|
Baltic Amber
Baltic amber or succinite is amber from the Baltic region, home of its largest known deposits. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that this forested region provided the resin for more than 100,000 tons of amber. Today, more than 90% of the world's amber comes from Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. It is a major source of income for the region; the local Kaliningrad Amber Combine extracted 250 tonnes of it in 2014 and 400 tonnes in 2015. Baltic amber is also found in Poland, as well as the Baltic states. Bitterfeld amber from the brown coal mines near Bitterfeld in Germany was previously thought to be redeposited Baltic amber, but is now known to be chemically distinct, though like with Ukrainian Rovno amber, it is thought to have been deposited around the same time as Baltic amber. Because Baltic amber contains from 3 to 8% succinic acid, it is also termed succinite. Geologic context ''In situ'' Balt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciadopitys Verticillata
''Sciadopitys verticillata'', the or Japanese umbrella-pine, is a unique conifer Endemism, endemic to Japan, Sakhalin, and the Kuril Islands. It is the sole living member of the family Sciadopityaceae and genus ''Sciadopitys'', a living fossil with no close relatives. The oldest fossils of ''Sciadopitys'' are from the Late Cretaceous of Japan, and the genus was widespread in Laurasia during most of the Cenozoic, especially in Europe until the Pliocene. A European relative of this species may have been the primary source of Baltic amber, according to some studies. Taxonomy Molecular evidence indicates that Sciadopityaceae is the sister group to a clade comprising Taxaceae and Cupressaceae, and has an extremely ancient divergence, having diverged from the rest of the conifers during the early mid-Permian. There is inconsistent evidence regarding the plant family which produced Baltic amber. Both macrofossil and microfossil evidence suggest a ''Pinus'' relative, whereas chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciadopityaceae
Sciadopityaceae, commonly called umbrella pines, are a family of conifers now endemic to Japan but in prehistoric times they could also be found in Europe and China. The sole living member of the family is ''Sciadopitys verticillata'' (the kōyamaki tree), while several extinct genera are known from the fossil record. Wood suggested to belong to the family has been reported from the Jurassic of China, though the relationship of pre-Cretaceous fossils to ''Sciadopitys'' is ambiguous. ''Sciadopitys'' species are known from the Late Cretaceous of Japan before becoming widespread across Laurasia during most of the Cenozoic, especially in Europe until the Pliocene The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
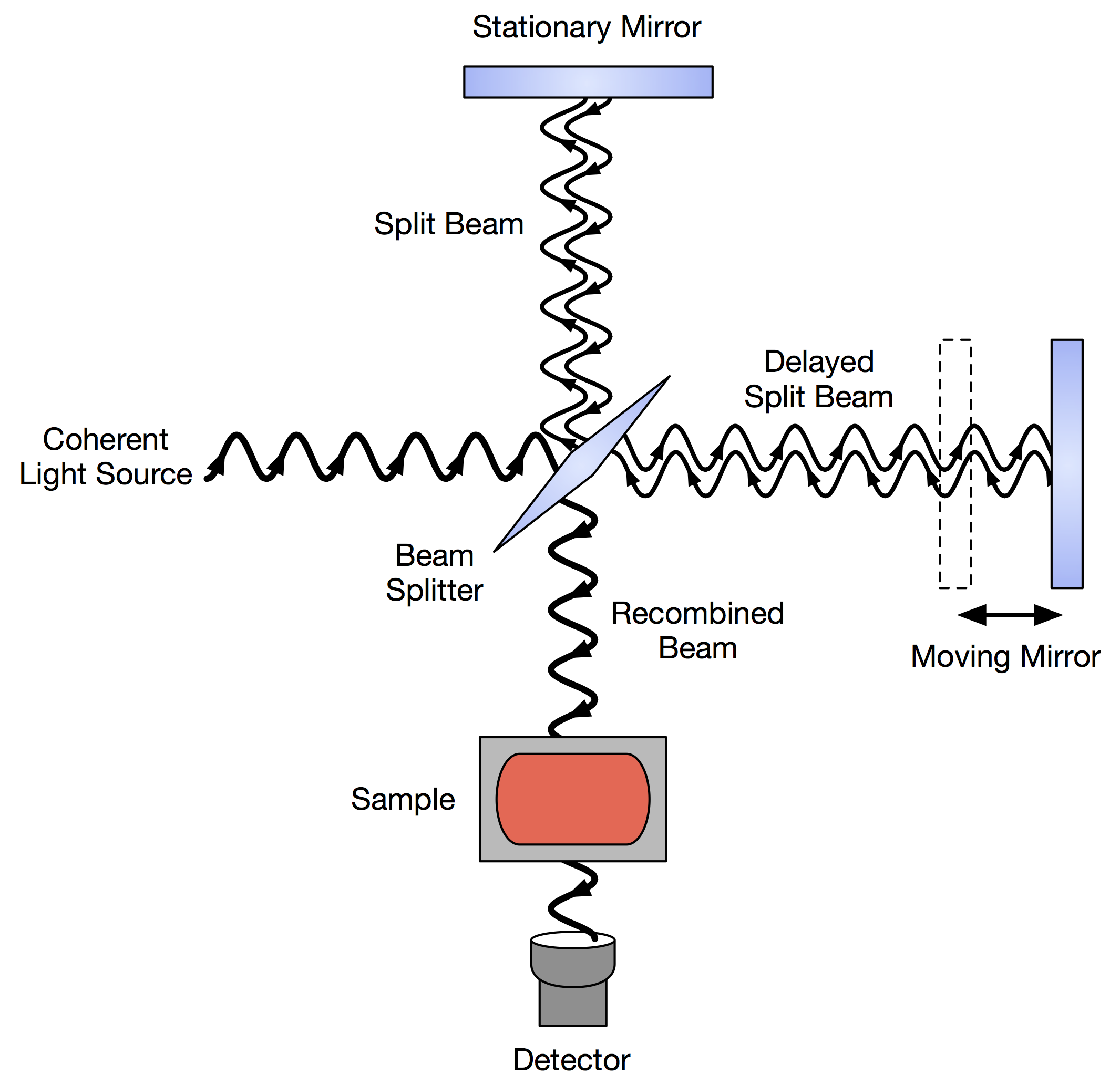
Fourier-transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption or emission of a solid, liquid, or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time. The term ''Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy'' originates from the fact that a Fourier transform (a mathematical process) is required to convert the raw data into the actual spectrum. Conceptual introduction The goal of absorption spectroscopy techniques (FTIR, ultraviolet-visible ("UV-vis") spectroscopy, etc.) is to measure how much light a sample absorbs at each wavelength. The most straightforward way to do this, the "dispersive spectroscopy" technique, is to shine a monochromatic light beam at a sample, measure how much of the light is absorbed, and repeat for each different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt ( ; ) is a States of Germany, state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the List of German states by area, 8th-largest state in Germany by area and the List of German states by population, 11th-largest by population. Its capital and most populous city is Magdeburg. The state of Saxony-Anhalt was formed in July 1945 after World War II, when the Soviet Military Administration in Germany, Soviet army administration in Allied-occupied Germany formed it from the former Free State of Prussia, Prussian Province of Saxony and the Free State of Anhalt. Saxony-Anhalt became part of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic in 1949, but was dissolved in 1952 during Administrative divisions of East Germany, administrative reforms and its territory was divided into the districts of Halle (Bezirk), Halle and Magdeburg (Bezirk), Magdeburg. Follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Transgression
A marine transgression is a geologic event where sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, resulting in flooding. Transgressions can be caused by the land sinking or by the ocean basins filling with water or decreasing in capacity. Transgressions and regressions may be caused by tectonic events like orogenies, severe climate change such as ice ages or isostatic adjustments following removal of ice or sediment load. During the Cretaceous, seafloor spreading created a relatively shallow Atlantic basin at the expense of a deeper Pacific basin. That reduced the world's ocean basin capacity and caused a rise in sea level worldwide. As a result of the sea level rise, the oceans transgressed completely across the central portion of North America and created the Western Interior Seaway from the Gulf of Mexico to the Arctic Ocean. The opposite of transgression is regression where the sea level falls relative to the land and exposes the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North European Plain
The North European Plain ( – North German Plain; ; – Central European Plain; and ; French: ''Plaine d'Europe du Nord'') is a geomorphological region in Europe that covers all or parts of Belgium, the Netherlands (i.e. the Low Countries), Germany, Denmark, and Poland. It consists of the low plains between the Hercynian Europe ( Central European Highlands) to the south and coastlines of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north. These two seas are separated by the Jutland Peninsula (Denmark). The North European Plain is connected to the East European Plain, together forming the majority of the Great European Plain (European Plain). Geography Elevations vary between 0 and 200 m (0 to about 650 ft). While mostly used as farmland, the region also contains bogs, heath and lakes. The Wadden Sea, a large tidal area, is located on the North Sea coast. A number of freshwater lagoons including the Szczecin Lagoon, the Vistula Lagoon and the Curonian Lagoon are foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is diagnostic of till. image:Glacial till exposed in roadcut-750px.jpg, Glacial till with tufts of grass Till or glacial till is unsorted glacier, glacial sediment. Till is derived from the erosion and entrainment of material by the moving ice of a glacier. It is deposited some distance down-ice to form terminal, lateral, medial and ground moraines. Till is classified into primary deposits, laid down directly by glaciers, and secondary deposits, reworked by fluvial transport and other processes. Description Till is a form of '' glacial drift'', which is rock material transported by a glacier and deposited directly from the ice or from running water emerging from the ice. It is distinguished from other forms of drift in that it is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sambia Peninsula
Sambia () or Samland () or Kaliningrad Peninsula (official name, , ''Kaliningradsky poluostrov'') is a peninsula in the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea. The peninsula is bounded by the Curonian Lagoon to the north-east, the Vistula Lagoon in the southwest, the Pregolya, Pregolya River in the south, and the Deyma River in the east. As Sambia is surrounded on all sides by water, it is technically an island. Historically it formed an important part of the historic region of Prussia (region), Prussia. Etymology Sambia is named after the Sambians, an extinct tribe of Old Prussians. ''Samland'' is the name for the peninsula in the Germanic languages. Polish language, Polish and Latin speakers call the area ''Sambia'', while the Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name is ''Semba''. Geography and geology Baedeker describes Sambia as "a fertile and wooded district, with several lakes, lying to the north of Königsberg" (since 1946 Kaliningrad). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |