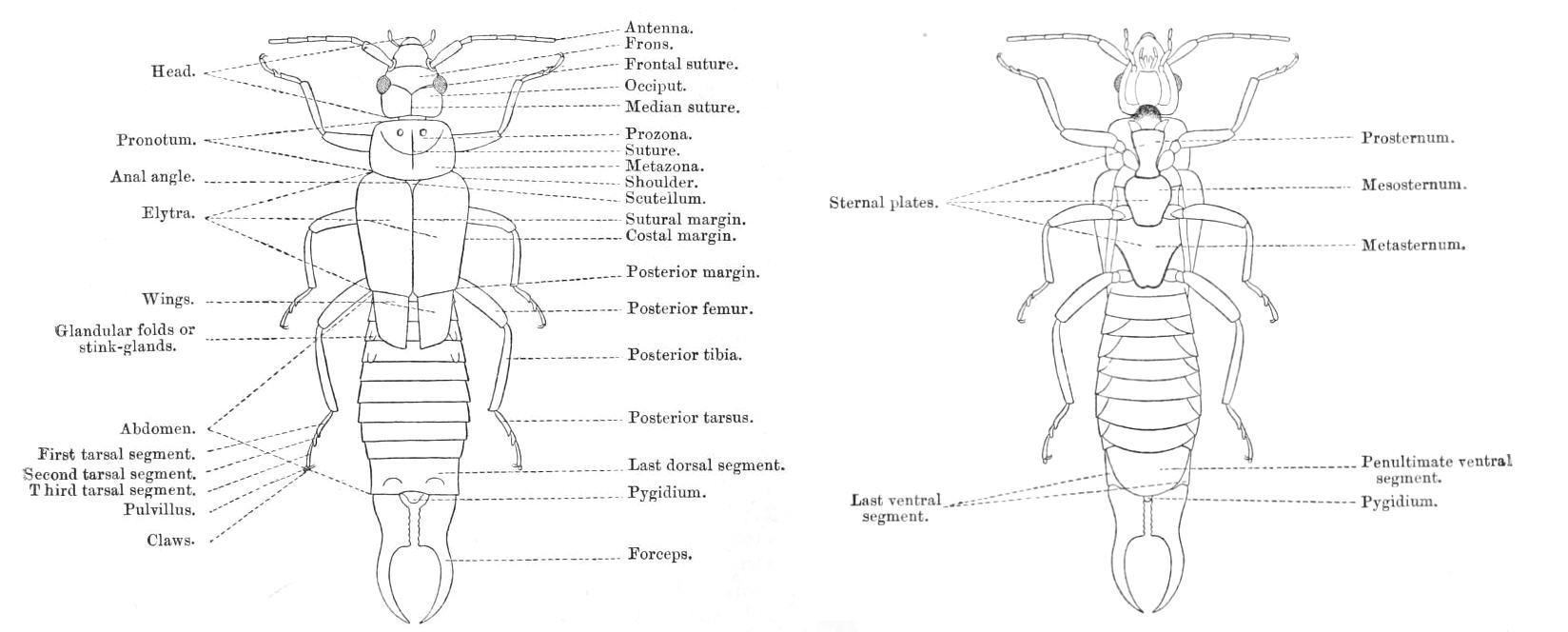 Most earwigs are flattened (which allows them to fit inside tight crevices, such as under bark) with an elongated body generally long. The largest
Most earwigs are flattened (which allows them to fit inside tight crevices, such as under bark) with an elongated body generally long. The largest  The forewings are short oblong leathery plates used to cover the hindwings like the elytra of a beetle, rather than to fly. Most species have short and leather-like forewings with very thin hindwings, though species in the former suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina (epizoic species, sometimes considered as ectoparasites) are wingless and blind with filiform segmented cerci (today these are both included merely as families in the suborder Neodermaptera). The hindwing is a very thin membrane that expands like a fan, radiating from one point folded under the forewing. Even though most earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, they are rarely seen in flight. These wings are unique in venation and in the pattern of folding that requires the use of the cerci.
The forewings are short oblong leathery plates used to cover the hindwings like the elytra of a beetle, rather than to fly. Most species have short and leather-like forewings with very thin hindwings, though species in the former suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina (epizoic species, sometimes considered as ectoparasites) are wingless and blind with filiform segmented cerci (today these are both included merely as families in the suborder Neodermaptera). The hindwing is a very thin membrane that expands like a fan, radiating from one point folded under the forewing. Even though most earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, they are rarely seen in flight. These wings are unique in venation and in the pattern of folding that requires the use of the cerci.
 Earwigs are hemimetabolous, meaning they undergo incomplete metamorphosis, developing through a series of four to six molts. The developmental stages between molts are called
Earwigs are hemimetabolous, meaning they undergo incomplete metamorphosis, developing through a series of four to six molts. The developmental stages between molts are called
File:Nesting Earwig Chester UK 1.jpg, Female earwig in her nest, with eggs
File:Nesting Earwig Chester UK 2.jpg, Female earwig in her nest with newly hatched young
The eggs hatch in about seven days. The mother may assist the nymphs in hatching. When the nymphs hatch, they eat the egg casing and continue to live with the mother. The nymphs look similar to their parents, only smaller, and will nest under their mother and she will continue to protect them until their second molt. The nymphs feed on food regurgitated by the mother, and on their own molts. If the mother dies before the nymphs are ready to leave, the nymphs may eat her.
After five to six
 The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting
The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting
 The fossil record of the Dermaptera starts in the
The fossil record of the Dermaptera starts in the
Google Books
on 25 November 2009. * ''General body shape'': Elongate; dorso-ventrally flattened. * ''Head'': Prognathous. Antennae are segmented. Biting-type mouthparts.
 Dermaptera is relatively small compared to the other orders of
Dermaptera is relatively small compared to the other orders of
Earwig Research Center
by Fabian Haas, Heilbronn
Dermaptera Species File
by Heidi Hopkins, Michael D. Maehr, Fabian Haas, and Lesley S. Deem
on the UF / IFAS Featured Creatures website * Langston RL & JA Powell (1975
The earwigs of California (Order Dermaptera)
Bulletin of the California Insect Survey. 20
Earwigs
from What's That Bug? {{DEFAULTSORT:Earwig Rhaetian first appearances Extant Late Triassic first appearances Exopterygota Polyneoptera
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forceps
Forceps (: forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forcep ...
-like pincer Pincer may refer to:
*Pincers (tool)
*Pincer (biology), part of an animal
*Pincer ligand, a terdentate, often planar molecule that tightly binds a variety of metal ions
*Pincer (Go), a move in the game of Go
*"Pincers!", an episode of the TV series ...
s on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short, rarely used forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs are found on all continents except Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
.
Earwigs are mostly nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
and often hide in small, moist crevices during the day, and are active at night, feeding on a wide variety of insects and plants. Damage to foliage, flowers, and various crops is commonly blamed on earwigs, especially the common earwig ''Forficula auricularia
''Forficula auricularia'' is a species complex comprising the common earwig. It is also known as the European earwig. It is an omnivorous insect belonging to the family Forficulidae. The name ''earwig'' comes from the appearance of the hindwings ...
.''
Earwigs have five molts in the year before they become adults. Many earwig species display maternal care, which is uncommon among insects. Female earwigs may care for their eggs; the ones that do will continue to watch over nymph
A nymph (; ; sometimes spelled nymphe) is a minor female nature deity in ancient Greek folklore. Distinct from other Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature; they are typically tied to a specific place, land ...
s until their second molt. As the nymphs molt, sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
such as differences in pincer shapes begins to show.
Extant Dermaptera belong to the suborder Neodermaptera
Neodermaptera, sometimes called Catadermaptera,BioLib.cz
suborder Catadermaptera Steinmann, 1986 (retrieved 16 Se ...
, which first appeared during the suborder Catadermaptera Steinmann, 1986 (retrieved 16 Se ...
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
. Some earwig specimen fossils are placed with extinct suborders Archidermaptera
Archidermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. It is one of two extinct suborders of earwigs, and contains two families ( Protodiplatyidae and Dermapteridae) known only from Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous fossils.F ...
or Eodermaptera
Eodermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs known from the Middle Jurassic to Mid Cretaceous. Defining characteristics include " tarsi three-segmented, tegmina retain venation, 8th and 9th abdominal tergite in females are narrowed, but separ ...
, the former dating to the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...
and the latter to the Middle Jurassic. Dermaptera belongs to the major grouping Polyneoptera, and are amongst the earliest diverging members of the group, alongside angel insects (Zoraptera
The insect order (biology), order Zoraptera, commonly known as angel insects, contains small and soft bodied insects with two forms: winged with wings sheddable as in termites, dark and with eyes (compound) and ocelli (simple); or wingless, pale ...
), and stoneflies (Plecoptera
Plecoptera is an order (biology), order of insects commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to b ...
), but the exact relationship among the three groups is uncertain.
Etymology
scientific name
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin gramm ...
for the order, ''Dermaptera'', is Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
in origin, stemming from the words , meaning , and (plural ), meaning . It was coined by Charles De Geer in 1773. The common term, ''earwig,'' is derived from the Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, which means , and , which means , or literally, . Entomologists suggest that the origin of the name is a reference to the appearance of the hindwings, which are unique and distinctive among insects, and resemble a human ear when unfolded. The name is more popularly thought to be related to the old wives' tale
An "old wives' tale" is a colloquial expression referring to spurious or superstitious claims. They can be said sometimes to be a type of urban legend, said to be passed down by older women to a younger generation. Such tales are considered super ...
that earwigs burrowed into the brains of humans through the ear and laid their eggs there. Earwigs are not known to purposefully climb into ear canals, but there has been at least one anecdotal report of earwigs being found in the ear.
Distribution
 Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the
Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
and Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
. The common earwig was introduced into North America in 1907 from Europe, but tends to be more common in the southern and southwestern parts of the United States. The only native species of earwig found in the north of the United States is the spine-tailed earwig (''Doru aculeatum''), found as far north as Canada, where it hides in the leaf axils of emerging plants in southern Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s. However, other families can be found in North America, including Forficulidae ('' Doru'' and '' Forficula'' being found there), Spongiphoridae, Anisolabididae, and Labiduridae.
Few earwigs survive winter outdoors in cold climates. They can be found in tight crevices in woodland, fields and gardens. Out of about 1,800 species, about 25 occur in North America, 45 in Europe (including 7 in Great Britain), and 60 in Australia.
Morphology
 Most earwigs are flattened (which allows them to fit inside tight crevices, such as under bark) with an elongated body generally long. The largest
Most earwigs are flattened (which allows them to fit inside tight crevices, such as under bark) with an elongated body generally long. The largest extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species is the Australian giant earwig ('' Titanolabis colossea'') which is approximately long, while the possibly extinct (declared extinct in 2014) Saint Helena earwig (''Labidura herculeana'') reached . Earwigs are characterized by the cerci, or the pair of forceps
Forceps (: forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forcep ...
-like pincers on their abdomen; male earwigs generally have more curved pincers than females. These pincers are used to capture prey, defend themselves and fold their wings under the short tegmina. The antennae are thread-like with at least 10 segments.
Males in the six families Karschiellidae, Pygidicranidae, Diplatyidae, Apachyidae, Anisolabisidae and Labiduridae have paired penises, while the males in the remaining groups have a single penis. Both penises are symmetrical in Pygidicranidae and Diplatyidae, but in Karschiellidae the left one is strongly reduced. Apachyidae, Anisolabisidae, and Labiduridae have an asymmetrical pair, with left and right one pointing on opposite directions when not in use. The females have just a single genital opening, so only one of the paired penises is ever used during copulation.
 The forewings are short oblong leathery plates used to cover the hindwings like the elytra of a beetle, rather than to fly. Most species have short and leather-like forewings with very thin hindwings, though species in the former suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina (epizoic species, sometimes considered as ectoparasites) are wingless and blind with filiform segmented cerci (today these are both included merely as families in the suborder Neodermaptera). The hindwing is a very thin membrane that expands like a fan, radiating from one point folded under the forewing. Even though most earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, they are rarely seen in flight. These wings are unique in venation and in the pattern of folding that requires the use of the cerci.
The forewings are short oblong leathery plates used to cover the hindwings like the elytra of a beetle, rather than to fly. Most species have short and leather-like forewings with very thin hindwings, though species in the former suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina (epizoic species, sometimes considered as ectoparasites) are wingless and blind with filiform segmented cerci (today these are both included merely as families in the suborder Neodermaptera). The hindwing is a very thin membrane that expands like a fan, radiating from one point folded under the forewing. Even though most earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, they are rarely seen in flight. These wings are unique in venation and in the pattern of folding that requires the use of the cerci.
Internal
The neuroendocrine system is typical of insects. There is a brain, a subesophagealganglion
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there are ...
, three thoracic ganglia, and six abdominal ganglia. Strong neuron connections connect the neurohemal corpora cardiaca to the brain and frontal ganglion, where the closely related median corpus allatum produces juvenile hormone III in close proximity to the neurohemal dorsal arota. The digestive system of earwigs is like all other insects, consisting of a fore-, mid-, and hindgut, but earwigs lack gastric caecae which are specialized for digestion in many species of insect. Long, slender (excretory) malpighian tubules
The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulation, osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids and tardigrades. It has also been described in some crustacean species, and is likely the same organ as the ...
can be found between the junction of the mid- and hind gut.
The reproductive system of females consist of paired ovaries, lateral oviducts, spermatheca
The spermatheca (pronounced : spermathecae ), also called ''receptaculum seminis'' (: ''receptacula seminis''), is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, Oligochaeta worms and certain other in ...
, and a genital chamber. The lateral ducts are where the eggs leave the body, while the spermatheca is where sperm is stored. Unlike other insects, the gonopore, or genital opening is behind the seventh abdominal segment. The ovaries are primitive in that they are polytrophic (the nurse cells and oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ger ...
s alternate along the length of the ovariole
An ovariole is a tubular component of the insect ovary, and the basic unit of egg production. Each ovariole is composed of a germarium (the germline Stem-cell niche, stem cell niche) at the anterior tip, a set of developing Oocyte, oocytes containe ...
). In some species these long ovarioles branch off the lateral duct, while in others, short ovarioles appear around the duct.
Life cycle and reproduction
instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'' 'form, likeness') is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, which occurs between each moult (''ecdysis'') until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to ...
s. Earwigs live for about a year from hatching. They start mating in the autumn, and can be found together in the autumn and winter. The male and female will live in a chamber in debris, crevices, or soil deep. After mating, the sperm may remain in the female for months before the eggs are fertilized. From midwinter to early spring, the male will leave, or be driven out by the female. Afterward the female will begin to lay 20 to 80 pearly white eggs in two days. Some earwigs, those parasitic in the suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina, are viviparous (give birth to live young); they would be fed by a sort of placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
. When first laid, the eggs are white or cream-colored and oval-shaped, but right before hatching they become kidney-shaped and brown. Each egg is approximately tall and wide.
Earwigs are among the few non-social insect species that show maternal care. The mother pays close attention to the needs of her eggs, such as warmth and protection. She faithfully defends the eggs from predators, not leaving them even to eat unless the clutch goes bad. She also continuously cleans the eggs to protect them from fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
. Studies have found that the urge to clean the eggs persists for only a few days after they are removed, and does not return even if the eggs are replaced; however, when the eggs were continuously replaced after hatching, the mother continued to clean the new eggs for up to three months.
Studies have also shown that the mother does not immediately recognize her own eggs. After laying them, she gathers them together, and studies have found mothers to pick up small egg-shaped wax balls or stones by accident. Eventually, the impostor eggs were rejected for not having the proper scent.
instars
An instar (, from the Latin ''wikt:instar#Latin, īnstar'' 'form, likeness') is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, which occurs between each ecdysis, moult (''ecdysis'') until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the ...
, the nymphs will molt into adults. The male's forceps will become curved, while the females' forceps remain straight. They will also develop their natural color, which can be anything from a light brown (as in the tawny earwig) to a dark black (as in the ringlegged earwig). In species of winged earwigs, the wings will start to develop at this time. The forewings of an earwig are sclerotized to serve as protection for the membranous hindwings.
Behavior
Most earwigs are nocturnal and inhabit small crevices, living in small amounts of debris, in various forms such as bark and fallen logs. Species have been found to be blind and living in caves, or cavernicolous, reported to be found on the island of Hawaii and in South Africa. Food typically consists of a wide array of living and dead plant and animal matter. For protection from predators, the species '' Doru taeniatum'' of earwigs can squirt foul-smelling yellow liquid in the form of jets from scent glands on the dorsal side of the third and fourth abdominal segment. It aims the discharges by revolving the abdomen, a maneuver that enables it simultaneously to use its pincers in defense. Under exceptional circumstances, earwigs form swarms and can take over significant areas of a district. In August 1755 they appeared in vast numbers near Stroud, Gloucestershire, UK, especially in the cracks and crevices of "old wooden buildings...so that they dropped out oftentimes in such multitudes as to literally cover the floor". A similar "plague" occurred in 2006, in and around a woodland cabin near theBlue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the United States, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern ...
of the eastern United States; it persisted through winter and lasted at least two years.
Ecology
Earwigs are mostly scavengers, but some are omnivorous or predatory. The abdomen of the earwig is flexible and muscular. It is capable of maneuvering as well as opening and closing the forceps. The forceps are used for a variety of purposes. In some species, the forceps have been observed in use for holdingprey
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not ki ...
, and in copulation. The forceps tend to be more curved in males than in females.
 The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting
The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s. To a large extent, this species is also a scavenger, feeding on decaying plant and animal matter if given the chance. Observed prey include largely plant lice, but also large insects such as bluebottle flies and woolly aphids. Plants that they feed on typically include clover
Clovers, also called trefoils, are plants of the genus ''Trifolium'' (), consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with the highest diversit ...
, dahlia
''Dahlia'' ( , ) is a genus of bushy, tuberous, herbaceous perennial plants native to Mexico and Central America. Dahlias are members of the Asteraceae (synonym name: Compositae) family of dicotyledonous plants, its relatives include the sun ...
s, zinnias, butterfly bush, hollyhock
''Alcea'' is a genus of over 80 species of flowering plants in the mallow family Malvaceae, commonly known as the hollyhocks. They are native to Asia and Europe. The single species of hollyhock from the Americas, the Iliamna rivularis, streamban ...
, lettuce
Lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'') is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae mostly grown as a leaf vegetable. The leaves are most often used raw in Green salad, green salads, although lettuce is also seen in other kinds of food, such as sandwiche ...
, cauliflower
Cauliflower is one of several vegetables cultivated from the species '' Brassica oleracea'' in the genus '' Brassica'', which is in the Brassicaceae (or mustard) family. Cauliflower usually grows with one main stem that carries a large, rou ...
, strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit ...
, blackberry
BlackBerry is a discontinued brand of handheld devices and related mobile services, originally developed and maintained by the Canadian company Research In Motion (RIM, later known as BlackBerry Limited) until 2016. The first BlackBerry device ...
, sunflowers, celery
Celery (''Apium graveolens'' Dulce Group or ''Apium graveolens'' var. ''dulce'') is a cultivated plant belonging to the species ''Apium graveolens'' in the family Apiaceae that has been used as a vegetable since ancient times.
The original wild ...
, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
es, plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in Prunus subg. Prunus, ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are often called prunes, though in the United States they may be labeled as 'dried plums', especially during the 21st century.
Plums are ...
s, grapes
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
, potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es, rose
A rose is either a woody perennial plant, perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred Rose species, species and Garden roses, tens of thousands of cultivar ...
s, seedling bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s and beet
The beetroot (British English) or beet (North American English) is the taproot portion of a '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' plant in the Conditiva Group. The plant is a root vegetable also known as the table beet, garden beet, dinner ...
s, and tender grass
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family (biology), family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and spe ...
shoots and roots; they have also been known to eat corn silk
Corn silk is a common name for ''Stigma maydis'', the shiny, thread-like, weak fibers that grow as part of ear (botany), ears of corn (maize); the tuft or tassel of silky fibers that protrude from the tip of the ear of corn. The ear is enclosed i ...
, damaging the crop.
Species of the suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina are generally considered epizoic, or living on the outside of other animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s, mainly mammals. In the Arixeniina, family Arixeniidae, species of the genus '' Arixenia'' are normally found deep in the skin folds and gular pouch of Malaysian hairless bulldog bats (''Cheiromeles torquatus''), apparently feeding on bats' body or glandular secretions. On the other hand, species in the genus '' Xeniaria'' (still of the suborder Arixeniina) are believed to feed on the guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a le ...
and possibly the guanophilous arthropods in the bat's roost, where it has been found. Hemimerina includes '' Araeomerus'' found in the nest of long-tailed pouch rats (''Beamys''), and '' Hemimerus'' which are found on giant '' Cricetomys'' rats.
Earwigs are generally nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
, and typically hide in small, dark, and often moist areas in the daytime. They can usually be seen on household walls and ceilings. Interaction with earwigs at this time results in a defensive free-fall to the ground followed by a scramble to a nearby cleft or crevice. During the summer they can be found around damp areas such as near sinks and in bathrooms. Earwigs tend to gather in shady cracks or openings or anywhere that they can remain concealed during daylight. Picnic tables, compost and waste bins, patios, lawn furniture, window frames, or anything with minute spaces (even artichoke blossoms) can potentially harbour them.
Predators and parasites
Earwigs are regularly preyed upon by birds, and like many other insect species they are prey for insectivorous mammals, amphibians, lizards, centipedes, assassin bugs, and spiders.Arnold, Richard A. "Earwigs." ''Endangered Wildlife and Plants of the World.'' Vol. 4. Eds. Anne Hildyard, Paul Thompson and Amy Prior. (Tarrytown, New York: Marshall Cavendish Corporation, 2001) 497. European naturalists have observed bats preying upon earwigs. Their primary insect predators are parasitic species of Tachinidae, or tachinid flies, whose larvae areendoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
s. One species of tachinid fly, '' Triarthria setipennis'', has been demonstrated to be successful as a biological control of earwigs for almost a century. Another tachinid fly and parasite of earwigs, ''Ocytata pallipes'', has shown promise as a biological control agent as well. The common predatory wasp, the yellow jacket (''Vespula maculifrons''), preys upon earwigs when abundant. A small species of roundworm, '' Mermis nigrescens'', is known to occasionally parasitize earwigs that have consumed roundworm eggs with plant matter. At least 26 species of parasitic fungus from the order Laboulbeniales have been found on earwigs. The eggs and nymphs are also cannibalized by other earwigs. A species of tyroglyphoid mite, ''Histiostoma polypori'' ( Histiostomatidae, Astigmata), are observed on common earwigs, sometimes in great densities; however, this mite feeds on earwig cadavers and not its live earwig transportation. Hippolyte Lucas
Pierre-Hippolyte Lucas (17 January 1814 – 5 July 1899) was a French entomologist.
Lucas was an assistant-naturalist at the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle. From 1839 to 1842 he studied fauna as part of the scientific commission on the ex ...
observed scarlet acarine mites on European earwigs.
Evolution
 The fossil record of the Dermaptera starts in the
The fossil record of the Dermaptera starts in the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...
to Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic� ...
period about in England and Australia, and comprises about 70 specimens in the extinct suborder Archidermaptera
Archidermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. It is one of two extinct suborders of earwigs, and contains two families ( Protodiplatyidae and Dermapteridae) known only from Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous fossils.F ...
. Some of the traits believed by neontologists to belong to modern earwigs are not found in the earliest fossils, but adults had five-segmented tarsi (the final segment of the leg), well developed ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
s, veined tegmina (forewings) and long segmented cerci; in fact the pincers would not have been curled or used as they are now. The theorized stem group of the Dermaptera are the Protelytroptera, which are similar to modern Blattodea
Blattodea is an order (biology), order of insects that contains cockroaches and termites. Formerly, termites were considered a separate order, Isoptera, but genetics, genetic and molecular evidence suggests they evolved from within the cockroach ...
(cockroaches) with shell-like forewings and the large, unequal anal fan, are known from the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
of North America, Europe and Australia. No fossils from the Triassic — during which Dermaptera would have evolved from Protelytroptera — have been found. Amongst the most frequently suggested order of insects to be the closest relatives of Dermaptera is Notoptera, theorized by Giles in 1963. However, other arguments have been made by other authors linking them to Phasmatodea
The Phasmatodea (also known as Phasmida or Phasmatoptera) are an Order (biology), order of insects whose members are variously known as stick insects, stick bugs, walkingsticks, stick animals, or bug sticks. They are also occasionally referred ...
, Embioptera
The order Embioptera, commonly known as webspinners or footspinners, are a small group of mostly tropical and subtropical insects, classified under the subclass Pterygota. The order has also been called Embiodea or Embiidina. More than 400 spe ...
, Plecoptera
Plecoptera is an order (biology), order of insects commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to b ...
, and Dictyoptera. A 2012 mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
study suggested that this order is the sister to stoneflies of the order Plecoptera
Plecoptera is an order (biology), order of insects commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to b ...
.Wan X, Kim MI, Kim MJ, Kim I (2012) Complete mitochondrial genome of the free-living earwig, ''Challia fletcheri'' (Dermaptera: Pygidicranidae) and phylogeny of Polyneoptera. PLoS One 7(8):e42056. A 2018 phylogenetic analysis found that their closest living relatives were angel insects of the order Zoraptera
The insect order (biology), order Zoraptera, commonly known as angel insects, contains small and soft bodied insects with two forms: winged with wings sheddable as in termites, dark and with eyes (compound) and ocelli (simple); or wingless, pale ...
, with very high support.
Archidermaptera is believed to be sister to the remaining earwig groups, the extinct Eodermaptera and the living suborder Neodermaptera (= former suborders Forficulina, Hemimerina, and Arixeniina). The extinct suborders have tarsi with five segments (unlike the three found in Neodermaptera) as well as unsegmented cerci. No fossil Hemimeridae and Arixeniidae are known. Species in Hemimeridae were at one time in their own order, Diploglassata, Dermodermaptera, or Hemimerina. Like most other epizoic species, there is no fossil record, but they are probably no older than late Tertiary.
Some evidence of early evolutionary history is the structure of the antennal heart, a separate circulatory organ consisting of two ampullae, or vesicles, that are attached to the frontal cuticle near the bases of the antennae. These features have not been found in other insects. An independent organ exists for each antenna, consisting of an ampulla, attached to the frontal cuticle medial to the antenna base and forming a thin-walled sac with a valved ostium on its ventral side. They pump blood by elastic connective tissue, rather than muscle.
Taxonomy
Distinguishing characteristics
The characteristics which distinguish the order Dermaptera from other insect orders are:Gillot, C. ''Entomology'' 2nd Ed. (1995) Springer, , . Accessed oGoogle Books
on 25 November 2009. * ''General body shape'': Elongate; dorso-ventrally flattened. * ''Head'': Prognathous. Antennae are segmented. Biting-type mouthparts.
Ocelli
A simple eye or ocellus (sometimes called a pigment pit) is a form of eye or an optical arrangement which has a single lens without the sort of elaborate retina that occurs in most vertebrates. These eyes are called "simple" to distinguish the ...
absent. Compound eyes in most species, reduced or absent in some taxa.
* ''Appendages'': Two pairs of wings normally present. The forewings are modified into short smooth, veinless tegmina. Hindwings are membranous and semicircular with veins
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
radiating outwards.
* ''Abdomen'': Cerci are unsegmented and resemble forceps
Forceps (: forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forcep ...
. The ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
in females is reduced or absent.
The overwhelming majority of earwig species are in the former suborder Forficulina, grouped into nine families of 180 genera, including ''Forficula auricularia
''Forficula auricularia'' is a species complex comprising the common earwig. It is also known as the European earwig. It is an omnivorous insect belonging to the family Forficulidae. The name ''earwig'' comes from the appearance of the hindwings ...
'', the common European Earwig. Species within Forficulina are free-living, have functional wings and are not parasites. The cerci are unsegmented and modified into large, forceps-like structures.
The first epizoic species of earwig was discovered by a London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
taxidermist
Taxidermy is the art of preserving an animal's body by mounting (over an armature) or stuffing, for the purpose of display or study. Animals are often, but not always, portrayed in a lifelike state. The word ''taxidermy'' describes the process ...
on the body of a Malaysian hairless bulldog bat in 1909, then described by Karl Jordan. By the 1950s, the two suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina had been added to Dermaptera. These were subsequently demoted to family Arixeniidae and superfamily Hemimeroidea (with sole family Hemimeridae), respectively. They are now grouped together with the former Forficulina in the new suborder Neodermaptera
Neodermaptera, sometimes called Catadermaptera,BioLib.cz
suborder Catadermaptera Steinmann, 1986 (retrieved 16 Se ...
.
Arixeniidae represents two genera, '' Arixenia'' and '' Xeniaria'', with a total of five species in them. As with Hemimeridae, they are blind and wingless, with filiform segmented cerci. Hemimeridae are viviparous ectoparasites, preferring the fur of African rodents in either '' Cricetomys'' or ''suborder Catadermaptera Steinmann, 1986 (retrieved 16 Se ...
Beamys
''Beamys'' is a genus of rodent in the family Nesomyidae.
It contains the following species:
* Lesser hamster-rat
The lesser hamster-rat or long-tailed pouched rat (''Beamys hindei'') is a species of rodent in the family Nesomyidae. It is fou ...
'' genera. Hemimerina also has two genera, '' Hemimerus'' and '' Araeomerus'', with a total of 11 species.
Phylogeny
 Dermaptera is relatively small compared to the other orders of
Dermaptera is relatively small compared to the other orders of Insecta
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed leg ...
, with only about 2,000 species, 3 suborders and 15 families, including the extinct suborders Archidermaptera
Archidermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. It is one of two extinct suborders of earwigs, and contains two families ( Protodiplatyidae and Dermapteridae) known only from Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous fossils.F ...
and Eodermaptera with their extinct families Protodiplatyidae, Dermapteridae, Semenoviolidae, and Turanodermatidae
Turanodermatidae is an extinct family of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. There is one genus, '' Turanoderma'', in Turanodermatidae.
References
Earwigs
Prehistoric insect families
Taxa named by Michael S. Engel
{{Jurassic-insect-st ...
. The phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or Taxon, taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, M ...
of the Dermaptera is still debated. The extant Dermaptera appear to be monophyletic and there is support for the monophyly of the families Forficulidae, Chelisochidae, Labiduridae and Anisolabididae, however evidence has supported the conclusion that the former suborder Forficulina was paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
through the exclusion of Hemimerina and Arixeniina which should instead be nested within the Forficulina. Thus, these former suborders were eliminated in the most recent higher classification.
Relationship with humans
Earwigs are fairly abundant and are found in many areas around the world. There is no evidence that they transmit diseases to humans or other animals. Their pincers are commonly believed to be dangerous, but in reality, even the curved pincers of males cause little or no harm to humans. Earwigs have been rarely known to crawl into the ears of humans, and they do not lay eggs inside the human body or human brain as is often claimed. There is a debate whether earwigs are harmful or beneficial to crops, as they eat both the foliage and the insects eating such foliage, such asaphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
s, though it would take a large population to do considerable damage. The common earwig eats a wide variety of plants, and also a wide variety of foliage, including the leaves and petals. They have been known to cause economic losses in fruit and vegetable crops. Some examples are the flowers, hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant ''Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to whic ...
, red raspberries, and corn crops in Germany, and in the south of France, earwigs have been observed feeding on peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
es and apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus ''Prunus''.
Usually an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also ...
s. The earwigs attacked mature plants and made cup-shaped bite marks in diameter.
In literature and folklore
* One of the primary characters of James Joyce's experimental novel ''Finnegans Wake
''Finnegans Wake'' is a novel by Irish literature, Irish writer James Joyce. It was published in instalments starting in 1924, under the title "fragments from ''Work in Progress''". The final title was only revealed when the book was publishe ...
'' is referred to by the initials "HCE," which primarily stand for "Humphrey Chimpden Earwicker," a reference to earwigs. Earwig imagery is found throughout the book, and also occurs in the author's '' Ulysses'' in the Laestrygonians chapter.
* Oscar Cook wrote the short story (appearing in ''Switch On The Light'', April, 1931; ''A Century Of Creepy Stories'' 1934; ''Pan Horror 2'', 1960) "Boomerang", which was later adapted by Rod Serling
Rodman Edward Serling (December 25, 1924 – June 28, 1975) was an American screenwriter and television producer best known for his live television dramas of the 1950s and his Anthology series, anthology television series ''The Twilight Zone (1 ...
for the ''Night Gallery
''Night Gallery'' is an American anthology television series that aired on NBC from December 16, 1970, to May 27, 1973, featuring stories of horror and the macabre. Rod Serling, who had gained fame from an earlier series, '' The Twilight Zon ...
'' TV-series episode, "The Caterpillar". It tells the tale of the use of an earwig as a murder instrument applied by a man obsessed with the wife of an associate.
* Thomas Hood
Thomas Hood (23 May 1799 – 3 May 1845) was an English poet, author and humorist, best known for poems such as "The Bridge of Sighs (poem), The Bridge of Sighs" and "The Song of the Shirt". Hood wrote regularly for ''The London Magazine'', '' ...
discusses the myth of earwigs finding shelter in the human ear in the poem "Love Lane" by saying the following: 'Tis vain to talk of hopes and fears, / And hope the least reply to win, / From any maid that stops her ears / In dread of earwigs creeping in!"
* In some parts of rural England the earwig is called "battle-twig", which is present in Alfred, Lord Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (; 6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of ...
's poem ''The Spinster's Sweet-Arts'': 'Twur as bad as battle-twig 'ere i' my oan blue chamber to me."
* In some regions of Japan, earwigs are called "Chinpo-Basami" or "Chinpo-Kiri", which means "penis cutter". Kenta Takada, a Japanese cultural entomologist, has inferred that these names may be derived from the fact that earwigs were seen around old Japanese-style toilets.
*In Roald Dahl
Roald Dahl (13 September 1916 – 23 November 1990) was a British author of popular children's literature and short stories, a poet, screenwriter and a wartime Flying ace, fighter ace. His books have sold more than 300 million copies ...
's children's book '' George's Marvellous Medicine'', George's Grandma encourages him to eat unwashed celery with beetles and earwigs still on them. A big fat earwig is very tasty,' Grandma said, licking her lips. 'But you've got to be very quick, my dear, when you put one of those in your mouth. It has a pair of sharp nippers on its back end and if it grabs your tongue with those, it never lets go. So you've got to bite the earwig first, chop chop, before it bites you.
See also
* List of Orthopteroid genera containing species recorded in EuropeReferences
External links
Earwig Research Center
by Fabian Haas, Heilbronn
Dermaptera Species File
by Heidi Hopkins, Michael D. Maehr, Fabian Haas, and Lesley S. Deem
on the UF / IFAS Featured Creatures website * Langston RL & JA Powell (1975
The earwigs of California (Order Dermaptera)
Bulletin of the California Insect Survey. 20
Earwigs
from What's That Bug? {{DEFAULTSORT:Earwig Rhaetian first appearances Extant Late Triassic first appearances Exopterygota Polyneoptera