Sambia Peninsula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sambia () or Samland () or Kaliningrad Peninsula (official name, , ''Kaliningradsky poluostrov'') is a
Sambia () or Samland () or Kaliningrad Peninsula (official name, , ''Kaliningradsky poluostrov'') is a

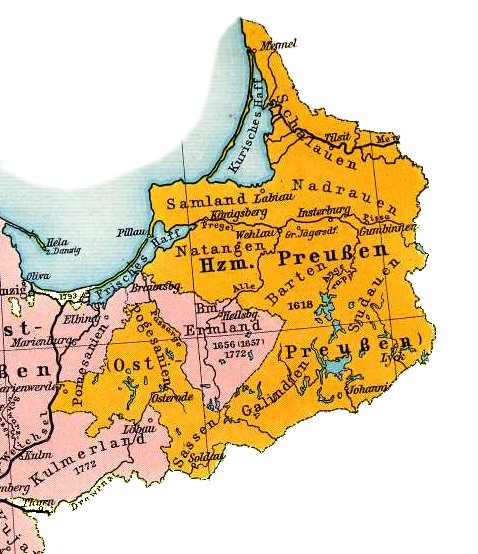 Sambia was originally sparsely populated by the
Sambia was originally sparsely populated by the
peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
in the Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. The peninsula is bounded by the Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; Prussian: ''Kursjanmari'', , ) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River () supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of ...
to the north-east, the Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 km) long, 6 to 15 miles (10 to 19 km) wide, and up to 17 feet (5 m) deep, separated from the Gdańsk Bay by the Vistula Spit.
Geography
The lag ...
in the southwest, the Pregolya River in the south, and the Deyma River in the east. As Sambia is surrounded on all sides by water, it is technically an island. Historically it formed an important part of the historic region of Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
.
Etymology
Sambia is named after theSambians
The Sambians were a Prussian tribe. They inhabited the Sambia Peninsula north of the city of Königsberg (now Kaliningrad). Sambians were located in a coastal territory rich in amber and engaged in trade early on (see Amber Road). Therefore, the ...
, an extinct tribe of Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon ...
. ''Samland'' is the name for the peninsula in the Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoke ...
. Polish and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
speakers call the area ''Sambia'', while the Lithuanian name is ''Semba''.
Geography and geology

Baedeker
Verlag Karl Baedeker, founded by Karl Baedeker on 1 July 1827, is a German publisher and pioneer in the business of worldwide travel guides. The guides, often referred to simply as "List of Baedeker Guides, Baedekers" (a term sometimes used to re ...
describes Sambia as "a fertile and wooded district, with several lakes, lying to the north of Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
" (since 1946 Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
). The landscape is hilly in the west, with coastal bluffs and beaches, while in the east it is low-lying and flat. The sections of coast adjacent to the Curonian and Vistula Lagoons are often swampy. Due to the moderating influence of the Baltic Sea, the climate is more mild than regions of comparable latitude further east. The highest point at 111 meters, Galtgarben, is found two kilometers southeast of Kumachyovo ().
Gvardeysk () is located at the southeastern end of the peninsula where the Deyma branches off from the Pregolya, while Polessk () is found at the northeastern end, nearby where that river enters the Curonian Lagoon. The peninsula is connected to the Curonian Spit to the north, while it is separated from the Vistula Spit
The Vistula Spit (; ; ; ) is an aeolian sand spit, or peninsular stretch of land, separating Vistula Lagoon from Gdańsk Bay, in the Baltic Sea, with its tip separated from the mainland by the Strait of Baltiysk. The border between Poland (Pom ...
by the Strait of Baltiysk next to the port city of Baltiysk
Baltiysk ( ); ; Old Prussian: ''Pillawa''; ; ; is a seaport town and the administrative center of Baltiysky District in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the northern part of the Vistula Spit, on the shore of the Strait of Baltiysk separ ...
(). Sambia also includes two famous seaside resorts on its northern coast, Zelenogradsk () and Svetlogorsk ().
Amber
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin. Examples of it have been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since the Neolithic times, and worked as a gemstone since antiquity."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia ...
has been found in the area for over two thousand years, especially on the coast near Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
. History and legends tell of the ancient trade routes known as the Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade. ...
leading from the Old Prussian
Old Prussian is an extinct West Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European languages, which was once spoken by the Old Prussians, the Baltic peoples of the Prussian region. The language is called Old Prussian to av ...
settlements of Kaup (in Sambia) and Truso (near Elbląg
Elbląg (; ; ) is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 127,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County.
Elbląg is one of the ol ...
, near the mouth of the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
) southwards to the Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
and Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
seas. In Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, the right to collect amber was restricted to the Hohenzollern dynasty, and visitors to Sambia's beaches were forbidden to pick up any fragments they found. Beginning in the 19th century, amber was mined on an industrial scale by the Germans before 1945 and by the Soviets / Russians thereafter at Yantarny (former German name: ''Palmnicken'').
History
Reference to the Sambia Peninsula begins with Greek travellerPytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéās ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explo ...
, referring to an amber island called "Abalus". The name probably described the whole lagoon area known in Finnic as AVA (open expanse = lagoon) and -LA (place of) Historic scholars could not find the mysterious amber island because the Sambia Peninsula did not look like an island since the whole Baltic area that was depressed by the Ice Age glaciers has been rising many meters in the last thousands of years and was no longer looking like an island by the 10th century. Based on finds of prehistoric amber carvings, nomadic boat using hunter gatherers were attracted to the area as early as 6,000 years ago,according to archeology.
 Sambia was originally sparsely populated by the
Sambia was originally sparsely populated by the Sambians
The Sambians were a Prussian tribe. They inhabited the Sambia Peninsula north of the city of Königsberg (now Kaliningrad). Sambians were located in a coastal territory rich in amber and engaged in trade early on (see Amber Road). Therefore, the ...
. The German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
conquered the region in the 13th century. The church administration was placed under the Bishopric of Samland
The Diocese of Samland (Sambia) (, ) was a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in Sambia Peninsula, Samland (Sambia) in Prussia (region), medieval Prussia. It was founded in 1243 by papal legate William of Modena. Its seat was Königsberg, ...
, established in 1243. Settlers from the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
began colonizing the region, and the Sambian Prussians gradually became assimilated. The peninsula was the last area in which the Old Prussian language
Old Prussian is an extinct West Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European languages, which was once spoken by the Old Prussians, the Baltic peoples of the Prussian region. The language is called Old Prussian to av ...
was spoken before becoming extinct at the beginning of the 18th century.
In 1454, the region was incorporated by King Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (Casimir Andrew Jagiellon; ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447 until his death in 1492. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers; under ...
to the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
upon the request of the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation. After the subsequent Thirteen Years' War, since 1466, it formed part of Poland as a fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
held by the Teutonic Order. The peninsula became part of the Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
, a vassal duchy of the Kingdom of Poland, founded when Albert of Brandenburg-Ansbach, the 37th Grand Master, secularized the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights
The State of the Teutonic Order () was a theocratic state located along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Europe. It was formed by the knights of the Teutonic Order during the early 13th century Northern Crusades in the region ...
in 1525. The Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg () was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that, having electoral status although being quite poor, grew rapidly in importance after inheriting the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 and then came ...
inherited the duchy in 1618 under Polish overlordship.
Because the Duchy of Prussia failed to fulfill its feudal obligations as a vassal of Poland during the Polish–Swedish wars
This is a List of wars between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to ...
, George William's rule in Prussia was suspended in 1635 and he was replaced by the Polish king by a viceroy, Jerzy Ossoliński. However, under the Treaty of Sztumska Wieś the Duchy (and so the Sambia peninsula) was given back to George William. In 1701 Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
ruler proclaimed the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
and Sambia became part of the newly formed Province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
in 1773. In 1871, the peninsula became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in the course of the unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was a process of building the first nation-state for Germans with federalism, federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without Habsburgs' multi-ethnic Austria or its German-speaking part). I ...
. After World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
Sambia formed part of the East Prussian province of Weimar Germany
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Germans operated two subcamps of the Stutthof concentration camp
Stutthof was a Nazi concentration camp established by Nazi Germany in a secluded, marshy, and wooded area near the village of Stutthof (now Sztutowo) 34 km (21 mi) east of the city of Danzig (Gdańsk) in the territory of the German-an ...
, and the AGSSt Samland assembly center for Allied POWs in the region. The Polish resistance movement was active in the region, with its activities including espionage of German activity and distribution of Polish underground press
The Polish underground press, devoted to prohibited materials ( sl. , lit. semitransparent blotting paper or, alternatively, , lit. second circulation), has a long history of combatting censorship of oppressive regimes in Poland. It existed th ...
.
In 1945 after World War II, the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
annexed northern East Prussia, including Sambia, while the southern part of the province became again part of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
. Sambia became part of the Soviet Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
, named after the nearby city of Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
(historically ), and the new authorities expelled its German inhabitants in accordance to the Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement () was the agreement among three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe that was signed on 1 August 1945 and published the following day. A ...
.
The Soviet Union gradually repopulated the Kaliningrad Oblast, including Sambia, with Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
and Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
. Until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, much of the district was a closed military area.
Kursenieki
While today theKursenieki
The Kursenieki (, – 'Curonians', , ) are a nearly extinct Baltic ethnic group living along the Curonian Spit. "Kuršiai" refers only to inhabitants of Lithuania and former East Prussia that speak a southwestern dialect of Latvian. Some auto ...
, also known as Kuršininkai are a nearly extinct Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
ethnic group living along the Curonian Spit, in 1649 Kuršininkai settlement spanned from Memel (Klaipėda) to Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
, Poland, including the coastline of the Sambian Peninsula. The Kuršininkai were eventually assimilated by the Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, except along the Curonian Spit where some still live. The Kuršininkai were considered Latvians
Latvians () are a Baltic ethnic group and nation native to Latvia and the immediate geographical region, the Baltics. They are occasionally also referred to as Letts, especially in older bibliography. Latvians share a common Latvian language ...
until after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
when Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
gained independence from the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, a consideration based on linguistic arguments. This was the rationale for Latvian claims over the Curonian Spit, Memel, and other territories of East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
which would be later dropped.
See also
* Amber Coast *Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; Prussian: ''Kursjanmari'', , ) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River () supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of ...
* Curonian Spit
* Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 km) long, 6 to 15 miles (10 to 19 km) wide, and up to 17 feet (5 m) deep, separated from the Gdańsk Bay by the Vistula Spit.
Geography
The lag ...
Footnotes
{{Authority control Peninsulas of Russia Peninsulas of the Baltic Sea Landforms of Kaliningrad Oblast