|
Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 110
Site 110 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome is a launch facility which was used by the N1 rocket during the late 1960s and early 1970s, and by the Energia rocket during the 1980s. Site Site 110 consists of two launch pads: The right (or east) pad, called "110/38" or "110R", was completed first. It was followed by the left (or west) pad, called "110/37" or "110L". The complex was built in the 1960s as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs, for use by the N1 rocket. A total of five launches were made from the complex: Four N1 launches as well as one Energia launch, carrying the '' Buran'' spaceplane. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union the Energia and Buran programmes were cancelled, and the complex was abandoned. Usage N1 Site 110 was intended as the launch site for crewed lunar landing missions using the Soyuz 7K-L3 spacecraft and the LK lander. The N1 made four flights, all of which were launched from Site 110, and all of which failed before the first stage had complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
''Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy'' rus, Космодром Байконур''Kosmodrom Baykonur'' , image = Baikonur Cosmodrome Soyuz launch pad.jpg , caption = The Baikonur Cosmodrome's " Gagarin's Start" Soyuz launch pad prior to the rollout of Soyuz TMA-13, 10 October 2008. , LID = GC0015 , type = Spaceport , owner-oper = Roscosmos Russian Aerospace Forces , location = Kazakhstan (leased to Russia) , opened = , built = , timezone = UTC+06:00 , utc = +06:00 , elevation-m = 90 , metric-elev = y , coordinates = , website = , image_map = , image_mapsize = , image_map_alt = , image_map_caption = , pushpin_map = Kazakhstan#Russia#Soviet Union , push ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
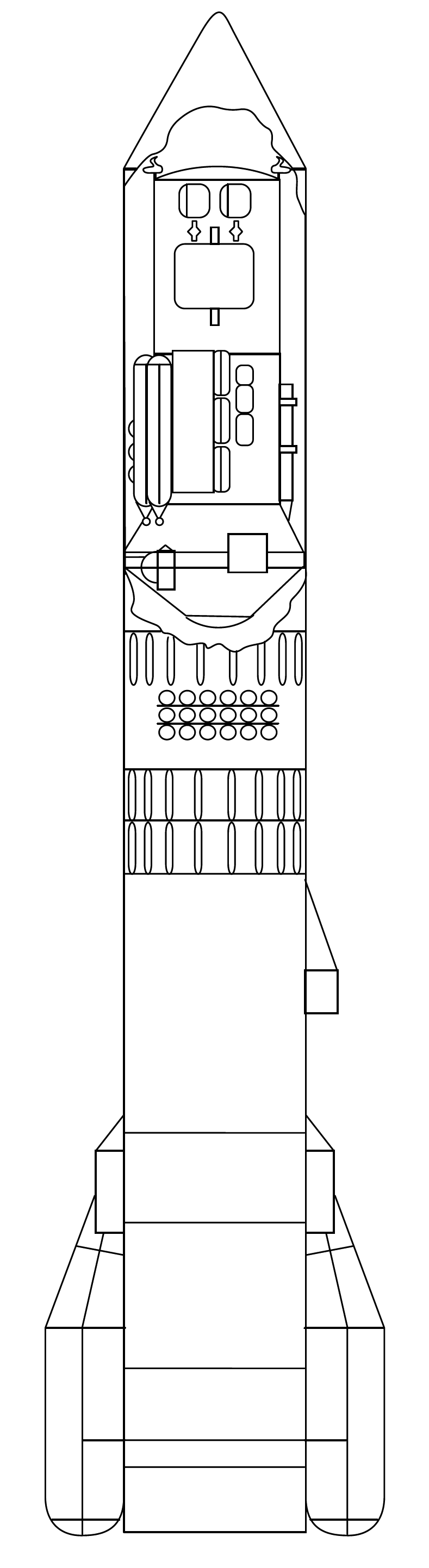
N1 (rocket)
The N1/L3 (from , "Carrier Rocket"; Cyrillic: Н1) was a super heavy-lift launch vehicle intended to deliver payloads beyond low Earth orbit. The N1 was the Soviet counterpart to the US Saturn V and was intended to enable crewed travel to the Moon and beyond, with studies beginning as early as 1959. Its first stage, Block A, remains the most powerful rocket stage ever flown. However, all four first stages flown failed mid-flight because a lack of static test firings meant that plumbing issues and other adverse characteristics with the large cluster of thirty engines and its complex fuel and oxidizer feeder system were not revealed earlier in development. The N1-L3 version was designed to compete with the United States Apollo program to land a person on the Moon, using a similar lunar orbit rendezvous method. The basic N1 launch vehicle had three stages, which were to carry the L3 lunar payload into low Earth orbit with two cosmonauts. The L3 contained one stage for trans-lun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
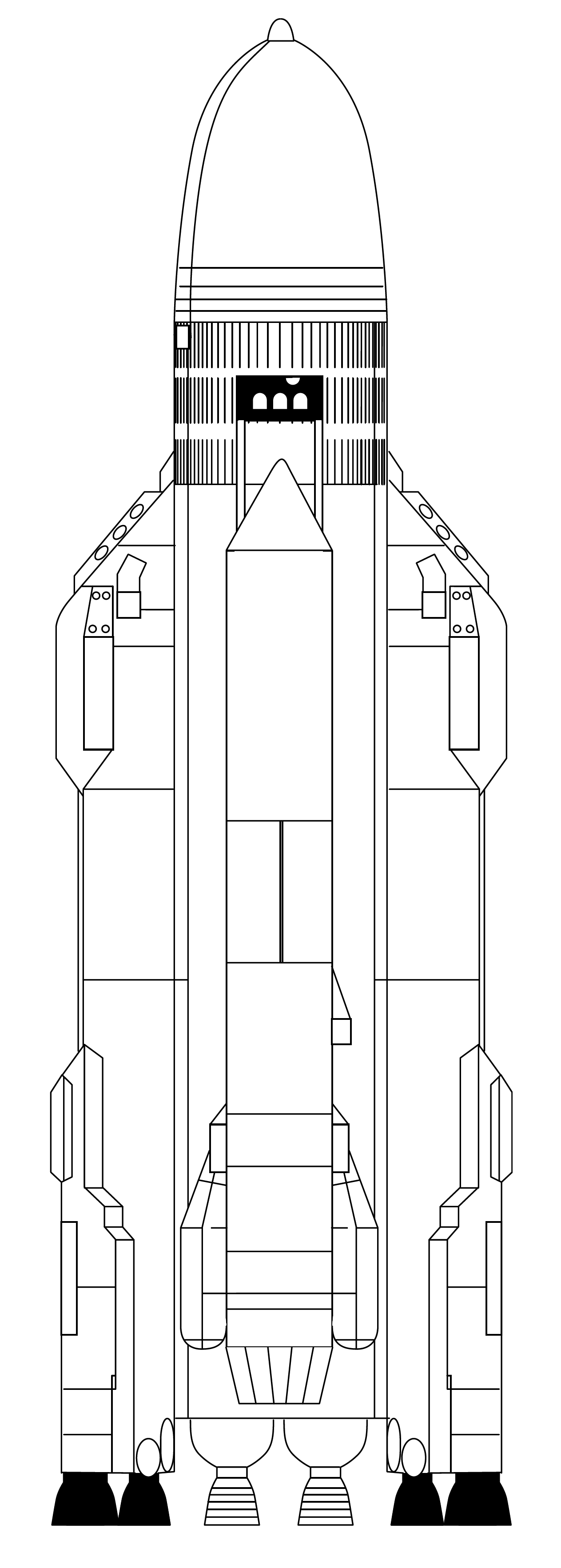
Energia (rocket)
Energia (russian: Энергия, Energiya, Energy; GRAU 11K25) was a 1980s super-heavy lift launch vehicle. It was designed by NPO Energia of the Soviet Union as part of the Buran program for a variety of payloads including the Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the Khartron NPO "Electropribor". The Energia used four strap-on boosters each powered by a four-chamber RD-170 engine burning kerosene/ LOX, and a central core stage with four single-chamber RD-0120 (11D122) engines fueled by liquid hydrogen/LOX. The launch vehicle had two functionally different operational variants: Energia-Polyus, the initial test configuration, in which the Polyus system was used as a final stage intended to put the payload into orbit, and Energia-Buran, in which the ''Buran'' orbiter was the payload and the source of the orbit insertion impulse. The launch vehicle had the capacity to place about 100 tonnes in Low Earth orbit, up to 20 tonnes to geostationary orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Crewed Lunar Programs
The Soviet crewed lunar programs were a series of programs pursued by the Soviet Union to land humans on the Moon, in competition with the United States Apollo program. The Soviet government publicly denied participating in such a competition, but secretly pursued two programs in the 1960s: crewed lunar flyby missions using Soyuz 7K-L1 (Zond) spacecraft launched with the Proton-K rocket, and a crewed lunar landing using Soyuz 7K-LOK and LK spacecraft launched with the N1 rocket. Following the dual American successes of the first crewed lunar orbit on 24–25 December 1968 (Apollo 8) and the first Moon landing on July 20, 1969 (Apollo 11), and a series of catastrophic N1 failures, both Soviet programs were eventually brought to an end. The Proton-based Zond program was canceled in 1970, and the N1-L3 program was ''de facto'' terminated in 1974 and officially canceled in 1976. Details of both Soviet programs were kept secret until 1990 when the government allowed them to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buran Program
The ''Buran'' program (russian: Буран, , "Snowstorm", "Blizzard"), also known as the "VKK Space Orbiter program" (russian: ВКК «Воздушно-Космический Корабль», lit=Air and Space Ship), was a Soviet and later Russian reusable spacecraft project that began in 1974 at the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute in Moscow and was formally suspended in 1993. In addition to being the designation for the whole Soviet/Russian reusable spacecraft project, ''Buran'' was also the name given to Orbiter K1, which completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988 and was the only Soviet reusable spacecraft to be launched into space. The ''Buran''-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket as a launch vehicle. Unlike the Space Shuttle, Buran had a capability of flying uncrewed missions, as well as performing fully automated landings. The Buran program was started by the Soviet Union as a response to the United States Space Shuttle program. The project was the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered but then landed as unpowered gliders. Four types of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran, U.S. X-37, and the Chinese CSSHQ. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2019 all past, current, and planned orbital vehicles launch vertically on a separate rocket. Orbital spaceflight takes place at high velocities, with orbital kinetic energies typically at least 50 times greater than suborbital trajectories. Consequently, heavy heat shielding is requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolution Of The Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Soviet Union (USSR) which resulted in the end of the country's and its federal government's existence as a sovereign state, thereby resulting in its constituent republics gaining full sovereignty on 26 December 1991. It brought an end to General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev's (later also President) effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of fifteen top-level republics that served as homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics alr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-L3
The Soyuz 7K-LOK, or simply LOK (russian: Лунный Орбитальный Корабль, translit=Lunniy Orbitalny Korabl meaning "Lunar Orbital Craft") was a Soviet crewed spacecraft designed to launch men from Earth to orbit the Moon, developed in parallel to the 7K-L1. The LOK would carry two cosmonauts, acting as a mother ship for the LK Lander which would land one crew member to the surface. It was part of the N1-L3 programme which also included the LK lander and the N1 rocket. Design Like the 7K-OK model, the 7K-LOK was divided into three sections, an ellipsoid Orbital Module, the "headlight"-shaped Descent Module, and a cylindrical equipment module. Like the 7K-OK, the 7K-LOK was capable of physically docking with another spacecraft, but lacked the transfer tunnel used on the Apollo (spacecraft), thus forcing the cosmonaut to make a spacewalk from the 7K-LOK's orbital module to the LK Lander using the new Krechet space suit (the predecessor to the Orlan space suit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LK (spacecraft)
The LK (russian: ЛК, from russian: Лунный корабль, Lunniy korabyl, lunar craft; GRAU index: 11F94) was a lunar module (lunar lander designed for human spaceflight) developed in the 1960s as a part of several Soviet crewed lunar programs. Its role was analogous to the American Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Three LK modules, of the T2K variant, were flown without crew in Earth orbit, but no LK ever reached the Moon. The development of the N1 launch vehicle required for the lunar flight suffered setbacks (including several launch failures), and the first Moon landings were achieved by US astronauts on Apollo 11. As a result, having lost the Space Race, both the N1 and the LK programs were cancelled without any further development. The N1-L3 flight plan Sergei Korolev, the lead Soviet rocket engineer and spacecraft designer during the 1950s and 1960s, planned to adopt the same lunar orbit rendezvous concept as seen in the Apollo programme. The lunar expedition spacec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur
Baikonur ( kk, Байқоңыр, ; russian: Байконур, translit=Baykonur), formerly known as Leninsk, is a city of republic significance in Kazakhstan on the northern bank of the Syr Darya river. It is currently leased and administered by the Russian Federation as an enclave until 2050. It was constructed to service the Baikonur Cosmodrome and was officially renamed Baikonur by Russian president Boris Yeltsin on December 20, 1995. During the Soviet period, it was sometimes referred to as Zvezdograd (), Russian for ''Star City''. The rented area is an ellipse measuring east to west by north to south, with the cosmodrome situated at the area's centre. Foreign visitors need pre-approval from the Russian authorities to visit both the town of Baikonur itself and the Cosmodrome. Foreign visitors need to obtain a written approval which is completely separate from having a regular Russian visa. History The original Baikonur (Kazakh for "wealthy brown", i.e. "fertile land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 250
Site 250 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, also known as UKSS (russian: Универсальный Комплекс Стенд-Старт, lit=Universal Complex Stand-Start) and Bayterek (russian: Байтерек), is a test facility and launch site which was used by the Energia rocket during the 1980s. The site consists of a single launch pad, which doubled as a test stand, and is supported by an engineering area and a propellant storage facility. the complex was planned to be rebuilt as the ''Bayterek Launch Complex'', which would be used by the Angara rocket from 2015; however development is yet to begin. Today the UKSS at Site 250 is still standing, however it is deteriorating. Construction work for Bayterek is yet to begin. Energia Site 250 was built in the late 1970s as the ''Universal Complex Stand-Start'' (UKSS) to support Energia development, and unlike other Soviet launch complexes it was designed to support long-duration static tests as well as launches, after Valentin Glush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyus (spacecraft)
The Polyus spacecraft (russian: Полюс, ''pole''), also known as Polus, Skif-DM, GRAU index 17F19DM, was a prototype Soviet orbital weapons platform designed to destroy Strategic Defense Initiative satellites with a megawatt carbon-dioxide laser. It had a Functional Cargo Block derived from a TKS spacecraft to control its orbit and it could launch test targets to demonstrate the fire control system. History The Polyus spacecraft was launched 15 May 1987 from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 250 as part of the first flight of the Energia system, but failed to reach orbit. According to Yuri Kornilov, Chief Designer of the Salyut Design Bureau, shortly before Polyus' launch, Mikhail Gorbachev visited the Baikonur Cosmodrome and expressly forbade the in-orbit testing of its capabilities. Kornilov claims that Gorbachev was worried that it would be possible for Western governments to view this activity as an attempt to create a weapon in space and that such an attempt would contrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)