|
Axel Brunger
Axel T. Brunger (born November 25, 1956) is a German American biophysicist. He is Professor of Molecular and Cellular Physiology at Stanford University, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. He served as the Chair of the Department of Molecular and Cellular Physiology (2013–2017). Early life Brunger was born in Leipzig, East Germany, on November 25, 1956. He graduated with a degree in Physics and Mathematics from the University of Hamburg in 1977. He completed his Diplom in Physics from the University of Hamburg in 1980. He completed his PhD in Biophysics from Technical University of Munich in 1982, advised by Klaus Schulten. Academic career Brunger held a NATO postdoctoral fellowship to work with Martin Karplus at Harvard University, where he subsequently became a research associate in the department of chemistry after a brief return to Germany. He joined the molecular biophysics and biochemistry department at Yale University in 1987 and moved to Stanford Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Germany and is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region. The name of the city is usually interpreted as a Slavic term meaning ''place of linden trees'', in line with many other Slavic placenames in the region. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (the Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster and its tributaries Pleiße and Parthe. The Leipzig Riverside Forest, Europe's largest intra-city riparian forest, has developed along these rivers. Leipzig is at the centre of Neuseenland (''new lake district''). This district has Bodies of water in Leipzig, several artificial lakes created from former lignite Open-pit_mining, open-pit mines. Leipzig has been a trade city s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kuriyan
John Kuriyan is the dean of basic sciences and a professor of biochemistry at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. He was formerly the Chancellor's Professor at the University of California, Berkeley in the departments of molecular and cell biology (MCB) and chemistry, a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab's physical biosciences division, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences and he has also been on the Life Sciences jury for the Infosys Prize in 2009, 2019 and 2020. Education Kuriyan received his B.S. in chemistry from Juniata College in Pennsylvania, followed by his PhD in physical chemistry at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology supervised by Gregory Petsko and Martin Karplus. Research and career Kuriyan did postdoctoral research work for one year supervised by Karplus at Harvard before becoming an assistant professor at the Rockefeller University. Kuriyan's laboratory studies the structure and mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emigrants From West Germany To The United States
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanently move to a country). A migrant ''emigrates'' from their old country, and ''immigrates'' to their new country. Thus, both emigration and immigration describe migration, but from different countries' perspectives. Demographers examine push and pull factors for people to be pushed out of one place and attracted to another. There can be a desire to escape negative circumstances such as shortages of land or jobs, or unfair treatment. People can be pulled to the opportunities available elsewhere. Fleeing from oppressive conditions, being a refugee and seeking asylum to get refugee status in a foreign country, may lead to permanent emigration. Forced displacement refers to groups that are forced to abandon their native country, such as by en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Munich Alumni
Technical may refer to: * Technical (vehicle), an improvised fighting vehicle * Technical area, an area which a manager, other coaching personnel, and substitutes are allowed to occupy during a football match * Technical advisor, a person who advises the director on the convincing portrayal of a subject in a film production * Technical analysis, a discipline for forecasting the future direction of prices through the study of past market data * Technical drawing, showing how something is constructed or functions (also known as drafting) ** Technical file, a set of technical drawings * Technical death metal, a subgenre of death metal that focuses on complex rhythms, riffs, and song structures * Technical foul, an infraction of the rules in basketball usually concerning unsportsmanlike non-contact behavior * Technical geography, one of the main branches of geography * Technical rehearsal for a performance, often simply referred to as a technical * Technical support, a range of servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hamburg Alumni
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century American Physicists
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men ( Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1956 Births
Events January * January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan after 57 years. * January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian Missionary, missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim Elliot and Pete Fleming, are killed for trespassing by the Waorani people of Ecuador, shortly after making contact with them. * January 16 – Egyptian leader Gamal Abdel Nasser vows to reconquer Palestine (region), Palestine. * January 25–January 26, 26 – Finnish troops reoccupy Porkkala, after Soviet Union, Soviet troops vacate its military base. Civilians can return February 4. * January 26 – The 1956 Winter Olympics open in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy. February * February 2 – Austria and Israel establish diplomatic Austria–Israel relations, relations. * February 11 – British Espionage, spies Guy Burgess and Donald Maclean (spy), Donald Maclean resurface in the Soviet Union, after being missing for 5 years. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron (the postsynaptic neuron) a short distance away. Changes in the concentration of ions, such as Ca2+, Na+, K+, underlie both chemical and electrical activity in the process. The increase in calcium levels is essential and can be promoted by protons. A similar process occurs in retrograde neurotransmission, where the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron release retrograde neurotransmitters (e.g., endocannabinoids; synthesized in response to a rise in intracellular calcium levels) that signal through receptors that are located on the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, mainly at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Neurotransmission is regulated by severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are exocytosis, released at the chemical synapse, synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicle (biology), Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell (biology), cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm. Structure Synaptic vesicles are relatively simple because only a limited number of proteins fit into a sphere of 40 nm diameter. Purified vesicles have a protein:phospholipid ratio of 1:3 with a lipid composition of 40% phosphatidylcholine, 32% phosphatidylethanola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Replacement
Molecular replacement (MR) is a method of solving the phase problem in X-ray crystallography. MR relies upon the existence of a previously solved protein structure which is similar to our unknown structure from which the diffraction data is derived. This could come from a homologous protein, or from the lower-resolution protein NMR structure of the same protein. The first goal of the crystallographer is to obtain an electron density map, density being related with diffracted wave as follows: : \rho(x,y,z)=\frac \sum_h\sum_k\sum_\ell, F_, \exp(2\pi i(hx+ky+\ell z)+i\Phi(hk\ell)). With usual detectors the intensity I=F\cdot F^* is being measured, and all the information about phase (\Phi) is lost. Then, in the absence of phases (Φ), we are unable to complete the shown Fourier transform relating the experimental data from X-ray crystallography (in reciprocal space) to real-space electron density, into which the atomic model is built. MR tries to find the model which fits best exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
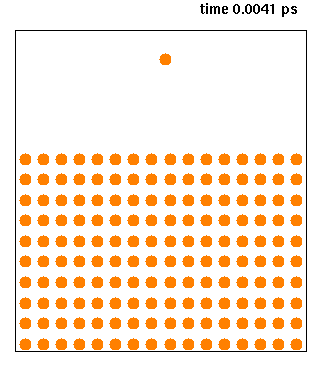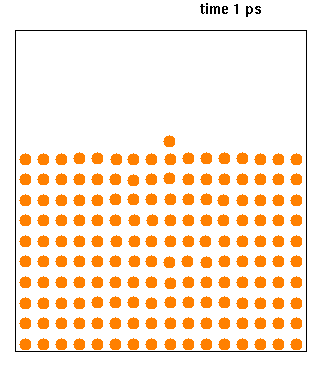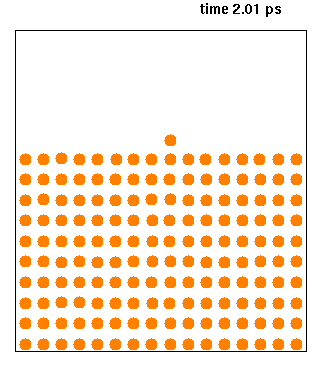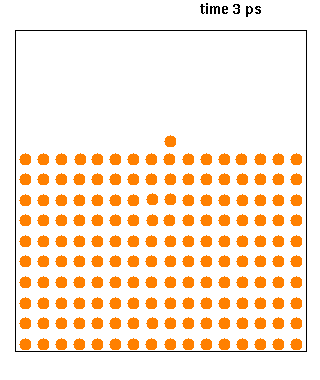
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulated Annealing
Simulated annealing (SA) is a probabilistic technique for approximating the global optimum of a given function. Specifically, it is a metaheuristic to approximate global optimization in a large search space for an optimization problem. For large numbers of local optima, SA can find the global optimum. It is often used when the search space is discrete (for example the traveling salesman problem, the boolean satisfiability problem, protein structure prediction, and job-shop scheduling). For problems where finding an approximate global optimum is more important than finding a precise local optimum in a fixed amount of time, simulated annealing may be preferable to exact algorithms such as gradient descent or branch and bound. The name of the algorithm comes from annealing in metallurgy, a technique involving heating and controlled cooling of a material to alter its physical properties. Both are attributes of the material that depend on their thermodynamic free energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |