|
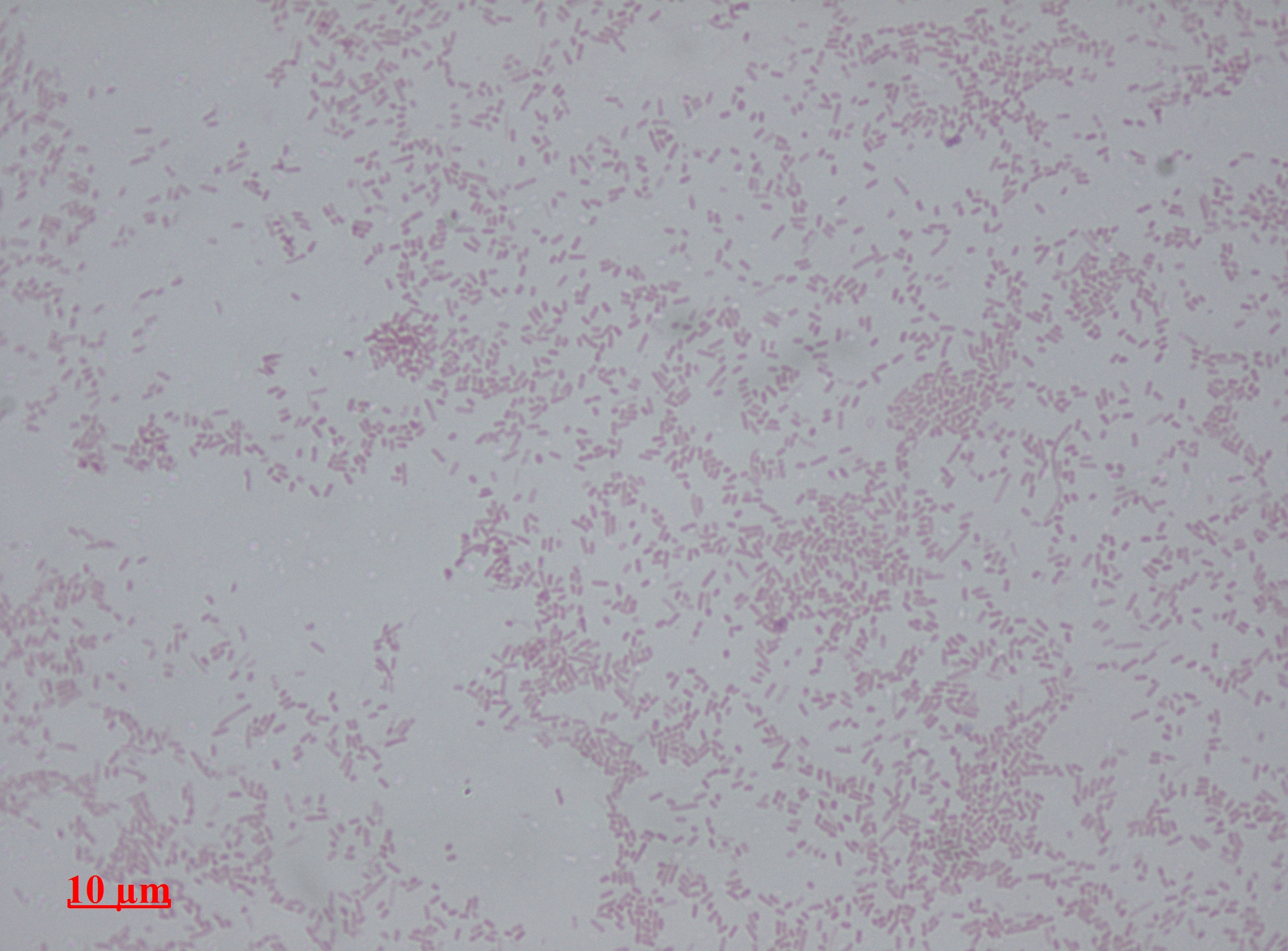
Arsenophonus Nasoniae
''Arsenophonus nasoniae'' is a species of bacterium which was previously isolated from '' Nasonia vitripennis'', a species of parasitoid wasp. These wasps are generalists which afflict the larvae of parasitic carrion flies such as blowflies, houseflies and flesh flies. ''A. nasoniae'' belongs to the phylum Pseudomonadota and family Morganellaceae. The genus '' Arsenophonus'', has a close relationship to the Proteus (bacterium) rather than to that of Salmonella and Escherichia. The genus is composed of gammaproteobacterial, secondary-endosymbionts which are gram-negative. Cells are non-flagellated, non-motile, non-spore forming and form long to highly filamentous rods. Cellular division is exhibited through septation. The name Arsenophonus nasoniae'' gen. nov., sp. nov.' was therefore proposed for the discovered bacterium due to its characteristics and its microbial interaction with ''N. vitripennis''. The type strain of ''A. nasoniae'' is Strain SKI4 (ATCC 49151). Isolat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasonia Vitripennis
''Nasonia vitripennis'' (or ''Mormoniella vitripennis'', or ''Nasonia brevicornis'') is one of four known species under the genus '' Nasonia'' - small parasitoid wasps that afflict the larvae of parasitic carrion flies such as blowflies and flesh flies, which themselves are parasitic toward nestling birds. It is the best known and most widely studied of the parasitoid wasps, and their study forms a vital part of the information used to describe the order Hymenoptera, along with information from bees and ants. This parasitoid behaviour makes the wasps an interest for the development of biopesticide and biological systems for controlling unwanted insects. The biosynthetic pathways for sex pheromones in Hymenoptera, determination of sex in development, and many protein and gene product comparisons to other insects have been studied using ''N. vitripennis'' (most often contrasted against the Western honey bee, ''Apis mellifera''). ''Nasonia vitripennis'' also has a high variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the Biological life cycle, life cycles of many plants, algae, fungus, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. In some rare cases, a diploid spore is also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photorhabdus
''Photorhabdus'' is a genus of bioluminescent, gram-negative bacilli which lives symbiotically within entomopathogenic nematodes, hence the name ''photo'' (which means light producing) and ''rhabdus'' (rod shape). ''Photorhabdus'' is known to be pathogenic to a wide range of insects and has been used as biopesticide in agriculture. Life cycle ''Photorhabdus'' species facilitate the reproduction of entomopathogenic nematodes by infecting and killing susceptible insect larvae. Entomopathogenic nematodes are normally found in soil. Nematodes infect larval hosts by piercing the larval cuticle. When the nematode enters an insect larvae, ''Photorhabdus'' species are released by the nematodes and will produce a range of toxins, killing the host within 48 hours. ''Photorhabdus'' species feed on the cadaver of the insect and the process converts the cadaver into a nutrient source for the nematode. Mature nematodes leave the depleted body of the insect and search for new hosts to infect. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yersinia
''Yersinia'' is a genus of bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. ''Yersinia'' species are Gram-negative, coccobacilli bacteria, a few micrometers long and fractions of a micrometer in diameter, and are facultative anaerobes. Some members of ''Yersinia'' are pathogenic in humans; in particular, '' Y. pestis'' is the causative agent of the plague. Rodents are the natural reservoirs of ''Yersinia''; less frequently, other mammals serve as the host. Infection may occur either through blood (in the case of ''Y. pestis'') or in an alimentary fashion, occasionally via consumption of food products (especially vegetables, milk-derived products, and meat) contaminated with infected urine or feces. Speculations exist as to whether or not certain ''Yersinia'' can also be spread by protozoonotic mechanisms, since ''Yersinia'' species are known to be facultative intracellular parasites; currently, there are studies and discussions of the possibility of amoeba-vectored (through the cyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteus
In Greek mythology, Proteus ( ; ) is an early prophetic sea god or god of rivers and oceanic bodies of water, one of several deities whom Homer calls the "Old Man of the Sea" (''hálios gérôn''). Some who ascribe a specific domain to Proteus call him the god of "elusive sea change", which suggests the changeable nature of the sea or the liquid quality of water. He can foretell the future, but, in a mytheme familiar to several cultures, will change his shape to avoid doing so; he answers only to those who are capable of capturing him. From this feature of Proteus comes the adjective protean, meaning "versatile", "mutable", or "capable of assuming many forms". "Protean" has positive connotations of flexibility, versatility and adaptability. Name origin Proteus's name suggests the "first" (from Greek language, Greek "" , "first"), as () is the "primordial" or the "firstborn". It is not certain to what this refers, but in myths where he is the son of Poseidon, it possibly refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an open reading frame (ORF) may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteus Mirabilis
''Proteus mirabilis'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. ''P. mirabilis'' causes 90% of all ''Proteus (bacterium), Proteus'' infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water. ''Proteus mirabilis'' can migrate across the surface of solid media or devices using a type of cooperative group motility called swarming. ''Proteus mirabilis'' is most frequently associated with Urinary tract infection, infections of the urinary tract, especially in complicated or catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Diagnosis An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of ''P. mirabilis''. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also ''P. mirabilis'' produces a very distinct fishy odor. Disease This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analyses
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and Morphology (biology), morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothesis, hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living Taxon, taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in questi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrachromosomal DNA
Extrachromosomal DNA (abbreviated ecDNA) is any DNA that is found off the chromosomes, either inside or outside the nucleus of a cell. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes contained in the nucleus. Multiple forms of extrachromosomal DNA exist, and, while some of these serve important biological functions, they can also play a role in diseases such as cancer. In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids, whereas, in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. The fact that this organelle contains its own DNA supports the hypothesis that mitochondria originated as bacterial cells engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research into replication because it is easy to identify and isolate. Although extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is found in normal eukaryotic cells, extrachromosomal DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a Redundancy (information theory), redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Assembly
In bioinformatics, sequence assembly refers to aligning and merging fragments from a longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence. This is needed as DNA sequencing technology might not be able to 'read' whole genomes in one go, but rather reads small pieces of between 20 and 30,000 bases, depending on the technology used. Typically, the short fragments (reads) result from shotgun sequencing genomic DNA, or gene transcript ( ESTs). The problem of sequence assembly can be compared to taking many copies of a book, passing each of them through a shredder with a different cutter, and piecing the text of the book back together just by looking at the shredded pieces. Besides the obvious difficulty of this task, there are some extra practical issues: the original may have many repeated paragraphs, and some shreds may be modified during shredding to have typos. Excerpts from another book may also be added in, and some shreds may be completely unrecognizable. Typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |