|
Atlantidosteus
''Atlantidosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early to Middle Devonian of Morocco and Queensland. It contains two known species, ''A. hollardi'' and ''A. pacifica''. Description ''Atlantidosteus pacifica'' is known from a right suborbital plate, found in the Broken River Group of Queensland, Australia. Phylogeny ''Atlantidosteus'' is part of the clade Migmatocephala, closer related to Homostius, than Antineosteus. {{Clade, style={{Clade , 1=''Tityosteus'' , 0=''Taemasosteus'', 4={{Clade , 1=''Antineosteus'' , 2={{Clade , 1=''Atlantidosteus'' , 2=''Homostius ''Homosteus'' is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migmatocephala
Migmatocephala is a clade of placoderm fish within the suborder Brachythoraci. Migmatocephala includes the homostiids ''Taemasosteus'', ''Tityosteus'', ''Antineosteus'', ''Atlantidosteus'', and ''Homosteus ''Homosteus'' is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had comparatively large, flattened he ...''. Phylogeny The cladogram shown here is based on "A new species of Atlantidosteus Lelièvre, 1984 (Placodermi, Arthrodira, Brachythoraci) from the Middle Devonian of the Broken River area (Queensland, Australia)". References Fossil taxa described in 1995 Arthrodires {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homostiidae
Homostiidae is a family of flattened arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Middle Devonian. Fossils appear in various strata in Europe, Russia, Morocco, Australia, Canada and Greenland. Many homostiids have " toothless" jaws, and large sizes. suggesting that many homostiids were probably filter feeders, like the also noticeably flattened Rhincodon typus. All homostiids have flattened and elongated skulls. According to Denison 1978, primitive homostiids have moderately long median dorsal plates, whereas in "advanced" homostiids, the median dorsal tends to be short and broad. Obruchev (1964) placed the following primitive genera ''Euleptaspis'', ''Lophostracon'' and ''Luetkeichthys'' in a separate family, "Euleptaspididae," and Ørvig (1969), claimed that the Euleptaspidids were totally unrelated to Homostiidae proper (i.e., being neither related to, nor ancestral), but, according to Denison, did not clearly explain his reasons why this was so. Genera ''Angarichthys'' A comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosteus
''Homosteus'' is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had comparatively large, flattened heads with, as suggested by the upward opening orbits, upward-pointing eyes. These adaptations suggest that the various species were benthic predators. A study on '' Titanichthys'', in contrast, suggests that species of ''Homosteus'' may have been filter-feeders instead. ''Homosteus'' specimens from the Old Red Sandstone of Scotland are known to be significantly radioactive, on the order of 1.2 * 104 gamma/min/g ic Notably, ''Homosteus'' specimens are the only fish fossils from the Old Red Sandstone to show significant radioactivity. This suggests that these specimens became radioactive from the animals ingesting radioactive isotopes in life (e.g., through ingesting radioactive sediment), rather than radioactive isotopes being absorbed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
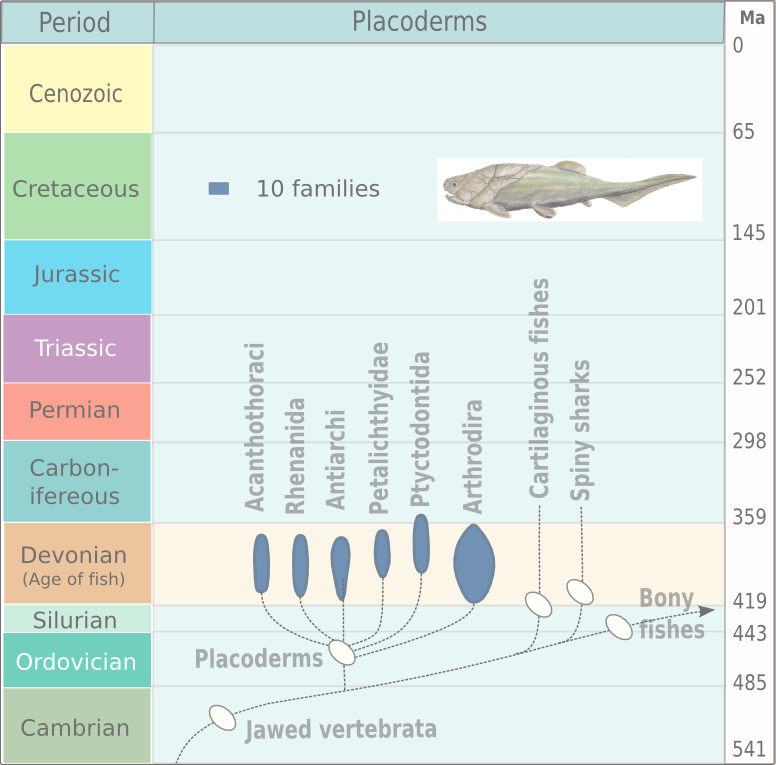
Arthrodire Genera
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Rolfosteus'' measured ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1984
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homostius
''Homosteus'' is a genus of flattened arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian. Fossils are found primarily in Eifelian-epoch aged strata of Europe, Canada, Greenland, and Estonia. All of the species had comparatively large, flattened heads with, as suggested by the upward opening orbits, upward-pointing eyes. These adaptations suggest that the various species were benthic predators. A study on ''Titanichthys'', in contrast, suggests that species of ''Homosteus'' may have been filter-feeders instead. ''Homosteus'' specimens from the Old Red Sandstone of Scotland are known to be significantly radioactive, on the order of 1.2 * 104 gamma/min/g ic Notably, ''Homosteus'' specimens are the only fish fossils from the Old Red Sandstone to show significant radioactivity. This suggests that these specimens became radioactive from the animals ingesting radioactive isotopes in life (e.g., through ingesting radioactive sediment), rather than radioactive isotopes being absorbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taemasosteus
''Taemasosteus'' is an extinct genus of arthrodire placoderm. Its fossils have been found in Emsian-aged marine strata in New South Wales, Australia. It contains two species, ''T. novaustrocambricus'', and ''T. maclartiensis''. The genus (and a monotypic family, "Taemasosteidae") was originally erected on the basis of "an imperfect" paranuchal, though, more specimens were found, eventually leading "Taemasosteidae" to be subsumed into Buchanosteidae. Even so, the reconstructed anatomy leads some researchers to conclude that ''Taemasosteus'' is close to the ancestry of Homostiidae. These researchers place ''Taemasosteus'' as the sister taxon of Homostiidae (or a select group of the better known homostiid genera) within the taxon In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tityosteus
''Tityosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Early Emsian of the Early Devonian, with fossils known from Germany, the Ibero-Armorican Trough, and southern Siberia. Description ''Tityosteus'' has only an 11 cm right marginal plate known, and margin ends and parts, in addition to the central plate overlap area being broken. According to "Tityosteus, A MARINE FISH (ARTHRODIRA, HOMOSTIIDAE) FROM THE EMSIAN OF ARAGÓN, SPAIN, AND ITS DISTRIBUTION", given Tityosteus's distribution, and Carolowilhelma (a pelagic arthrodire), being from similar facies as Tityosteus (Eifelian of Aragón, Spain), it may have been pelagic, and able to cross open waters. Diet While the inferognathals of ''Tityosteus'' have not been found, they could be either "toothless", like '' Homosteus'', which has been suggested to be planktivorous, or possessing fine denticles, like ''Antineosteus''. It has been suggested that ''Tityosteus'' probably was similar to the whale shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineosteus
''Antineosteus'' is an extinct genus of homostiid arthrodire from the Emsian, Early Devonian Kess-Kess Mounds, in the eastern Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco, and the Barrandian area of the Czech Republic. Description ''Antineosteus lehmani'' is rather fragmentary, known from a left anterior dorsolateral plate, a left paranuchal plate, and an inferognathal. ''A. rufus'' is known from a nearly-complete right head shield plate, and a right anterior dorsolateral plate. ''A. rufus'' is estimated to exceed , from measuring the plates with the ones from better-preserved, related taxa. Diet ''Antineosteus'', like many other members of Homostiidae, lacked bladed dentition on their jaws, and was large in size. These traits all in one animal support a planktivorous lifestyle, like baleen whales, or the whale shark, as supported by Denison, 1978, suggesting similar lifestyles for arthrodires like ''Homostius'', making it reasonable for many homostiids to be suspension-feeders like th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emsian
The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 407.6 ± 2.6 million years ago to 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian Stage and followed by the Eifelian Stage. It is named after the Ems river in Germany. The GSSP is located in the Zinzil'ban Gorge in the Kitab State Geological Reserve of Uzbekistan, above the contact with the Madmon Formation. In North America the Emsian Stage is represented by Sawkill or Sawkillian time. Biological events During this period, earliest known agoniatitid ammonoid fossils began appearing within this stage after first appearing in previous stage and began to evolutionarily radiate within this stage, in which a new ammonoid order Goniatitida rises in the end of Zlichovian stage (Siberian representation; corresponds to early Eifelian and after the end of Early Devonian, before 391.9 mya Mya may refer to: Brands and product names * Mya (program), an intelligent personal as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eifelian
The Eifelian is the first of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago to 387.7 ± 0.8 million years ago. It was preceded by the Emsian Stage and followed by the Givetian Stage. North American subdivisions of the Eifelian Stage include Southwood, and part of Cazenovia (or Cazenovian). Name and definition The Eifelian is named after the Eifel Mountains of Western Germany, which exposed the GSSP section at the Wetteldorf Richtschnitt outcrop. The base of the Eifelian is defined by the start of the '' Polygnathus partitus'' conodont zone. This layer lies within the Upper Heisdorf Formation, below the base of the Lauch Formation. Extinctions The end of the Eifelian was marked by a biological crisis known as the Kačák Event, a two-part interval of extinction which led to ecological turnover among ammonoids, conodonts, and other free-swimming animals. In deep marine waters, the event is indicated by anoxic black shales. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |