|
Buran Program
The ''Buran'' programme (, , "Snowstorm", "Blizzard"), also known as the "VKK Space Orbiter programme" (), was a Soviet Union, Soviet and later Russian reusable spacecraft project that began in 1974 at the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute in Moscow and was formally suspended in 1993. In addition to being the designation for the whole Soviet/Russian reusable spacecraft project, ''Buran'' was also the name given to Buran (spacecraft), orbiter 1K, which completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988 and was the only Soviet reusable spacecraft to be launched into space. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia (rocket), Energia rocket as a launch vehicle. The Buran programme was started by the Soviet Union as a response to the United States Space Shuttle program and benefited from extensive espionage undertaken by the KGB of the unclassified US Space Shuttle program, resulting in many superficial and functional similarities between American and Soviet Shuttle designs. Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov An-225 Mriya
The Antonov An-225 Mriya (; NATO reporting name: Cossack) was a large strategic airlift cargo aircraft designed and produced by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. It was originally developed during the 1980s as an enlarged derivative of the Antonov An-124 airlifter for transporting ''Buran'' spacecraft. On 21 December 1988, the An-225 performed its maiden flight; only one aircraft was ever completed, although a second airframe with a slightly different configuration was partially built. After a brief period of use in the Soviet space programme, the aircraft was mothballed during the early 1990s. Towards the turn of the century, it was decided to refurbish the An-225 and reintroduce it for commercial operations, carrying oversized payloads for the operator Antonov Airlines. Multiple announcements were made regarding the potential completion of the second airframe, though its construction largely remained on hold due to a lack of funding. By 2009, it had reportedl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can flight, fly and gliding flight, glide as an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and function as a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceflight, Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes as of 2024 have been rocket engine, rocket-powered for takeoff and climb, but have then landed as unpowered glider (aircraft), gliders. Four examples of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, Atmospheric entry, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and Landing#Aircraft, landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran (spacecraft), Buran, U.S. Boeing X-37, X-37, and the Chinese Shenlong (spacecraft), Shenlong. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2024 all past and current orbital spaceplanes VTHL, launch vertically; some are carried as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gleb Lozino-Lozinskiy
Gleb Yevgenyevich Lozino-Lozinskiy (; Kyiv, January 7, 1910 – Moscow, November 28, 2001) was a Ukrainian Віталій Абліцов. «Галактика „Україна“. Українська діаспора: видатні постаті» — К.: КИТ, 2007. — 436 с. engineer, General Director and General Designer of the JSC NPO Molniya, lead developer of the Russian Spiral and Shuttle Buran programme, Doctor of Sciences, Hero of Socialist Labour, laureate of Lenin Prize (1962) and Stalin Prizes (1950, 1952). Biography Born in Kyiv, Gleb moved with his family to Kremenchuk where he received his early education in and graduated from Kremenchuk technical high school as a plumber. He later enrolled in 1926 and graduated from the Kharkiv Mechanical and Machine-building Institute in 1930 as an engineer specializing in steam turbines. Initially he worked at a power station but in 1932 transferred to work in the aviation industry where he was involved in the devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Chertok
Boris Yevseyevich Chertok (; – 14 December 2011) was a Russian engineer in the former Soviet space program, mainly working in control systems, and later found employment in Roscosmos. Major responsibility under his guidance was primarily based on computerized control system of the Russian missiles and rocketry system, and authored the four-volume book ''Rockets and People''– the definitive source of information about the history of the Soviet space program. From 1974, he was the deputy chief designer of the Korolev design bureau, the space aircraft designer bureau which he started working for in 1946. He retired in 1992. Personal life Born in Łódź (modern Poland), his family moved to Moscow when he was aged 3. Starting from 1930, he worked as an electrician in a metropolitan suburb. Since 1934, he was already designing military aircraft in Bolkhovitinov design bureau. In 1946, he entered the rocket-pioneering NII-88 as a head of control systems department, working al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Ustinov
Dmitriy Fyodorovich Ustinov (; 30 October 1908 – 20 December 1984) was a Soviet politician and a Marshal of the Soviet Union during the Cold War. He served as a Central Committee secretary in charge of the Soviet military–industrial complex from 1965 to 1976 and as Minister of Defence of the Soviet Union from 1976 until his death in 1984. Ustinov was born in the city of Samara to a Russian working-class family in 1908. Upon reaching adulthood, he joined the Communist Party in 1927 before pursuing a career in engineering. After graduating from the Institute of Military Mechanical Engineering in 1934, he became a construction engineer at the Leningrad Artillery Marine Research Institute. By 1937, he transferred to the Bolshevik "Arms" Factory where he ultimately rose to become the director. While serving as People's Commissar of Armaments during World War II, he achieved distinction within the party's ranks by successfully overseeing the evacuation of Leningrad's industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and Spacecraft thermal control, radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvezda (ISS Module)
''Zvezda'', also known as the ''Zvezda'' Service Module, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provided all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the US Orbital Segment (USOS), as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station. The module was manufactured in the Soviet Union, USSR by Energia (corporation), Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev. ''Zvezda'' was launched on a Proton (rocket family), Proton launch vehicle on 12 July 2000, and docked with the ''Zarya (ISS module), Zarya'' module on 26 July 2000 at 01:45 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC. It is a descendant of the Salyut programme, ''Salyut'' programme's. Origins The basic structural frame of ''Zvezda'', known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvezda (spacecraft)
Zvezda means "star" in some Slavic languages, and may refer to: Entertainment * ''Zvezda'' (magazine), Russian literary magazine * Zvezda (TV channel), Russian TV channel * ''Star'' (2014 film), a Russian film * ''The Star'' (1953 film), a Russian film * ''The Star'' (2002 film), a Russian film * Zvezda (cinema) a squatted cinema in Belgrade * ''Zvezda'', Serbian literary journal founded and edited by Serbian writer Janko Veselinović Places * Lake Zvezda, Antarctica * Zvezda, Burgas Province, Bulgaria * Zvezda, Targovishte Province, a village in Targovishte Province, Bulgaria * Zvezde, Village in Albania Space * ''Zvezda'' (ISS module), component of the International Space Station * Zvezda (moonbase), non-realized Soviet moonbase as well as a fictional Soviet base on the moon in the lunar south pole in the ''For All Mankind'' TV Series. * Zvezda spaceplane, a Soviet spaceplane project; see Buran programme#History of the Buran programme * NPP Zvezda, Russian aeron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conventional weapon, Conventional, Chemical weapon, chemical, and Biological agent, biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The Nuclear weapons of the United States, United States, Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Russia, China and weapons of mass destruction, China, France and weapons of mass destruction, France, India and weapons of mass destruction, India, the United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, United Kingdom, Nuclear weapons and Israel, Israel, and North Korea and weapons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
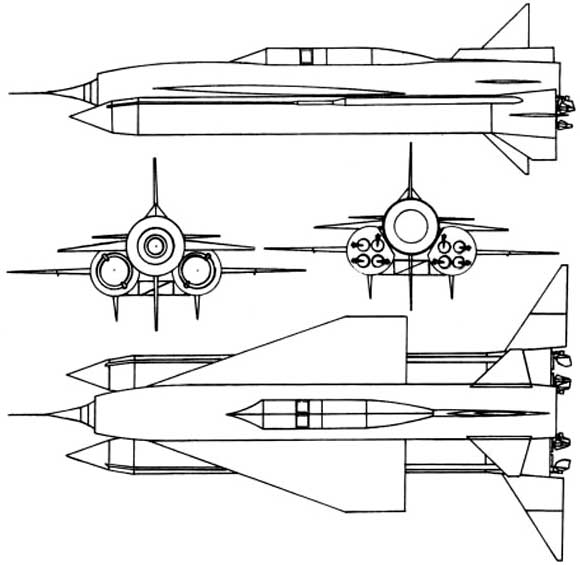
Burya
The ''Burya'' ("Storm" in Russian; ) was a supersonic, intercontinental cruise missile, developed by the Lavochkin design bureau (chief designer Naum Semyonovich Chernyakov) under designation La-350 () from 1954 until the program cancellation in February 1960. The request for proposal issued by the Soviet government in 1954, called for a cruise missile capable of delivering a nuclear payload to the United States. Analogous developments in the United States were the SM-62 Snark and SM-64 Navaho cruise missiles, particularly the latter, which used parallel technology and had similar performance goals. Development The first steps towards development of Burya was the idea of Mstislav Vsevolodovich Keldysh of Keldysh bomber. The Burya was planned as a Mach 3 intercontinental nuclear ramjet cruise missile. The Burya was remarkably advanced for its time, and despite setbacks and several crashes, the vehicle demonstrated a range in excess of 6,000 km with a thermonuclear (hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Exploration
Space exploration is the process of utilizing astronomy and space technology to investigate outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted both by robotic spacecraft, uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight. Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one of the main sources for space science. While the observation of objects in space, known as astronomy, predates reliable recorded history, it was the development of large and relatively efficient rockets during the mid-twentieth century that allowed physical space exploration to become a reality. Common rationales for exploring space include advancing scientific research, national prestige, uniting different nations, ensuring the future survival of humanity, and developing military and strategic advantages against other countries. The early era of space exploration was driven by a "Space Race" between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |