|
Aryanization In Slovakia
The Holocaust in Slovakia was the systematic dispossession, deportation, and murder of Judaism, Jews in the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, a client state of Nazi Germany, during World War II. Out of 89,000 Slovak Jews, Jews in the country in 1940, an estimated 69,000 were murdered in the Holocaust. After the September 1938 Munich Agreement, Slovakia unilaterally declared its autonomy within Czechoslovakia, but lost significant territory to Hungary in the First Vienna Award, signed in November. The following year, with German encouragement, the ruling ethnonationalist Slovak People's Party declared independence from Czechoslovakia. The Slovak government blamed the Jews for the territorial losses. Jews were targeted for discrimination and harassment, including the #Aryanization, confiscation of their property and businesses. The exclusion of Jews from the economy impoverished the community, which encouraged the government to conscript them for forced labor. On 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
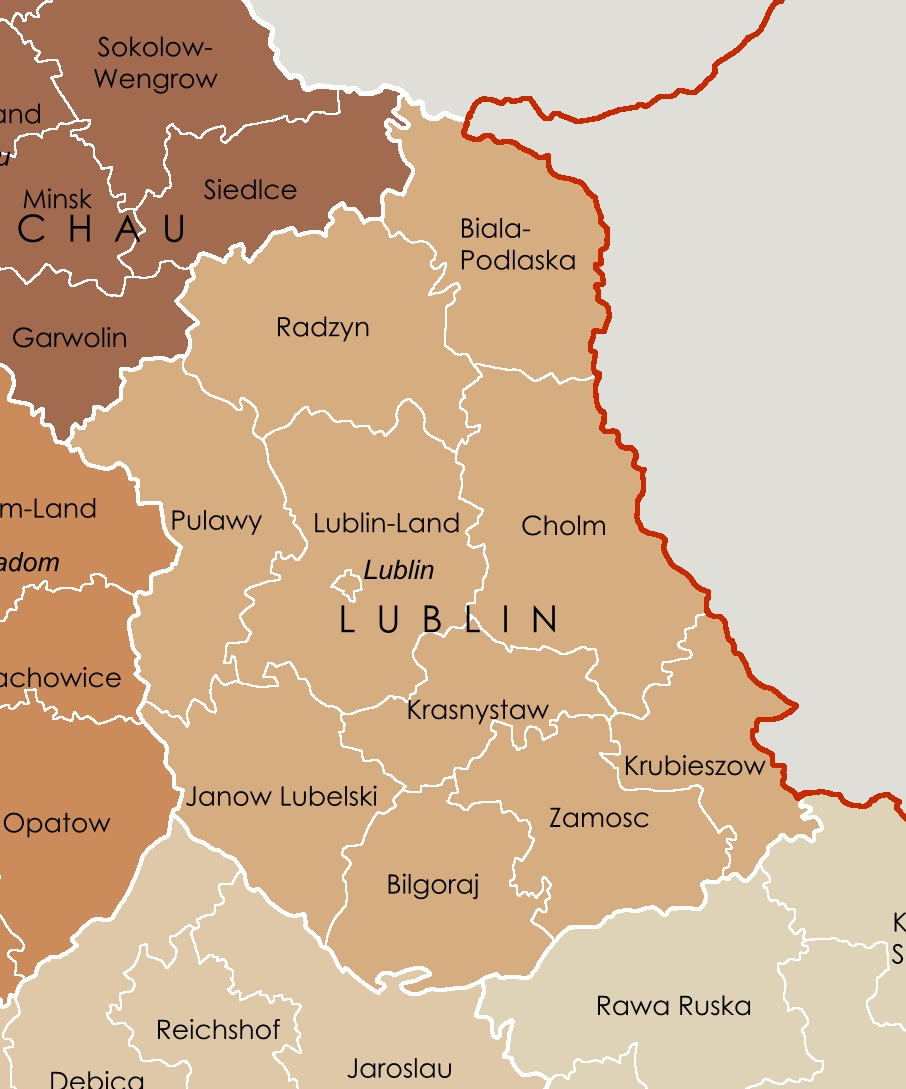
Lublin District
Lublin District () was one of the first four Nazi districts of the General Governorate region of German-occupied Poland during World War II, along with Warsaw District, Radom District, and Kraków District. On the south and east, it initially bordered the Soviet Union. After Operation Barbarossa, it bordered Reichskommissariat Ukraine to the east and Galizien District to the south, which was also part of the General Governorate. Nisko Plan The Nisko Plan was an operation organized by Nazi Germany to deport Jews to the Lublin District of the General Governorate of occupied Poland in 1939. The plan was developed in September 1939, after the invasion of Poland, and implemented between October 1939 and April 1940, in contrast to the similar Nazi "Madagascar Plan" and other Jewish relocation plans that had been drawn up before the attack on Poland, at the beginning of World War II. Christopher R. Browning''The Path to Genocide: Essays on Launching the Final Solution.''Camb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of European Jews In The Middle Ages
History of European Jews in the Middle Ages covers Jewish history in Europe in the period from the 5th to the 15th century. During the course of this period, the Jewish population experienced a gradual diaspora shifting from their motherland of the Levant to Europe. These Jewish individuals settled primarily in the regions of Central Europe dominated by the Holy Roman Empire and Southern Europe dominated by various Iberian kingdoms. As with Christianity, the Middle Ages were a period in which Judaism became mostly overshadowed by Islam in the Middle East, and an increasingly influential part of the socio-cultural and intellectual landscape of Europe. Jewish tradition traces the origins of the Jews to the 12 Israelite tribes. However, most Jewish traditions state that modern Jews descend from Judah, Benjamin and Levi. As early as the Babylonian exile Jews, through exile under military constraint or otherwise, came to live in many other Middle Eastern countries, and later formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coronation of the Hungarian monarch, coronation of the first king Stephen I of Hungary, Stephen I at Esztergom around the year 1000;Kristó Gyula – Barta János – Gergely Jenő: Magyarország története előidőktől 2000-ig (History of Hungary from the prehistory to 2000), Pannonica Kiadó, Budapest, 2002, , pp. 37, 113, 678 ("Magyarország a 12. század második felére jelentős európai tényezővé, középhatalommá vált."/"By the 12th century Hungary became an important European factor, became a middle power.", "A Nyugat részévé vált Magyarország.../Hungary became part of the West"), pp. 616–644 his family (the Árpád dynasty) led the monarchy for 300 years. By the 12th century, the kingdom became a European power. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogue Zilina 1931
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as weddings, bar and bat mitzvahs, choir performances, and children's plays. They often also have rooms for study, social halls, administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious and Hebrew studies, and many places to sit and congregate. They often display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork alongside items of Jewish historical significance or history about the synagogue itself. Synagogues are buildings used for Jewish prayer, study, assembly, and reading of the Torah. The Torah (Pentateuch or Five Books of Moses) is traditionally read in its entirety over a period of a year in weekly portions during services, or in some synagogues on a triennial cycle. However, the edifice of a synagogue as such is not essential for holdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velvet Revolution
The Velvet Revolution () or Gentle Revolution () was a non-violent transition of power in what was then Czechoslovakia, occurring from 17 November to 28 November 1989. Popular demonstrations against the one-party government of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia included students and older dissidents. The result was the end of Czechoslovak Socialist Republic, 41 years of one-party rule in Czechoslovakia, and the subsequent dismantling of the command economy and conversion to a parliamentary republic. On 17 November 1989 (International Students' Day), riot police suppressed a Student activism, student demonstration in Prague. The event marked the 50th anniversary of a violently suppressed demonstration against the Nazi storming of Prague University in 1939 where 1,200 students were arrested and 9 killed (see International Students' Day#Origin, Origin of International Students' Day). The 1989 event sparked a series of demonstrations from 17 November to late December and turned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Czechoslovakia
The Communist Party of Czechoslovakia ( Czech and Slovak: ''Komunistická strana Československa'', KSČ) was a communist and Marxist–Leninist political party in Czechoslovakia that existed between 1921 and 1992. It was a member of the Comintern. Between 1929 and 1953, it was led by Klement Gottwald. The KSČ was the sole governing party in the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic though it was a leading party along with the Slovak branch and four other legally permitted non-communist parties. After its election victory in 1946, it seized power in the 1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état and established a one-party state allied with the Soviet Union. Nationalization of virtually all private enterprises followed, and a command economy was implemented. The KSČ was committed to the pursuit of communism, and after Joseph Stalin's rise to power Marxism–Leninism became formalized as the party's guiding ideology and would remain so throughout the rest of its existence. Consequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Communist Coup
Events January * January 1 ** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated. ** The current Constitutions of Italy and of New Jersey (both later subject to amendment) go into effect. ** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British Railways. * January 4 – Burma gains its independence from the United Kingdom, becoming an independent republic, named the ' Union of Burma', with Sao Shwe Thaik as its first President and U Nu its first Prime Minister. * January 5 – In the United States: ** Warner Brothers shows the first color newsreel (''Tournament of Roses Parade'' and the ''Rose Bowl Game''). ** The first Kinsey Report, ''Sexual Behavior in the Human Male'', is published. * January 7 – Mantell UFO incident: Kentucky Air National Guard pilot Thomas Mantell crashes while in pursuit of an unidentified flying object. * January 12 – Mahatma Gandhi begins his fast-unto-death in Delhi, to stop communal violence during the Parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions
The Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions or Flying Squads of the Hlinka Guard (, POHG) were Slovak paramilitary formations set up to counter the August 1944 Slovak National Uprising. They are best known for the role they played in murdering Jews, Romani people, and actual or suspected Slovak partisans in conjunction with Einsatzgruppe H, especially for their participation in the Kremnička massacre. Formation Many Slovak Army units and Slovak gendarmes sided with the rebels during the Slovak National Uprising. Relying on German troops to suppress the uprising was politically undesirable. Therefore, the Hlinka Guard, the paramilitary force of the clericofascist Slovak People's Party, was drafted to combat the partisans. President Jozef Tiso was an influential advocate of this, because he saw the Hlinka Guard as loyal to the Slovak Republic. Slovak fascist propaganda claimed that the uprising had been fomented by the Czech and Jewish minorities, considered " enemies of the state" beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einsatzgruppe H
Einsatzgruppe H was one of the ''Einsatzgruppen'', the paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany. A special task force of more than 700 soldiers, it was created at the end of August 1944 to deport or murder the remaining Jews in Slovakia following the German suppression of the Slovak National Uprising. During its seven-month existence, ''Einsatzgruppe'' H collaborated closely with the Hlinka Guard Emergency Divisions and arrested 18,937 people, of whom at least 2,257 were murdered; thousands of others were deported to Nazi concentration camps (primarily Auschwitz). The victims included Jews, Romani people, actual or suspected Slovak partisans, and real or perceived political opponents. One of its component units, ''Einsatzkommando'' 14, committed two of the largest massacres in the history of Slovakia, at Kremnička and Nemecká. Background On 14 March 1939, the Slovak State proclaimed its independence under the protection of Nazi Germany. According to the United States Holoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak National Uprising
Slovak National Uprising ( Slovak: ''Slovenské národné povstanie'', abbreviated SNP; alternatively also ''Povstanie roku 1944'', English: ''The Uprising of 1944'') was organised by the Slovak resistance during the Second World War, directed against the German invasion of Slovakia by the German military, which began on 29 August 1944, and on the other against the Slovak collaborationist regime of the Ludaks under Jozef Tiso. Along with the Warsaw Uprising, it was the largest uprising against Nazism and its allies in Europe. Carried by parts of the Slovak army, the main area of the uprising was in central Slovakia, with the town of Banská Bystrica as its centre. The Slovak insurgent army (officially the 1st Czechoslovak Army in Slovakia) was under the overall command of a military headquarters of the opposition Slovak National Council. This represented a coalition of the civic Democratic Party and the Slovak communists and was linked to the Czechoslovak government-in-exile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |